Main Content





















Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice
-
Jump to topic
- Introduction
- Geography
-
People and Society
- Age structure
- Birth rate
- Death rate
- Dependency ratios
- Drinking water source
- HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
- HIV/AIDS - deaths
- HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
- Infant mortality rate
- Languages
- Life expectancy at birth
- Literacy
- Maternal mortality rate
- Median age
- Population
- Population distribution
- Population growth rate
- Religions
- Sanitation facility access
- School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- Sex ratio
- Total fertility rate
- Urbanization
- Government
-
Economy
- Budget
- Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
- Debt - external
- Distribution of family income - Gini index
- Economy - overview
- Exports
- Exports - commodities
- GDP - composition, by end use
- GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- GDP - per capita (PPP)
- GDP - real growth rate
- GDP (official exchange rate)
- GDP (purchasing power parity)
- Gross national saving
- Household income or consumption by percentage share
- Imports
- Imports - commodities
- Industrial production growth rate
- Industries
- Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Labor force
- Labor force - by occupation
- Market value of publicly traded shares
- Public debt
- Stock of broad money
- Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad
- Stock of direct foreign investment - at home
- Stock of domestic credit
- Stock of narrow money
- Taxes and other revenues
- Unemployment rate
-
Energy
- Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy
- Crude oil - exports
- Crude oil - imports
- Crude oil - production
- Crude oil - proved reserves
- Electricity - consumption
- Electricity - exports
- Electricity - from fossil fuels
- Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
- Electricity - from nuclear fuels
- Electricity - from other renewable sources
- Electricity - imports
- Electricity - installed generating capacity
- Electricity - production
- Electricity access
- Natural gas - consumption
- Natural gas - exports
- Natural gas - imports
- Natural gas - production
- Natural gas - proved reserves
- Refined petroleum products - consumption
- Refined petroleum products - exports
- Refined petroleum products - imports
- Refined petroleum products - production
- Communications
- Transportation
- Military and Security
- Transnational Issues
-
Introduction :: World
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.
 Globally, the 20th century was marked by: (a) two devastating world wars; (b) the Great Depression of the 1930s; (c) the end of vast colonial empires; (d) rapid advances in science and technology, from the first airplane flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina (US) to the landing on the moon; (e) the Cold War between the Western alliance and the Warsaw Pact nations; (f) a sharp rise in living standards in North America, Europe, and Japan; (g) increased concerns about environmental degradation including deforestation, energy and water shortages, declining biological diversity, and air pollution; (h) the onset of the AIDS epidemic; and (i) the ultimate emergence of the US as the only world superpower. The planet's population continues to explode: from 1 billion in 1820 to 2 billion in 1930, 3 billion in 1960, 4 billion in 1974, 5 billion in 1987, 6 billion in 1999, and 7 billion in 2012. For the 21st century, the continued exponential growth in science and technology raises both hopes (e.g., advances in medicine and agriculture) and fears (e.g., development of even more lethal weapons of war).
Globally, the 20th century was marked by: (a) two devastating world wars; (b) the Great Depression of the 1930s; (c) the end of vast colonial empires; (d) rapid advances in science and technology, from the first airplane flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina (US) to the landing on the moon; (e) the Cold War between the Western alliance and the Warsaw Pact nations; (f) a sharp rise in living standards in North America, Europe, and Japan; (g) increased concerns about environmental degradation including deforestation, energy and water shortages, declining biological diversity, and air pollution; (h) the onset of the AIDS epidemic; and (i) the ultimate emergence of the US as the only world superpower. The planet's population continues to explode: from 1 billion in 1820 to 2 billion in 1930, 3 billion in 1960, 4 billion in 1974, 5 billion in 1987, 6 billion in 1999, and 7 billion in 2012. For the 21st century, the continued exponential growth in science and technology raises both hopes (e.g., advances in medicine and agriculture) and fears (e.g., development of even more lethal weapons of war). -
Geography :: World
-
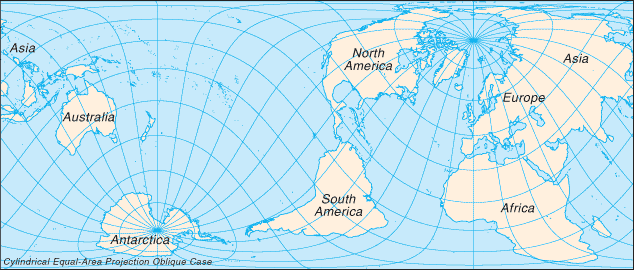
The surface of the earth is approximately 70.9% water and 29.1% land. The former portion is divided into large bodies termed oceans. The World Factbook recognizes and describes five oceans, which are in decreasing order of size: the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Because of their immense size, the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans are generally divided at the equator into the North and South Pacific Oceans and the North and South Atlantic Oceans, thus creating seven major water bodies - the so-called "Seven Seas."
Some 97.5% of the earth's water is saltwater. Of the 2.5% that is fresh, about two-thirds is frozen mostly locked up in the Antarctic ice sheets and mountain glaciers worldwide. If all the surface ice on earth fully melted, the sea level would rise about 70 m.
Earth's land portion is generally divided into several, large, discrete landmasses termed continents. Depending on the convention used, the number of continents can vary from five to seven. The most common classification recognizes seven, which are (from largest to smallest): Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Asia and Europe are sometimes lumped together into a Eurasian continent resulting in six continents. Alternatively, North and South America are sometimes grouped as simply the Americas, resulting in a continent total of six (or five, if the Eurasia designation is used).
North America is commonly understood to include the island of Greenland, the isles of the Caribbean, and to extend south all the way to the Isthmus of Panama. The easternmost extent of Europe is generally defined as being the Ural Mountains and the Ural River; on the southeast the Caspian Sea; and on the south the Caucasus Mountains, the Black Sea, and the Mediterranean. Portions of five countries - Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkey - fall within both Europe and Asia, but in every instance the larger section is in Asia. These countries are considered part of both continents. Armenia and Cyprus, which lie completely in Western Asia, are geopolitically European countries.
Asia usually incorporates all the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia. The islands of the Pacific are often lumped with Australia into a "land mass" termed Oceania or Australasia. Africa's northeast extremity is frequently delimited at the Isthmus of Suez, but for geopolitical purposes, the Egyptian Sinai Peninsula is often included as part of Africa.
Although the above groupings are the most common, different continental dispositions are recognized or taught in certain parts of the world, with some arrangements more heavily based on cultural spheres rather than physical geographic considerations.
Based on the seven-continent model, and grouping islands with adjacent continents, Africa has the most countries with 54. Europe contains 49 countries and Asia 48, but these two continents share five countries: Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkey. North America consists of 23 sovereign states, Oceania has 14, and South America 12.
countries by continent: Africa (54): Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Cote d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe;
Europe (49): Albania, Andorra, Austria, Azerbaijan*, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia*, Germany, Greece, Holy See (Vatican City), Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Kazakhstan*, Kosovo, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia*, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey*, Ukraine, United Kingdom (* indicates part of the country is also in Asia);
Asia (48): Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan*, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Brunei, Burma, Cambodia, China, Cyprus, Georgia*, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan*, North Korea, South Korea, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Lebanon, Malaysia, Maldives, Mongolia, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Russia*, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, Tajikistan, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Turkey*, Turkmenistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Yemen (* indicates part of the country is also in Europe);
North America (23): Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Canada, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, United States;
Oceania (14): Australia, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, New Zealand, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu;
South America (12): Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela
Map references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. Physical Map of the WorldArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
Physical Map of the WorldArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. total: 510.072 million sq kmland: 148.94 million sq kmwater: 361.132 million sq km
total: 510.072 million sq kmland: 148.94 million sq kmwater: 361.132 million sq kmnote: 70.9% of the world's surface is water, 29.1% is land
Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres).
land area about 16 times the size of the US
top fifteen World Factbook entities ranked by size: 155,557,000 Pacific Ocean; 76,762,000 Atlantic Ocean; 68,556,000 Indian Ocean; 20,327,000 Southern Ocean; 17,098,242 Russia; 14,056,000 Arctic Ocean; 14,000,000 Antarctica; 9,984,670 Canada; 9,826,675 United States; 9,596,960 China; 8,515,770 Brazil; 7,741,220 Australia; 4,324,782 European Union; 3,287,263 India; 2,780,400 Argentina
top ten largest water bodies: 155,557,000 Pacific Ocean; 76,762,000 Atlantic Ocean; 68,556,000 Indian Ocean; 20,327,000 Southern Ocean; 14,056,000 Arctic Ocean; 4,184,100 Coral Sea; 3595900 South China Sea; 2,834,000 Caribbean Sea; 2,520,000 Bering Sea; 2,469,000 Mediterranean Sea
top ten largest landmasses: 44,568,500 Asia; 30,065,000 Africa; 24,473,000 North America; 17,819,000 South America; 14,000,000 Antarctica; 9,948,000 Europe; 7,741,220 Australia; 2,166,086 Greenland; 785,753 New Guinea; 751,929 Borneo
top ten largest islands: 2,166,086 Greenland; 785,753 New Guinea (Indonesia, Papua New Guinea); 751,929 Borneo (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia); 587,713 Madagascar; 507,451 Baffin Island (Canada); 472,784 Sumatra (Indonesia); 227,963 Honshu (Japan); 217,291 Victoria Island (Canada); 209,331 Great Britain (United Kingdom); 196,236 Ellesmere Island (Canada)
ten smallest independent countries: 0.44 Holy See (Vatican City); 2 Monaco; 21 Nauru; 26 Tuvalu; 61 San Marino; 160 Liechtenstein; 181 Marshall Islands; 261 Saint Kitts and Nevis; 298 Maldives; 316 Malta
Land boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ.
the land boundaries in the world total 251,060 km (not counting shared boundaries twice); two nations, China and Russia, each border 14 other countries
note: 46 nations and other areas are landlocked, these include: Afghanistan, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bhutan, Bolivia, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Czechia, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Holy See (Vatican City), Hungary, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Lesotho, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malawi, Mali, Moldova, Mongolia, Nepal, Niger, Paraguay, Rwanda, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, South Sudan, Switzerland, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Uzbekistan, West Bank, Zambia, Zimbabwe; two of these, Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan, are doubly landlocked
Coastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 356,000 km
356,000 kmnote: 95 nations and other entities are islands that border no other countries, they include: American Samoa, Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, Ashmore and Cartier Islands, The Bahamas, Bahrain, Baker Island, Barbados, Bermuda, Bouvet Island, British Indian Ocean Territory, British Virgin Islands, Cabo Verde, Cayman Islands, Christmas Island, Clipperton Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Comoros, Cook Islands, Coral Sea Islands, Cuba, Curacao, Cyprus, Dominica, Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas), Faroe Islands, Fiji, French Polynesia, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, Greenland, Grenada, Guam, Guernsey, Heard Island and McDonald Islands, Howland Island, Iceland, Isle of Man, Jamaica, Jan Mayen, Japan, Jarvis Island, Jersey, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Kiribati, Madagascar, Maldives, Malta, Marshall Islands, Mauritius, Mayotte, Federated States of Micronesia, Midway Islands, Montserrat, Nauru, Navassa Island, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Norfolk Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Palmyra Atoll, Paracel Islands, Philippines, Pitcairn Islands, Puerto Rico, Saint Barthelemy, Saint Helena, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Samoa, Sao Tome and Principe, Seychelles, Singapore, Sint Maarten, Solomon Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, Spratly Islands, Sri Lanka, Svalbard, Taiwan, Tokelau, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Turks and Caicos Islands, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, Virgin Islands, Wake Island, Wallis and Futuna
Maritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its . . . more
a variety of situations exist, but in general, most countries make the following claims measured from the mean low-tide baseline as described in the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea: territorial sea - 12 nm, contiguous zone - 24 nm, and exclusive economic zone - 200 nm; additional zones provide for exploitation of continental shelf resources and an exclusive fishing zone; boundary situations with neighboring states prevent many countries from extending their fishing or economic zones to a full 200 nm
Climate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year. a wide equatorial band of hot and humid tropical climates, bordered north and south by subtropical temperate zones that separate two large areas of cold and dry polar climatesTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
a wide equatorial band of hot and humid tropical climates, bordered north and south by subtropical temperate zones that separate two large areas of cold and dry polar climatesTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
tremendous variation of terrain on each of the continents; check the World 'Elevation' entry for a compilation of terrain extremes; the world's ocean floors are marked by mid-ocean ridges while the ocean surfaces form a dynamic, continuously changing environment; check the 'Terrain' field and its 'major surface currents' subfield under each of the five ocean (Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and Southern) entries for further information on oceanic environs
Elevation: This entry includes both the mean elevation and the elevation extremes. mean elevation: 840 melevation extremes: -2,555 m lowest point: Bentley Subglacial Trench (Antarctica) (in the oceanic realm, Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is the lowest point, lying -10,924 m below the surface of the Pacific Ocean)highest point: Mount Everest 8,850 m
mean elevation: 840 melevation extremes: -2,555 m lowest point: Bentley Subglacial Trench (Antarctica) (in the oceanic realm, Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is the lowest point, lying -10,924 m below the surface of the Pacific Ocean)highest point: Mount Everest 8,850 m
top ten highest mountains (measured from sea level): Mount Everest (China-Nepal) 8,850 m; K2 (Pakistan) 8,611 m; Kanchenjunga (India-Nepal) 8,598 m; Lhotse (Nepal) 8,516 m; Makalu (China-Nepal) 8,463 m; Cho Oyu (China-Nepal) 8,201 m; Dhaulagiri (Nepal) 8,167 m; Manaslu (Nepal) 8,163 m; Nanga Parbat (Pakistan) 8,125 m; Anapurna (Nepal) 8,091 m
note: Mauna Kea (United States) is the world's tallest mountain as measured from base to summit; the peak of this volcanic colossus lies on the island of Hawaii, but its base begins more than 70 km offshore and at a depth of about 6,000 m; total height estimates range from 9,966 m to 10,203 mhighest point on each continent: Asia - Mount Everest (China-Nepal) 8,850 m; South America - Cerro Aconcagua (Argentina) 6,960 m; North America - Denali (Mount McKinley) (United States) 6,190 m; Africa - Kilimanjaro (Tanzania) 5,895 m; Europe - El'brus (Russia) 5,633 m; Antarctica - Vinson Massif 4,897 m; Australia - Mount Kosciuszko 2,229 m
highest capital on each continent: South America - La Paz (Bolivia) 3,640 m; Africa - Addis Ababa (Ethiopia) 2,355 m; Asia - Thimphu (Bhutan) 2,334 m; North America - Mexico City (Mexico) 2,240 m; Europe - Andorra la Vella (Andorra) 1,023 m; Australia - Canberra (Australia) 605 mlowest point on each continent: Antarctica - Bentley Subglacial Trench -2,555 m; Asia - Dead Sea (Israel-Jordan) -408 m; Africa - Lac Assal (Djibouti) -155 m; South America - Laguna del Carbon (Argentina) -105 m; North America - Death Valley (United States) -86 m; Europe - Caspian Sea (Azerbaijan-Kazakhstan-Russia) -28 m; Australia - Lake Eyre -15 m
lowest capital on each continent: Asia - Baku (Azerbaijan) -28 m; Europe - Amsterdam (Netherlands) -2 m; Africa - Banjul (Gambia); Bissau (Guinea-Bissau), Conakry (Guinea), Djibouti (Djibouti), Libreville (Gabon), Male (Maldives), Monrovia (Liberia), Tunis (Tunisia), Victoria (Seychelles) 0 m; North America - Basseterre (Saint Kitts and Nevis), Kingstown (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Panama City (Panama), Port of Spain (Trinidad and Tobago), Roseau (Dominica), Saint John's (Antigua and Barbuda), Santo Domingo (Dominican Republic) 0 m; South America - Georgetown (Guyana) 0 m; Australia - Canberra (Australia) 605 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. the rapid depletion of nonrenewable mineral resources, the depletion of forest areas and wetlands, the extinction of animal and plant species, and the deterioration in air and water quality pose serious long-term problemsIrrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water.
the rapid depletion of nonrenewable mineral resources, the depletion of forest areas and wetlands, the extinction of animal and plant species, and the deterioration in air and water quality pose serious long-term problemsIrrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water. 3,242,917 sq km (2012 est.)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
3,242,917 sq km (2012 est.)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. six of the world's seven continents are widely and permanently inhabited; Asia is easily the most populous continent with about 60% of the world's population (China and India together account for over 35%); Africa comes in second with over 15% of the earth's populace, Europe has about 10%, North America 8%, South America almost 6%, and Oceania less than 1%; the harsh conditions on Antarctica prevent any permanent habitationNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
six of the world's seven continents are widely and permanently inhabited; Asia is easily the most populous continent with about 60% of the world's population (China and India together account for over 35%); Africa comes in second with over 15% of the earth's populace, Europe has about 10%, North America 8%, South America almost 6%, and Oceania less than 1%; the harsh conditions on Antarctica prevent any permanent habitationNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
large areas subject to severe weather (tropical cyclones); natural disasters (earthquakes, landslides, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions)
volcanism: volcanism is a fundamental driver and consequence of plate tectonics, the physical process reshaping the Earth's lithosphere; the world is home to more than 1,500 potentially active volcanoes, with over 500 of these having erupted in historical times; an estimated 500 million people live near these volcanoes; associated dangers include lava flows, lahars (mudflows), pyroclastic flows, ash clouds, ash fall, ballistic projectiles, gas emissions, landslides, earthquakes, and tsunamis; in the 1990s, the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, created a list of 16 Decade Volcanoes worthy of special study because of their great potential for destruction: Avachinsky-Koryaksky (Russia), Colima (Mexico), Etna (Italy), Galeras (Colombia), Mauna Loa (United States), Merapi (Indonesia), Nyiragongo (Democratic Republic of the Congo), Rainier (United States), Sakurajima (Japan), Santa Maria (Guatemala), Santorini (Greece), Taal (Philippines), Teide (Spain), Ulawun (Papua New Guinea), Unzen (Japan), Vesuvius (Italy); see second note under "Geography - note"
Environment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more large areas subject to overpopulation, industrial disasters, pollution (air, water, acid rain, toxic substances), loss of vegetation (overgrazing, deforestation, desertification), loss of biodiversity; soil degradation, soil depletion, erosion; ozone layer depletion; waste disposal; global warming becoming a greater concernGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
large areas subject to overpopulation, industrial disasters, pollution (air, water, acid rain, toxic substances), loss of vegetation (overgrazing, deforestation, desertification), loss of biodiversity; soil degradation, soil depletion, erosion; ozone layer depletion; waste disposal; global warming becoming a greater concernGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
note: the world is now thought to be about 4.55 billion years old, just about one-third of the 13.8-billion-year age estimated for the universe
note: although earthquakes can strike anywhere at any time, the vast majority occur in three large zones of the earth; the world's greatest earthquake belt, the Circum-Pacific Belt (popularly referred to as the Ring of Fire), is the zone of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; about 90% of the world's earthquakes (81% of the largest earthquakes) and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire; the belt extends northward from Chile, along the South American coast, through Central America, Mexico, the western US, southern Alaska and the Aleutian Islands, to Japan, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, island groups in the southwestern Pacific, and New Zealand
the second prominent belt, the Alpide, extends from Java to Sumatra, northward along the mountains of Burma, then eastward through the Himalayas, the Mediterranean, and out into the Atlantic Ocean; it accounts for about 17% of the world's largest earthquakes; the third important belt follows the long Mid-Atlantic Ridge -
People and Society :: World
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 7,405,107,650 (2017 est.)top ten most populous countries (in millions): China 1379.3; India 1281.93; United States 326.63; Indonesia 260.58; Brazil 207.35; Pakistan 204.92; Nigeria 190.63; Bangladesh 157.83; Russia 142.26; Japan 126.45;
7,405,107,650 (2017 est.)top ten most populous countries (in millions): China 1379.3; India 1281.93; United States 326.63; Indonesia 260.58; Brazil 207.35; Pakistan 204.92; Nigeria 190.63; Bangladesh 157.83; Russia 142.26; Japan 126.45;ten least populous countries: Holy See (Vatican City) 1,000; Montserrat 5,292; Saint Pierre and Miquelon 5,533; Saint Barthelemy 7,184; Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan de Cunha 7,828; Cook Islands 9,290; Tuvalu 11,052; Nauru 11359; Wallis and Futuna 15,714; Anguilla 17,087;
ten most densely populated countries (population per sq km): Macau 21,346; Monaco 15,322; Singapore 8,572; Hong Kong 6,702; Gaza Strip 4,987; Gibraltar 4,523; Bahrain 1,857; Maldives 1,318; Malta 1,317; Bermuda 1,312;
ten least densely populated countries (population per sq km): Greenland less than 1; Mongolia 2; Western Sahara 2.3; Australia 3; Namibia 3; Iceland 3.4; Mauritania 3.6; Guyana 3.7; Libya 3.8; Suriname 3.8
Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language.
Mandarin Chinese 12.3%, Spanish 6%, English 5.1%, Arabic 5.1%, Hindi 3.5%, Bengali 3.3%, Portuguese 3%, Russian 2.1%, Japanese 1.7%, Punjabi, Western 1.3%, Javanese 1.1% (2018 est.)
note 1: percents are for "first language" speakers only; the six UN languages - Arabic, Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian, and Spanish (Castilian) - are the mother tongue or second language of about 45% of the world's population, and are the official languages in more than half the states in the world; some 400 languages have more than a million first-language speakers
note 2: all told, there are an estimated 7,100 languages spoken in the world; approximately 80% of these languages are spoken by less than 100,000 people; about 150 languages are spoken by less than 10 people; communities that are isolated from each other in mountainous regions often develop multiple languages; Papua New Guinea, for example, boasts about 840 separate languages
note 3: approximately 2,300 languages are spoken in Asia, 2,140, in Africa, 1,310 in the Pacific, 1,060 in the Americas, and 290 in Europe (2018)
Religions: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. The core characteristics and beliefs of the world's major religions are described below. Baha'i - Founded by Mirza Husayn-Ali (known as Baha'u'llah) in Iran in 1852, Baha'i faith emphasizes monotheism and believes in one eternal transcendent God. Its guiding focus is to encourage the unity of all peoples on the earth so that justice and peace m . . . more
Christian 31.4%, Muslim 23.2%, Hindu 15%, Buddhist 7.1%, folk religions 5.9%, Jewish 0.2%, other 0.8%, unaffiliated 16.4%
Age structure: This entry provides the distribution of the population according to age. Information is included by sex and age group as follows: 0-14 years (children), 15-24 years (early working age), 25-54 years (prime working age), 55-64 years (mature working age), 65 years and over (elderly). The age structure of a population affects a nation's key socioeconomic issues. Countries with young populations (high percentage under age 15) need to invest more in schools, while countries with older population . . . more 0-14 years: 25.44% (male 963,981,944/female 898,974,458) (2017 est.)15-24 years: 16.16% (male 611,311,930/female 572,229,547) (2017 est.)25-54 years: 41.12% (male 1,522,999,578/female 1,488,011,505) (2017 est.)55-64 years: 8.6% (male 307,262,939/female 322,668,546) (2017 est.)65 years and over: 8.68% (male 283,540,918/female 352,206,092) (2017 est.)population pyramid:
0-14 years: 25.44% (male 963,981,944/female 898,974,458) (2017 est.)15-24 years: 16.16% (male 611,311,930/female 572,229,547) (2017 est.)25-54 years: 41.12% (male 1,522,999,578/female 1,488,011,505) (2017 est.)55-64 years: 8.6% (male 307,262,939/female 322,668,546) (2017 est.)65 years and over: 8.68% (male 283,540,918/female 352,206,092) (2017 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalWorld Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalWorld Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for World. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for World. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios: Dependency ratios are a measure of the age structure of a population. They relate the number of individuals that are likely to be economically "dependent" on the support of others. Dependency ratios contrast the ratio of youths (ages 0-14) and the elderly (ages 65+) to the number of those in the working-age group (ages 15-64). Changes in the dependency ratio provide an indication of potential social support requirements resulting from changes in population age structures. As fertility lev . . . more total dependency ratio: 52.5 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 39.9 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 12.6 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 7.9 (2015 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more
total dependency ratio: 52.5 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 39.9 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 12.6 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 7.9 (2015 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more total: 30.6 yearsmale: 29.9 yearsfemale: 31.4 years (2018 est.)Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more
total: 30.6 yearsmale: 29.9 yearsfemale: 31.4 years (2018 est.)Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more 1.06% (2017 est.)
1.06% (2017 est.)note: this rate results in about 149 net additions to the worldwide population every minute or 2.5 every second
Birth rate: This entry gives the average annual number of births during a year per 1,000 persons in the population at midyear; also known as crude birth rate. The birth rate is usually the dominant factor in determining the rate of population growth. It depends on both the level of fertility and the age structure of the population. 18.4 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
18.4 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)note: this rate results in about 259 worldwide births per minute or 4.3 births every second
Death rate: This entry gives the average annual number of deaths during a year per 1,000 population at midyear; also known as crude death rate. The death rate, while only a rough indicator of the mortality situation in a country, accurately indicates the current mortality impact on population growth. This indicator is significantly affected by age distribution, and most countries will eventually show a rise in the overall death rate, in spite of continued decline in mortality at all ages, as declining . . . more 7.7 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
7.7 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)note: this rate results in about 108 worldwide deaths per minute or 1.8 deaths every second
Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. six of the world's seven continents are widely and permanently inhabited; Asia is easily the most populous continent with about 60% of the world's population (China and India together account for over 35%); Africa comes in second with over 15% of the earth's populace, Europe has about 10%, North America 8%, South America almost 6%, and Oceania less than 1%; the harsh conditions on Antarctica prevent any permanent habitationUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. Additionally, the World entry includes a list of the ten largest urban agglomerations. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising th . . . more
six of the world's seven continents are widely and permanently inhabited; Asia is easily the most populous continent with about 60% of the world's population (China and India together account for over 35%); Africa comes in second with over 15% of the earth's populace, Europe has about 10%, North America 8%, South America almost 6%, and Oceania less than 1%; the harsh conditions on Antarctica prevent any permanent habitationUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. Additionally, the World entry includes a list of the ten largest urban agglomerations. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising th . . . more urban population: 55.3% of total population (2017)rate of urbanization: 1.9% annual rate of change (2017)ten largest urban agglomerations: Tokyo (Japan) - 38,241,000; New Delhi (India) - 27,197,000; Shanghai (China) - 25,202,000; Beijing (China) - 22,063,000; Mumbai (India) - 21,690,000; Sao Paulo (Brazil) - 21,519,000; Mexico City (Mexico) - 21,321,000; Osaka (Japan) - 20,415,000; Cairo (Egypt) - 19,486,000; Dhaka (Bangladesh) - 18,898,000 (2017)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more
urban population: 55.3% of total population (2017)rate of urbanization: 1.9% annual rate of change (2017)ten largest urban agglomerations: Tokyo (Japan) - 38,241,000; New Delhi (India) - 27,197,000; Shanghai (China) - 25,202,000; Beijing (China) - 22,063,000; Mumbai (India) - 21,690,000; Sao Paulo (Brazil) - 21,519,000; Mexico City (Mexico) - 21,321,000; Osaka (Japan) - 20,415,000; Cairo (Egypt) - 19,486,000; Dhaka (Bangladesh) - 18,898,000 (2017)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female (2017 est.)0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female (2017 est.)15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female (2017 est.)25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2017 est.)55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female (2017 est.)65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female (2017 est.)total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Maternal mortality rate: The maternal mortality rate (MMR) is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding accidental or incidental causes). The MMR includes deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, for a specified year.
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female (2017 est.)0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female (2017 est.)15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female (2017 est.)25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2017 est.)55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female (2017 est.)65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female (2017 est.)total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Maternal mortality rate: The maternal mortality rate (MMR) is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding accidental or incidental causes). The MMR includes deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, for a specified year. 216 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country.
216 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country. total: 32.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)male: 34.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)female: 30.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures.
total: 32.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)male: 34.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)female: 30.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures. total population: 69 years (2017 est.)male: 67 years (2017 est.)female: 71.1 years (2017 est.)Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more
total population: 69 years (2017 est.)male: 67 years (2017 est.)female: 71.1 years (2017 est.)Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more 2.42 children born/woman (2017 est.)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more
2.42 children born/woman (2017 est.)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more improved: urban: 96.5% of populationrural: 84.7% of populationtotal: 91.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 3.5% of populationrural: 15.3% of populationtotal: 8.9% of population (2015 est.)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more
improved: urban: 96.5% of populationrural: 84.7% of populationtotal: 91.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 3.5% of populationrural: 15.3% of populationtotal: 8.9% of population (2015 est.)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more improved: urban: 82.3% of population (2015 est.)rural: 50.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 67.7% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 17.7% of population (2015 est.)rural: 49.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 32.3% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend.
improved: urban: 82.3% of population (2015 est.)rural: 50.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 67.7% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 17.7% of population (2015 est.)rural: 49.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 32.3% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend. 0.8% (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS.
0.8% (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS. 36.9 million (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year.
36.9 million (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year. 940,000 (2017 est.)Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and Census Bureau percentages for the total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Information on literacy, while not a perfect measu . . . more
940,000 (2017 est.)Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and Census Bureau percentages for the total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Information on literacy, while not a perfect measu . . . more definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 86.2%male: 89.8%female: 82.6% (2016 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 86.2%male: 89.8%female: 82.6% (2016 est.)note: more than three-quarters of the world's 750 million illiterate adults are found in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa; of all the illiterate adults in the world, almost two-thirds are women (2016)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education): School life expectancy (SLE) is the total number of years of schooling (primary to tertiary) that a child can expect to receive, assuming that the probability of his or her being enrolled in school at any particular future age is equal to the current enrollment ratio at that age. Caution must be maintained when utilizing this indicator in international comparisons. For example, a year or grade completed in one country is not necessarily the same in terms of educational content or qualit . . . more total: 12 years (2014)male: 12 years (2014)female: 12 years (2014)
total: 12 years (2014)male: 12 years (2014)female: 12 years (2014) -
Government :: World
-
Capital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones.
 there are 21 World entities (20 countries and 1 dependency) with multiple time zones: Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ecuador, France, Greenland, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kiribati, Mexico, Micronesia, Mongolia, Netherlands, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Portugal, Russia, Spain, United Statesnote: in some instances, the time zones pertain to portions of a country that lie overseasAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters.
there are 21 World entities (20 countries and 1 dependency) with multiple time zones: Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ecuador, France, Greenland, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kiribati, Mexico, Micronesia, Mongolia, Netherlands, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Portugal, Russia, Spain, United Statesnote: in some instances, the time zones pertain to portions of a country that lie overseasAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters. 195 countries, 72 dependent areas and other entitiesLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more
195 countries, 72 dependent areas and other entitiesLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more the legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including English and US law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law); an additional type of legal system - international law - governs the conduct of independent nations in their relationships with one anotherInternational law organization participation: This entry includes information on a country's acceptance of jurisdiction of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and of the International Criminal Court (ICCt); 59 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction with reservations and 11 have accepted ICJ jurisdiction without reservations; 122 countries have accepted ICCt jurisdiction. Appendix B: International Organizations and Groups explains the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt.
the legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including English and US law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law); an additional type of legal system - international law - governs the conduct of independent nations in their relationships with one anotherInternational law organization participation: This entry includes information on a country's acceptance of jurisdiction of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and of the International Criminal Court (ICCt); 59 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction with reservations and 11 have accepted ICJ jurisdiction without reservations; 122 countries have accepted ICCt jurisdiction. Appendix B: International Organizations and Groups explains the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt. all members of the UN are parties to the statute that established the International Court of Justice (ICJ) or World Court; 62 countries have accepted jurisdiction of the ICJ as compulsory with reservations and 12 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction as compulsory without reservations; states parties to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICCt) are those countries that have ratified or acceded to the Rome Statute, the treaty that established the Court; a total of 123 (as of October 2017) countries have accepted jurisdiction of the ICCt (see Appendix B for a clarification on the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt)Legislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more
all members of the UN are parties to the statute that established the International Court of Justice (ICJ) or World Court; 62 countries have accepted jurisdiction of the ICJ as compulsory with reservations and 12 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction as compulsory without reservations; states parties to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICCt) are those countries that have ratified or acceded to the Rome Statute, the treaty that established the Court; a total of 123 (as of October 2017) countries have accepted jurisdiction of the ICCt (see Appendix B for a clarification on the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt)Legislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more
there are 230 political entities with legislative bodies; of these 144 are unicameral (a single “house”) and 86 are bicameral (both upper and lower houses); note - while there are 195 countries in the world, 35 territories, possessions, or other special administrative units also have their own governing bodies
Flag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
note: the flags of 12 nations: Austria, Botswana, Georgia, Jamaica, Japan, Laos, Latvia, Macedonia, Micronesia, Nigeria, Switzerland, and Thailand have no top or bottom and may be flown with either long edge on top without any notice being taken
-
Economy :: World
-
Economy - overview: This entry briefly describes the type of economy, including the degree of market orientation, the level of economic development, the most important natural resources, and the unique areas of specialization. It also characterizes major economic events and policy changes in the most recent 12 months and may include a statement about one or two key future macroeconomic trends.

The international financial crisis of 2008-09 led to the first downturn in global output since 1946 and presented the world with a major new challenge: determining what mix of fiscal and monetary policies to follow to restore growth and jobs, while keeping inflation and debt under control. Financial stabilization and stimulus programs that started in 2009-11, combined with lower tax revenues in 2009-10, required most countries to run large budget deficits. Treasuries issued new public debt - totaling $9.1 trillion since 2008 - to pay for the additional expenditures. To keep interest rates low, most central banks monetized that debt, injecting large sums of money into their economies - between December 2008 and December 2013 the global money supply increased by more than 35%. Governments are now faced with the difficult task of spurring current growth and employment without saddling their economies with so much debt that they sacrifice long-term growth and financial stability. When economic activity picks up, central banks will confront the difficult task of containing inflation without raising interest rates so high they snuff out further growth.
Fiscal and monetary data for 2013 are currently available for 180 countries, which together account for 98.5% of world GDP. Of the 180 countries, 82 pursued unequivocally expansionary policies, boosting government spending while also expanding their money supply relatively rapidly - faster than the world average of 3.1%; 28 followed restrictive fiscal and monetary policies, reducing government spending and holding money growth to less than the 3.1% average; and the remaining 70 followed a mix of counterbalancing fiscal and monetary policies, either reducing government spending while accelerating money growth, or boosting spending while curtailing money growth.
(For more information, see attached spreadsheet.)
In 2013, for many countries the drive for fiscal austerity that began in 2011 abated. While 5 out of 6 countries slowed spending in 2012, only 1 in 2 countries slowed spending in 2013. About 1 in 3 countries actually lowered the level of their expenditures. The global growth rate for government expenditures increased from 1.6% in 2012 to 5.1% in 2013, after falling from a 10.1% growth rate in 2011. On the other hand, nearly 2 out of 3 central banks tightened monetary policy in 2013, decelerating the rate of growth of their money supply, compared with only 1 out of 3 in 2012. Roughly 1 of 4 central banks actually withdrew money from circulation, an increase from 1 out of 7 in 2012. Growth of the global money supply, as measured by the narrowly defined M1, slowed from 8.7% in 2009 and 10.4% in 2010 to 5.2% in 2011, 4.6% in 2012, and 3.1% in 2013. Several notable shifts occurred in 2013. By cutting government expenditures and expanding money supplies, the US and Canada moved against the trend in the rest of the world. France reversed course completely. Rather than reducing expenditures and money as it had in 2012, it expanded both. Germany reversed its fiscal policy, sharply expanding federal spending, while continuing to grow the money supply. South Korea shifted monetary policy into high gear, while maintaining a strongly expansionary fiscal policy. Japan, however, continued to pursue austere fiscal and monetary policies.
Austere economic policies have significantly affected economic performance. The global budget deficit narrowed to roughly $2.7 trillion in 2012 and $2.1 trillion in 2013, or 3.8% and 2.5% of World GDP, respectively. But growth of the world economy slipped from 5.1% in 2010 and 3.7% in 2011, to just 3.1% in 2012, and 2.9% in 2013.
Countries with expansionary fiscal and monetary policies achieved significantly higher rates of growth, higher growth of tax revenues, and greater success reducing the public debt burden than those countries that chose contractionary policies. In 2013, the 82 countries that followed a pro-growth approach achieved a median GDP growth rate of 4.7%, compared to 1.7% for the 28 countries with restrictive fiscal and monetary policies, a difference of 3 percentage points. Among the 82, China grew 7.7%, Philippines 6.8%, Malaysia 4.7%, Pakistan and Saudi Arabia 3.6%, Argentina 3.5%, South Korea 2.8%, and Russia 1.3%, while among the 28, Brazil grew 2.3%, Japan 2.0%, South Africa 2.0%, Netherlands -0.8%, Croatia -1.0%, Iran -1.5%, Portugal -1.8%, Greece -3.8%, and Cyprus -8.7%.
Faster GDP growth and lower unemployment rates translated into increased tax revenues and a less cumbersome debt burden. Revenues for the 82 expansionary countries grew at a median rate of 10.7%, whereas tax revenues fell at a median rate of 6.8% for the 28 countries that chose austere economic policies. Budget balances improved for about three-quarters of the 28, but, for most, debt grew faster than GDP, and the median level of their public debt as a share of GDP increased 9.1 percentage points, to 59.2%. On the other hand, budget balances deteriorated for most of the 82 pro-growth countries, but GDP growth outpaced increases in debt, and the median level of public debt as a share of GDP increased just 1.9%, to 39.8%.
The world recession has suppressed inflation rates - world inflation declined 1.0 percentage point in 2012 to about 4.1% and 0.2 percentage point to 3.9% in 2013. In 2013 the median inflation rate for the 82 pro-growth countries was 1.3 percentage points higher than that for the countries that followed more austere fiscal and monetary policies. Overall, the latter countries also improved their current account balances by shedding imports; as a result, current account balances deteriorated for most of the countries that pursued pro-growth policies. Slow growth of world income continued to hold import demand in check and crude oil prices fell. Consequently, the dollar value of world trade grew just 1.3% in 2013.
Beyond the current global slowdown, the world faces several long standing economic challenges. The addition of 80 million people each year to an already overcrowded globe is exacerbating the problems of pollution, waste-disposal, epidemics, water-shortages, famine, over-fishing of oceans, deforestation, desertification, and depletion of non-renewable resources. The nation-state, as a bedrock economic-political institution, is steadily losing control over international flows of people, goods, services, funds, and technology. The introduction of the euro as the common currency of much of Western Europe in January 1999, while paving the way for an integrated economic powerhouse, has created economic risks because the participating nations have varying income levels and growth rates, and hence, require a different mix of monetary and fiscal policies. Governments, especially in Western Europe, face the difficult political problem of channeling resources away from welfare programs in order to increase investment and strengthen incentives to seek employment. Because of their own internal problems and priorities, the industrialized countries are unable to devote sufficient resources to deal effectively with the poorer areas of the world, which, at least from an economic point of view, are becoming further marginalized. The terrorist attacks on the US on 11 September 2001 accentuated a growing risk to global prosperity - the diversion of resources away from capital investments to counter-terrorism programs.
Despite these vexing problems, the world economy also shows great promise. Technology has made possible further advances in a wide range of fields, from agriculture, to medicine, alternative energy, metallurgy, and transportation. Improved global communications have greatly reduced the costs of international trade, helping the world gain from the international division of labor, raise living standards, and reduce income disparities among nations. Much of the resilience of the world economy in the aftermath of the financial crisis resulted from government and central bank leaders around the globe working in concert to stem the financial onslaught, knowing well the lessons of past economic failures.
Fiscal and Monetary Data, 2008-2012: Spreadsheet
GDP (purchasing power parity): This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more
Spreadsheet
GDP (purchasing power parity): This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more $127.8 trillion (2017 est.)$123.3 trillion (2016 est.)$119.5 trillion (2015 est.)
$127.8 trillion (2017 est.)$123.3 trillion (2016 est.)$119.5 trillion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate): This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at official exchange rates (OER) is the home-currency-denominated annual GDP figure divided by the bilateral average US exchange rate with that country in that year. The measure is simple to compute and gives a precise measure of the value of output. Many economists prefer this measure when gauging the economic power an economy maintains vis- . . . more $80.27 trillion SGWP (gross world product) (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate: This entry gives GDP growth on an annual basis adjusted for inflation and expressed as a percent. The growth rates are year-over-year, and not compounded.
$80.27 trillion SGWP (gross world product) (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate: This entry gives GDP growth on an annual basis adjusted for inflation and expressed as a percent. The growth rates are year-over-year, and not compounded. 3.7% (2017 est.)3.2% (2016 est.)3.3% (2014 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year.
3.7% (2017 est.)3.2% (2016 est.)3.3% (2014 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year. $17,500 (2017 est.)$17,000 (2016 est.)$16,800 (2015 est.)
$17,500 (2017 est.)$17,000 (2016 est.)$16,800 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
Gross national saving: Gross national saving is derived by deducting final consumption expenditure (household plus government) from Gross national disposable income, and consists of personal saving, plus business saving (the sum of the capital consumption allowance and retained business profits), plus government saving (the excess of tax revenues over expenditures), but excludes foreign saving (the excess of imports of goods and services over exports). The figures are presented as a percent of GDP. A negative . . . more 27.9% of GDP (2017 est.)27.4% of GDP (2016 est.)27.8% of GDP (2015 est.)GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more
27.9% of GDP (2017 est.)27.4% of GDP (2016 est.)27.8% of GDP (2015 est.)GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more household consumption: 56.4% (2017 est.)government consumption: 16.1% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 25.7% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 1.4% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 28.8% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -28.3% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin: This entry shows where production takes place in an economy. The distribution gives the percentage contribution of agriculture, industry, and services to total GDP, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other private economic activities that do not prod . . . more
household consumption: 56.4% (2017 est.)government consumption: 16.1% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 25.7% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 1.4% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 28.8% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -28.3% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin: This entry shows where production takes place in an economy. The distribution gives the percentage contribution of agriculture, industry, and services to total GDP, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other private economic activities that do not prod . . . more agriculture: 6.4% (2017 est.)industry: 30% (2017 est.)services: 63% (2017 est.)Industries: This entry provides a rank ordering of industries starting with the largest by value of annual output.
agriculture: 6.4% (2017 est.)industry: 30% (2017 est.)services: 63% (2017 est.)Industries: This entry provides a rank ordering of industries starting with the largest by value of annual output.
dominated by the onrush of technology, especially in computers, robotics, telecommunications, and medicines and medical equipment; most of these advances take place in OECD nations; only a small portion of non-OECD countries have succeeded in rapidly adjusting to these technological forces; the accelerated development of new technologies is complicating already grim environmental problems
Industrial production growth rate: This entry gives the annual percentage increase in industrial production (includes manufacturing, mining, and construction). 3.2% (2017 est.)Labor force: This entry contains the total labor force figure.
3.2% (2017 est.)Labor force: This entry contains the total labor force figure. 3.432 billion (2017 est.)Labor force - by occupation: This entry lists the percentage distribution of the labor force by sector of occupation. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other economic activities that do not produce material goods. The distribution will total less than 100 percent if the data are incomplete and may range from 99-101 percent due to rounding. more
3.432 billion (2017 est.)Labor force - by occupation: This entry lists the percentage distribution of the labor force by sector of occupation. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other economic activities that do not produce material goods. The distribution will total less than 100 percent if the data are incomplete and may range from 99-101 percent due to rounding. more agriculture: 31%industry: 23.5%services: 45.5% (2014 est.)Unemployment rate: This entry contains the percent of the labor force that is without jobs. Substantial underemployment might be noted.
agriculture: 31%industry: 23.5%services: 45.5% (2014 est.)Unemployment rate: This entry contains the percent of the labor force that is without jobs. Substantial underemployment might be noted. 7.7% (2017 est.)7.5% (2016 est.)
7.7% (2017 est.)7.5% (2016 est.)note: combined unemployment and underemployment in many non-industrialized countries; developed countries typically 4%-12% unemployment (2007 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share: Data on household income or consumption come from household surveys, the results adjusted for household size. Nations use different standards and procedures in collecting and adjusting the data. Surveys based on income will normally show a more unequal distribution than surveys based on consumption. The quality of surveys is improving with time, yet caution is still necessary in making inter-country comparisons. lowest 10%: 30.2% (2008 est.)highest 10%: 30.2% (2007.75 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index: This index measures the degree of inequality in the distribution of family income in a country. The index is calculated from the Lorenz curve, in which cumulative family income is plotted against the number of families arranged from the poorest to the richest. The index is the ratio of (a) the area between a country's Lorenz curve and the 45 degree helping line to (b) the entire triangular area under the 45 degree line. The more nearly equal a country's income distribution, the closer its . . . more
lowest 10%: 30.2% (2008 est.)highest 10%: 30.2% (2007.75 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index: This index measures the degree of inequality in the distribution of family income in a country. The index is calculated from the Lorenz curve, in which cumulative family income is plotted against the number of families arranged from the poorest to the richest. The index is the ratio of (a) the area between a country's Lorenz curve and the 45 degree helping line to (b) the entire triangular area under the 45 degree line. The more nearly equal a country's income distribution, the closer its . . . more 37.9 (2012 est.)37.9 (2005 est.)Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
37.9 (2012 est.)37.9 (2005 est.)Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. revenues: 21.68 trillion (2017 est.)expenditures: 23.81 trillion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more
revenues: 21.68 trillion (2017 est.)expenditures: 23.81 trillion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more 26.7% (of GDP) (2016 est.)Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more
26.7% (of GDP) (2016 est.)Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more -3% (of GDP) (2016 est.)Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings.
-3% (of GDP) (2016 est.)Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings. 67.2% of GDP (2017 est.)67.2% of GDP (2016 est.)Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices.
67.2% of GDP (2017 est.)67.2% of GDP (2016 est.)Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices. 6.4% (2017 est.)3.7% (2016 est.)developed countries: 1.9% (2017 est.) 0.9% (2016 est.)
6.4% (2017 est.)3.7% (2016 est.)developed countries: 1.9% (2017 est.) 0.9% (2016 est.)
developing countries: 8.8% (2017 est.) 3.7% (2016 est.)
note: the above estimates are weighted averages; inflation in developed countries is 0% to 4% typically, in developing countries, 4% to 10% typically; national inflation rates vary widely in individual cases; inflation rates have declined for most countries for the last several years, held in check by increasing international competition from several low wage countries and by soft demand due to the world financial crisisStock of narrow money: This entry, also known as "M1," comprises the total quantity of currency in circulation (notes and coins) plus demand deposits denominated in the national currency held by nonbank financial institutions, state and local governments, nonfinancial public enterprises, and the private sector of the economy, measured at a specific point in time. National currency units have been converted to US dollars at the closing exchange rate for the date of the information. Because of exchange rate moveme . . . more $34.4 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$30.17 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of broad money: This entry covers all of "Narrow money," plus the total quantity of time and savings deposits, credit union deposits, institutional money market funds, short-term repurchase agreements between the central bank and commercial deposit banks, and other large liquid assets held by nonbank financial institutions, state and local governments, nonfinancial public enterprises, and the private sector of the economy. National currency units have been converted to US dollars at the closing exchange r . . . more
$34.4 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$30.17 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of broad money: This entry covers all of "Narrow money," plus the total quantity of time and savings deposits, credit union deposits, institutional money market funds, short-term repurchase agreements between the central bank and commercial deposit banks, and other large liquid assets held by nonbank financial institutions, state and local governments, nonfinancial public enterprises, and the private sector of the economy. National currency units have been converted to US dollars at the closing exchange r . . . more $86.47 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$77.71 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of domestic credit: This entry is the total quantity of credit, denominated in the domestic currency, provided by financial institutions to the central bank, state and local governments, public non-financial corporations, and the private sector. The national currency units have been converted to US dollars at the closing exchange rate on the date of the information.
$86.47 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$77.71 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of domestic credit: This entry is the total quantity of credit, denominated in the domestic currency, provided by financial institutions to the central bank, state and local governments, public non-financial corporations, and the private sector. The national currency units have been converted to US dollars at the closing exchange rate on the date of the information. $111.7 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$100.4 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares: This entry gives the value of shares issued by publicly traded companies at a price determined in the national stock markets on the final day of the period indicated. It is simply the latest price per share multiplied by the total number of outstanding shares, cumulated over all companies listed on the particular exchange.
$111.7 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$100.4 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares: This entry gives the value of shares issued by publicly traded companies at a price determined in the national stock markets on the final day of the period indicated. It is simply the latest price per share multiplied by the total number of outstanding shares, cumulated over all companies listed on the particular exchange. $67.47 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)$68.51 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)$68.37 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
$67.47 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)$68.51 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)$68.37 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $17.31 trillion (2017 est.)$15.82 trillion (2016 est.)Exports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued exported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
$17.31 trillion (2017 est.)$15.82 trillion (2016 est.)Exports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued exported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services
top ten - share of world trade: 14.8 electrical machinery, including computers; 14.4 mineral fuels, including oil, coal, gas, and refined products; 14.2 nuclear reactors, boilers, and parts; 8.9 cars, trucks, and buses; 3.5 scientific and precision instruments; 3.4 plastics; 2.7 iron and steel; 2.6 organic chemicals; 2.6 pharmaceutical products; 1.9 diamonds, pearls, and precious stones
(2007 est.)Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $20.01 trillion (2018 est.)$16.02 trillion (2017 est.)Imports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued imported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
$20.01 trillion (2018 est.)$16.02 trillion (2017 est.)Imports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued imported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services
top ten - share of world trade: see listing for exports
Debt - external: This entry gives the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods, or services. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $76.56 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$75.09 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)note: this figure is the sum total of all countries' external debt, both public and privateStock of direct foreign investment - at home: This entry gives the cumulative US dollar value of all investments in the home country made directly by residents - primarily companies - of other countries as of the end of the time period indicated. Direct investment excludes investment through purchase of shares.
$76.56 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$75.09 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)note: this figure is the sum total of all countries' external debt, both public and privateStock of direct foreign investment - at home: This entry gives the cumulative US dollar value of all investments in the home country made directly by residents - primarily companies - of other countries as of the end of the time period indicated. Direct investment excludes investment through purchase of shares. $33.6 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$31.62 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad: This entry gives the cumulative US dollar value of all investments in foreign countries made directly by residents - primarily companies - of the home country, as of the end of the time period indicated. Direct investment excludes investment through purchase of shares.
$33.6 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$31.62 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad: This entry gives the cumulative US dollar value of all investments in foreign countries made directly by residents - primarily companies - of the home country, as of the end of the time period indicated. Direct investment excludes investment through purchase of shares. $34.73 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$32.94 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)
$34.73 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$32.94 trillion (31 December 2016 est.) -
Energy :: World
-
Electricity access: This entry provides information on access to electricity. Electrification data – collected from industry reports, national surveys, and international sources – consists of four subfields. Population without electricity provides an estimate of the number of citizens that do not have access to electricity. Electrification – total population is the percent of a country’s total population with access to electricity, electrification – urban areas is the percent of a country’s urban population w . . . more
 population without electricity: 1.201 billion (2013)electrification - total population: 83% (2013)electrification - urban areas: 95% (2013)electrification - rural areas: 70% (2013)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
population without electricity: 1.201 billion (2013)electrification - total population: 83% (2013)electrification - urban areas: 95% (2013)electrification - rural areas: 70% (2013)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 23.65 trillion kWh (2015 est.)Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
23.65 trillion kWh (2015 est.)Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 21.78 trillion kWh (2015 est.)Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
21.78 trillion kWh (2015 est.)Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 696.1 billion kWh (2016)Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
696.1 billion kWh (2016)Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 721.9 billion kWh (2016 est.)Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour.
721.9 billion kWh (2016 est.)Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour. 6.386 billion kW (2015 est.)Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
6.386 billion kW (2015 est.)Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 63% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
63% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 6% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
6% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 18% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
18% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 14% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
14% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 80.77 million bbl/day (2016 est.)Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
80.77 million bbl/day (2016 est.)Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 43.57 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
43.57 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 44.58 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
44.58 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 1.665 trillion bbl (1 January 2017 est.)Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
1.665 trillion bbl (1 January 2017 est.)Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 88.4 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
88.4 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 96.26 million bbl/day (2015 est.)Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
96.26 million bbl/day (2015 est.)Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 29.66 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
29.66 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 28.62 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
28.62 million bbl/day (2014 est.)Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 3.481 trillion cu m (2015 est.)Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
3.481 trillion cu m (2015 est.)Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 3.477 trillion cu m (2015 est.)Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m).
3.477 trillion cu m (2015 est.)Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m). 1.156 trillion cu m (2013 est.)Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m).
1.156 trillion cu m (2013 est.)Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m). 1.496 trillion cu m (2013 est.)Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
1.496 trillion cu m (2013 est.)Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 196.1 trillion cu m (1 January 2016 est.)Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy.
196.1 trillion cu m (1 January 2016 est.)Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy. 33.62 billion Mt (2013 est.)
33.62 billion Mt (2013 est.) -
Communications :: World
-
Telephones - fixed lines: This entry gives the total number of fixed telephone lines in use, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants.
 total subscriptions: 984,289,950 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2017 est.)Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100.
total subscriptions: 984,289,950 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2017 est.)Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100. total subscriptions: 7,806,142,681 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11 (2017 est.)Internet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months.
total subscriptions: 7,806,142,681 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11 (2017 est.)Internet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months. 3.174 billion (July 2016 est.)
3.174 billion (July 2016 est.)top ten countries by Internet usage (in millions): 730.7 China; 374.3 India; 246.8 United States; 122.8 Brazil; 116.6 Japan; 108.8 Russia; 73.3 Mexico; 72.3 Germany; 65.5 Indonesia; 61 United Kingdom
Broadband - fixed subscriptions: This entry gives the total number of fixed-broadband subscriptions, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Fixed broadband is a physical wired connection to the Internet (e.g., coaxial cable, optical fiber) at speeds equal to or greater than 256 kilobits/second (256 kbit/s). total: 1,002,793,951subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1Communications - note: This entry includes miscellaneous communications information of significance not included elsewhere.
total: 1,002,793,951subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1Communications - note: This entry includes miscellaneous communications information of significance not included elsewhere.
three major data centers - which provide colocation, telecommunications, cloud services, and content ecosystems - compete to be called the world's biggest in terms of physical space occupied:
no. 1. - a data farm in Langfang, Hebei Province, China, identified as the Range International Information Group, claims to be the largest with 585,000 sq m (6.3 million sq ft),
no. 2. - a data farm in Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, known as the Switch SuperNAP data center, comes in second with over 325,000 sq m (3.5 million sq ft); it intends to expand to over 1.615 million sq m (17.4 million sq ft) by 2020,
no. 3. - a data farm in Ashburn, Virginia, USA, referred to as the DFT Data Center, is a transit point for 70% of the world's Internet traffic; it includes 150,000 sq m (1.6 million sq ft) spread out over six separate buildings -
Transportation :: World
-
Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
 41,820 (2016)
41,820 (2016)top ten by passengers: Atlanta (ATL) - 104,171,935; Beijing (PEK) - 94,393,454; Dubai (DXB) - 83,654,250; Los Angeles (LAX) - 80,921,527; Tokyo (HND) - 79,699,762; Chicago (ORD) - 77,960,588; London (LHR) - 75,715,474; Hong Kong (HKG) 70,305,857; Shanghai (PVG) 66, 002,414; Paris (CDG) - 65,933,145 (2016)
top ten by cargo (metric tons): Hong Kong (HKG) - 4,615,241; Memphis, TN (MEM) - 4,322,071; Shanghai (PVG) - 3,440,280; Incheon (ICN) - 2,714,341; Dubai (DXB) - 2,592,454; Anchorage, AK (ANC) - 2,542,526; Louisville, KY (SDF) - 2,437,010; Tokyo (NRT) - 2,165427; Paris (CDG) - 2,135,172; Frankfurt (FRA) - 2,113,594 (2016)
Heliports: This entry gives the total number of heliports with hard-surface runways, helipads, or landing areas that support routine sustained helicopter operations exclusively and have support facilities including one or more of the following facilities: lighting, fuel, passenger handling, or maintenance. It includes former airports used exclusively for helicopter operations but excludes heliports limited to day operations and natural clearings that could support helicopter landings and takeoffs. 6,524 (2013)Railways: This entry states the total route length of the railway network and of its component parts by gauge, which is the measure of the distance between the inner sides of the load-bearing rails. The four typical types of gauges are: broad, standard, narrow, and dual. Other gauges are listed under note. Some 60% of the world's railways use the standard gauge of 1.4 m (4.7 ft). Gauges vary by country and sometimes within countries. The choice of gauge during initial construction was mainly in resp . . . more
6,524 (2013)Railways: This entry states the total route length of the railway network and of its component parts by gauge, which is the measure of the distance between the inner sides of the load-bearing rails. The four typical types of gauges are: broad, standard, narrow, and dual. Other gauges are listed under note. Some 60% of the world's railways use the standard gauge of 1.4 m (4.7 ft). Gauges vary by country and sometimes within countries. The choice of gauge during initial construction was mainly in resp . . . more total: 1,148,186 km (2013)Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions.
total: 1,148,186 km (2013)Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions. total: 64,285,009 km (2013)Waterways: This entry gives the total length of navigable rivers, canals, and other inland bodies of water.
total: 64,285,009 km (2013)Waterways: This entry gives the total length of navigable rivers, canals, and other inland bodies of water. 2,293,412 km (2017)top ten longest rivers: Nile (Africa) 6,693 km; Amazon (South America) 6,436 km; Mississippi-Missouri (North America) 6,238 km; Yenisey-Angara (Asia) 5,981 km; Ob-Irtysh (Asia) 5,569 km; Yangtze (Asia) 5,525 km; Yellow (Asia) 4,671 km; Amur (Asia) 4,352 km; Lena (Asia) 4,345 km; Congo (Africa) 4,344 km
2,293,412 km (2017)top ten longest rivers: Nile (Africa) 6,693 km; Amazon (South America) 6,436 km; Mississippi-Missouri (North America) 6,238 km; Yenisey-Angara (Asia) 5,981 km; Ob-Irtysh (Asia) 5,569 km; Yangtze (Asia) 5,525 km; Yellow (Asia) 4,671 km; Amur (Asia) 4,352 km; Lena (Asia) 4,345 km; Congo (Africa) 4,344 kmnote: rivers are not necessarily navigable along the entire length; if measured by volume, the Amazon is the largest river in the world, responsible for about 20% of the Earth's freshwater entering the ocean
top ten largest natural lakes (by surface area): Caspian Sea (Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkmenistan) 372,960 sq km; Lake Superior (Canada, United States) 82,414 sq km; Lake Victoria (Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda) 69,490 sq km; Lake Huron (Canada, United States) 59,596 sq km; Lake Michigan (United States) 57,441 sq km; Lake Tanganyika (Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Zambia) 32,890 sq km; Great Bear Lake (Canada) 31,800 sq km; Lake Baikal (Russia) 31,494 sq km; Lake Nyasa (Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania) 30,044 sq km; Great Slave Lake (Canada) 28,400 sq km
note: the areas of the lakes are subject to seasonal variation; only the Caspian Sea is saline, the rest are fresh water
note: Lakes Huron and Michigan are technically a single lake because the flow of water between the Straits of Mackinac that connects the two lakes keeps their water levels at near-equilibrium; combined, Lake Huron-Michigan is the largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world
Merchant marine: Merchant marine may be defined as all ships engaged in the carriage of goods; or all commercial vessels (as opposed to all nonmilitary ships), which excludes tugs, fishing vessels, offshore oil rigs, etc. This entry contains information in four fields - total, ships by type, foreign-owned, and registered in other countries. Total includes the number of ships (1,000 GRT or over), total DWT for those ships, and total GRT for those ships. DWT or dead weight tonnage is the total weight of ca . . . more total: 91,557 (2017)by type: bulk carrier 10872, container ship 5137, general cargo 19160, oil tanker 9995, other 46396 (2017)Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more
total: 91,557 (2017)by type: bulk carrier 10872, container ship 5137, general cargo 19160, oil tanker 9995, other 46396 (2017)Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more
top twenty container ports as measured by Twenty-Foot Equivalent Units (TEUs) throughput: Shanghai (China) - 37,133,000; Singapore (Singapore) - 30,922,600; Shenzhen (China) - 23,979,300; Ningbo (China) - 21,560,000; Busan (South Korea) - 19,850,000; Hong Kong (China) - 19,813,000; Guangzhou (China) - 18,857,700; Qingdao (China) - 18,010,000; Dubai (UAE) - 14,772,000; - Tianjin (China) - 14,490,000; Port Kelang (Malaysia) - 13,169,577; Rotterdam (Netherlands) - 12,385,168; Kaohsiung (Taiwan) - 10,464,860; Antwerp (Belgium) - 10,037,341; Dalian (China) - 9,614,000; Xiamen (China) - 9,613,679; Hamburg (Germany) - 8,910,000; Los Angeles (US) - 8,856,783; Tanjung Pelepas (Malaysia) - 8,280,661; Laem Chabang (Thailand) - 7,227,431 (2016)
-
Military and Security :: World
-
Military expenditures: This entry gives spending on defense programs for the most recent year available as a percent of gross domestic product (GDP); the GDP is calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). For countries with no military forces, this figure can include expenditures on public security and police.
 2.22% of GDP (2016)2.27% of GDP (2015)2.26% of GDP (2014)2.3% of GDP (2013)2.36% of GDP (2012)Maritime threats: This entry describes the threat of piracy, as defined in Article 101, UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), or armed robbery against ships, as defined in Resolution A. 1025 (26) adopted on 2 December 2009 at the 26th Assembly Session of the International Maritime Organization. The entry includes the number of ships on the high seas or in territorial waters that were boarded or attacked by pirates, and the number of crewmen abducted or killed, as compiled by the International Mariti . . . more
2.22% of GDP (2016)2.27% of GDP (2015)2.26% of GDP (2014)2.3% of GDP (2013)2.36% of GDP (2012)Maritime threats: This entry describes the threat of piracy, as defined in Article 101, UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), or armed robbery against ships, as defined in Resolution A. 1025 (26) adopted on 2 December 2009 at the 26th Assembly Session of the International Maritime Organization. The entry includes the number of ships on the high seas or in territorial waters that were boarded or attacked by pirates, and the number of crewmen abducted or killed, as compiled by the International Mariti . . . more
the International Maritime Bureau (IMB) reports that 2017 saw a continued slight decrease in global pirate activities; in 2017, pirates attacked a total of 180 ships world-wide including boarding 136 ships, hijacking six ships, and firing on 16; this activity is down from 191 incidents in 2016; in 2017, the number of hostages dropped to 91, however, the number of seafarers kidnapped for ransom increased dramatically to 75 with nearly all taken off West Africa; three mariners were killed world-wide in 2017
Operation Ocean Shield, the NATO naval task force established in 2009 to combat Somali piracy, concluded its operations in December 2016 as a result of the drop in reported incidents over the last few years; the EU naval mission, Operation ATALANTA, continues its operations in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean through 2020; naval units from Japan, India, and China also operate in conjuction with EU forces; China has established a logistical base in Djibouti to support its deployed naval units in the Horn of Africa
the Horn of Africa continued to see pirate activities with 12 incidents in 2017, a slight increase over 2016; the decrease in successful pirate attacks off the Horn of Africa since the peak in 2007 was due, in part, to anti-piracy operations by international naval forces, the hardening of vessels, and the increased use of armed security teams aboard merchant ships; despite these preventative measures, the assessed risk remains high
West African piracy is a continuing threat with 33 attacks in 2017 compared to 36 in 2016; Nigerian pirates are very aggressive, operating as far as 200 nm offshore and boarding 20 ships in 2017; attacks in South Asian waters remain at low levels with an increase in Bangladesh from three incidents in 2016 to 11 in 2017; Peru reported two incidents in 2017, down from 11 in 2016; attacks in Vietnam declined from nine in 2016 to two in 2017; the majority of global attacks against shipping have occured in the offshore waters of five countries - Nigeria, Indonesia, Philippines, Venezuela, and Bangladesh
-
Transnational Issues :: World
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more
 stretching over 250,000 km, the world's 325 international land boundaries separate 195 independent states and 71 dependencies, areas of special sovereignty, and other miscellaneous entitiesethnicity, culture, race, religion, and language have divided states into separate political entities as much as history, physical terrain, political fiat, or conquest, resulting in sometimes arbitrary and imposed boundariesmost maritime states have claimed limits that include territorial seas and exclusive economic zones; overlapping limits due to adjacent or opposite coasts create the potential for 430 bilateral maritime boundaries of which 209 have agreements that include contiguous and non-contiguous segmentsboundary, borderland/resource, and territorial disputes vary in intensity from managed or dormant to violent or militarizedundemarcated, indefinite, porous, and unmanaged boundaries tend to encourage illegal cross-border activities, uncontrolled migration, and confrontationterritorial disputes may evolve from historical and/or cultural claims, or they may be brought on by resource competitionethnic and cultural clashes continue to be responsible for much of the territorial fragmentation and internal displacement of the estimated 20.8 million people and cross-border displacements of approximately 12.1 million refugees and asylum seekers around the world as of mid-2013over half a million refugees were repatriated during 2012other sources of contention include access to water and mineral (especially hydrocarbon) resources, fisheries, and arable landarmed conflict prevails not so much between the uniformed armed forces of independent states as between stateless armed entities that detract from the sustenance and welfare of local populations, leaving the community of nations to cope with resultant refugees, hunger, disease, impoverishment, and environmental degradationRefugees and internally displaced persons: This entry includes those persons residing in a country as refugees, internally displaced persons (IDPs), or stateless persons. Each country's refugee entry includes only countries of origin that are the source of refugee populations of 5,000 or more. The definition of a refugee according to a UN Convention is "a person who is outside his/her country of nationality or habitual residence; has a well-founded fear of persecution because of his/her race, religion, nationality, membership in a . . . more
stretching over 250,000 km, the world's 325 international land boundaries separate 195 independent states and 71 dependencies, areas of special sovereignty, and other miscellaneous entitiesethnicity, culture, race, religion, and language have divided states into separate political entities as much as history, physical terrain, political fiat, or conquest, resulting in sometimes arbitrary and imposed boundariesmost maritime states have claimed limits that include territorial seas and exclusive economic zones; overlapping limits due to adjacent or opposite coasts create the potential for 430 bilateral maritime boundaries of which 209 have agreements that include contiguous and non-contiguous segmentsboundary, borderland/resource, and territorial disputes vary in intensity from managed or dormant to violent or militarizedundemarcated, indefinite, porous, and unmanaged boundaries tend to encourage illegal cross-border activities, uncontrolled migration, and confrontationterritorial disputes may evolve from historical and/or cultural claims, or they may be brought on by resource competitionethnic and cultural clashes continue to be responsible for much of the territorial fragmentation and internal displacement of the estimated 20.8 million people and cross-border displacements of approximately 12.1 million refugees and asylum seekers around the world as of mid-2013over half a million refugees were repatriated during 2012other sources of contention include access to water and mineral (especially hydrocarbon) resources, fisheries, and arable landarmed conflict prevails not so much between the uniformed armed forces of independent states as between stateless armed entities that detract from the sustenance and welfare of local populations, leaving the community of nations to cope with resultant refugees, hunger, disease, impoverishment, and environmental degradationRefugees and internally displaced persons: This entry includes those persons residing in a country as refugees, internally displaced persons (IDPs), or stateless persons. Each country's refugee entry includes only countries of origin that are the source of refugee populations of 5,000 or more. The definition of a refugee according to a UN Convention is "a person who is outside his/her country of nationality or habitual residence; has a well-founded fear of persecution because of his/her race, religion, nationality, membership in a . . . more
the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) estimated that as of the end of 2017 there were 68.5 million people forcibly displaced worldwide, the highest level ever recorded; this includes 25.4 million refugees, 3.1 million asylum seekers, and 40 million conflict IDPs; the UNHCR estimates there are currently at least 10 million stateless persons
Trafficking in persons: Trafficking in persons is modern-day slavery, involving victims who are forced, defrauded, or coerced into labor or sexual exploitation. The International Labor Organization (ILO), the UN agency charged with addressing labor standards, employment, and social protection issues, estimated in 2011 that 20.9 million people worldwide were victims of forced labor, bonded labor, forced child labor, sexual servitude, and involuntary servitude. Human trafficking is a multi-dimensional threat, depri . . . more current situation: the International Labour Organization conservatively estimated that 20.9 million people in 2012 were victims of forced labor, representing the full range of human trafficking (also referred to as 'modern-day slavery') for labor and sexual exploitation; about one-third of reported cases involved crossing international borders, which is often associated with sexual exploitation; trafficking in persons is most prevalent in southeastern Europe, Eurasia, and Africa and least frequent in EU member states, Canada, the US, and other developed countries (2012)tier rating: (2015)Tier 2 Watch List: countries that do not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but are making significant efforts to do so; (44 countries) Antigua and Barbuda, Bolivia, Botswana, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Burma, Cambodia, China, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Costa Rica, Cuba, Djibouti, Egypt, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Laos, Lebanon, Lesotho, Malaysia, Maldives, Mali, Mauritius, Namibia, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Suriname, Tanzania, Timor-Leste, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan
current situation: the International Labour Organization conservatively estimated that 20.9 million people in 2012 were victims of forced labor, representing the full range of human trafficking (also referred to as 'modern-day slavery') for labor and sexual exploitation; about one-third of reported cases involved crossing international borders, which is often associated with sexual exploitation; trafficking in persons is most prevalent in southeastern Europe, Eurasia, and Africa and least frequent in EU member states, Canada, the US, and other developed countries (2012)tier rating: (2015)Tier 2 Watch List: countries that do not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but are making significant efforts to do so; (44 countries) Antigua and Barbuda, Bolivia, Botswana, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Burma, Cambodia, China, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Costa Rica, Cuba, Djibouti, Egypt, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Laos, Lebanon, Lesotho, Malaysia, Maldives, Mali, Mauritius, Namibia, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Suriname, Tanzania, Timor-Leste, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, UzbekistanTier 3: countries that neither satisfy the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking nor demonstrate a significant effort to do so; (23 countries) Algeria, Belarus, Belize, Burundi, Central African Republic, Comoros, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, The Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Iran, North Korea, Kuwait, Libya, Marshall Islands, Mauritania, Russia, South Sudan, Syria, Thailand, Venezuela, Yemen, Zimbabwe
Illicit drugs: This entry gives information on the five categories of illicit drugs - narcotics, stimulants, depressants (sedatives), hallucinogens, and cannabis. These categories include many drugs legally produced and prescribed by doctors as well as those illegally produced and sold outside of medical channels. Cannabis (Cannabis sativa) is the common hemp plant, which provides hallucinogens with some sedative properties, and includes marijuana (pot, Acapulco gold, grass, reefer), tetrahydroca . . . more
cocaine: worldwide coca leaf cultivation in 2013 likely amounted to 165,000 hectares, assuming a stable crop in Bolivia; Colombia produced slightly less than half of the worldwide crop, followed by Peru and Bolivia; potential pure cocaine production increased 7% to 640 metric tons in 2013; Colombia conducts an aggressive coca eradication campaign, Peru has increased its eradication efforts, but remains hesitant to eradicate coca in key growing areas;
opiates: worldwide illicit opium poppy cultivation increased in 2013, with potential opium production reaching 6,800 metric tons; Afghanistan is world's primary opium producer, accounting for 82% of the global supply; Southeast Asia was responsible for 12% of global opium; Pakistan produced 3% of global opium; Latin America produced 4% of global opium, and most was refined into heroin destined for the US market
(2015)