

-
Introduction :: Angola
-
Background:Angola scores low on human development indexes despite using its large oil reserves to rebuild since the end of a 27-year civil war in 2002. Fighting between the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS, and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), led by Jonas SAVIMBI, followed independence from Portugal in 1975. Peace seemed imminent in 1992 when Angola held national elections, but fighting picked up again in 1993. Up to 1.5 million lives may have been lost - and 4 million people displaced - during the more than a quarter century of fighting. SAVIMBI's death in 2002 ended UNITA's insurgency and cemented the MPLA's hold on power. DOS SANTOS stepped down from the presidency in 2017, having led the country since 1979. He pushed through a new constitution in 2010. Joao LOURENCO was elected president in August 2017 and became president of the MPLA in September 2018.
-
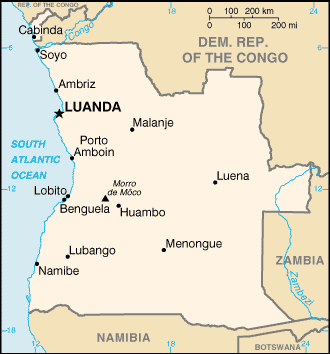
Geography :: Angola
-
Location:Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and Democratic Republic of the CongoGeographic coordinates:12 30 S, 18 30 EMap references:AfricaArea:total: 1,246,700 sq kmland: 1,246,700 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 24Area - comparative:about eight times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of TexasArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Angola Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Angola Print Image Description
Image Descriptionabout eight times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Texas
Land boundaries:total: 5,369 kmborder countries (4): Democratic Republic of the Congo 2646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province), Republic of the Congo 231 km, Namibia 1427 km, Zambia 1065 kmCoastline:1,600 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmClimate:semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April)Terrain:narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateauElevation:mean elevation: 1,112 mlowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Moca 2,620 mNatural resources:petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uraniumLand use:agricultural land: 47.5% (2016 est.)arable land: 3.9% (2016 est.) / permanent crops: 0.3% (2016 est.) / permanent pasture: 43.3% (2016 est.)forest: 46.3% (2016 est.)other: 6.2% (2016 est.)Irrigated land:860 sq km (2014)Population distribution:most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of LuandaNatural hazards:locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateauEnvironment - current issues:overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion attributable to population pressures; desertification; deforestation of tropical rain forest, in response to both international demand for tropical timber and to domestic use as fuel, resulting in loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and siltation of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable waterEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollutionsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo -
People and Society :: Angola
-
Population:30,355,880 (July 2018 est.)
note: Angola's national statistical agency projects the country's 2017 population to be 28.4 million
country comparison to the world: 45Nationality:noun: Angolan(s)adjective: AngolanEthnic groups:Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22%Languages:Portuguese 71.2% (official), Umbundu 23%, Kikongo 8.2%, Kimbundu 7.8%, Chokwe 6.5%, Nhaneca 3.4%, Nganguela 3.1%, Fiote 2.4%, Kwanhama 2.3%, Muhumbi 2.1%, Luvale 1%, other 3.6% (2014 est.)note: most widely spoken languages; shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Religions:Roman Catholic 41.1%, Protestant 38.1%, other 8.6%, none 12.3% (2014 est.)Demographic profile:More than a decade after the end of Angola's 27-year civil war, the country still faces a variety of socioeconomic problems, including poverty, high maternal and child mortality, and illiteracy. Despite the country's rapid post-war economic growth based on oil production, about 40 percent of Angolans live below the poverty line and unemployment is widespread, especially among the large young-adult population. Only about 70% of the population is literate, and the rate drops to around 60% for women. The youthful population - about 45% are under the age of 15 - is expected to continue growing rapidly with a fertility rate of more than 5 children per woman and a low rate of contraceptive use. Fewer than half of women deliver their babies with the assistance of trained health care personnel, which contributes to Angola's high maternal mortality rate.
Of the estimated 550,000 Angolans who fled their homeland during its civil war, most have returned home since 2002. In 2012, the UN assessed that conditions in Angola had been stable for several years and invoked a cessation of refugee status for Angolans. Following the cessation clause, some of those still in exile returned home voluntarily through UN repatriation programs, and others integrated into host countries.
Age structure:0-14 years: 48.07% (male 7,257,155 /female 7,336,084)15-24 years: 18.33% (male 2,701,123 /female 2,863,950)25-54 years: 27.95% (male 4,044,944 /female 4,441,028)55-64 years: 3.32% (male 466,085 /female 540,452)65 years and over: 2.32% (male 296,411 /female 408,648) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Angola Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Angola Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Angola. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Angola. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 97.6 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 93 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 4.6 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 21.9 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 15.9 years (2018 est.)male: 15.4 yearsfemale: 16.3 yearscountry comparison to the world: 224Population growth rate:3.49% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Birth rate:43.7 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Death rate:9 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Net migration rate:0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Population distribution:most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of LuandaUrbanization:urban population: 66.2% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 4.32% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:8.045 million LUANDA (capital), 787,000 Lubango (2019)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 0.99 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.94 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.91 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.86 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.73 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:19.4 years (2015/16 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:241 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 45Infant mortality rate:total: 65.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 71.4 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 60.1 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 10Life expectancy at birth:total population: 60.6 years (2018 est.)male: 58.5 yearsfemale: 62.7 yearscountry comparison to the world: 207Total fertility rate:6.09 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Contraceptive prevalence rate:13.7% (2015/16)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 75.4% of populationrural: 28.2% of populationtotal: 49% of populationunimproved: urban: 24.6% of populationrural: 71.8% of populationtotal: 51% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:2.9% (2016)Physicians density:0.21 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 88.6% of population (2015 est.)rural: 22.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 51.6% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 11.4% of population (2015 est.)rural: 77.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 48.4% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:2% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 23HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:330,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 21HIV/AIDS - deaths:14,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very high (2019)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever (2019)vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria (2019)water contact diseases: schistosomiasis (2019)animal contact diseases: rabies (2019)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:8.2% (2016)country comparison to the world: 154Children under the age of 5 years underweight:19% (2016)country comparison to the world: 29Education expenditures:3.4% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 124Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 71.1%male: 82%female: 60.7% (2015)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 10 yearsmale: 13 yearsfemale: 8 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 39.4%male: 39%female: 39.8% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 13 -
Government :: Angola
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Angolaconventional short form: Angolalocal long form: Republica de Angolalocal short form: Angolaformer: People's Republic of Angolaetymology: name derived by the Portuguese from the title "ngola" held by kings of the Ndongo (Ndongo was a kingdom in what is now northern Angola)Government type:presidential republicCapital:name: Luandageographic coordinates: 8 50 S, 13 13 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings timeetymology: originally named "Sao Paulo da Assuncao de Loanda" (Saint Paul of the Assumption of Loanda), which over time was shortened and corrupted to just LuandaAdministrative divisions:18 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Bengo, Benguela, Bie, Cabinda, Cunene, Huambo, Huila, Kwando Kubango, Kwanza Norte, Kwanza Sul, Luanda, Lunda Norte, Lunda Sul, Malanje, Moxico, Namibe, Uige, ZaireIndependence:11 November 1975 (from Portugal)National holiday:Independence Day, 11 November (1975)Constitution:history: previous 1975, 1992; latest passed by National Assembly 21 January 2010, adopted 5 February 2010amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one third of the National Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly subject to prior Constitutional Court review if requested by the president of the republic (2017)Legal system:civil legal system based on Portuguese civil law; no judicial review of legislationInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Angoladual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 10 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 26 September 2017); Vice President Bornito De Sousa Baltazar DIOGO (since 26 September 2017); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 26 September 2017); Vice President Bornito De Sousa Baltazar DIOGO (since 26 September 2017)cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: the candidate of the winning party or coalition in the last legislative election becomes the president; president serves a 5-year term (eligible for a second consecutive or discontinuous term); last held on 23 August 2017 (next to be held in 2022)election results: Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (MPLA) elected president by the winning party following the 23 August 2017 general electionLegislative branch:description: unicameral National Assembly or Assembleia Nacional (220 seats; members directly elected in a single national constituency and in multi-seat constituencies by closed list proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)elections: last held on 23 August 2017 (next to be held in August 2022)election results: percent of vote by party - MPLA 61.1%, UNITA 26.7%, CASA-CE 9.5%, PRS 1.4%, FNLA 0.9%, other 0.5%; seats by party - MPLA 150, UNITA 51, CASA-CE 16, PRS 2, FNLA 1; composition - men 136, women 84, percent of women 38.2%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Supremo Tribunal de Justica (consists of the court president, vice president, and a minimum of 16 judges); Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional (consists of 11 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president upon recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, an 18-member body chaired by the president; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges - 4 nominated by the president, 4 elected by National Assembly, 2 elected by Supreme National Council, 1 elected by competitive submission of curricula; judges serve single 7-year termssubordinate courts: provincial and municipal courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Broad Convergence for the Salvation of Angola Electoral Coalition or CASA-CE [Andre Mendes de CARVALHO]
National Front for the Liberation of Angola or FNLA; note - party has two factions; one led by Lucas NGONDA; the other by Ngola KABANGU
National Union for the Total Independence of Angola or UNITA [Isaias SAMAKUVA] (largest opposition party)
Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola or MPLA [Joao LOURENCO]; note - Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS stepped down 8 Sept 2018 ruling party in power since 1975
Social Renewal Party or PRS [Benedito DANIEL]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CPLP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OPEC, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Agostinho Tavares da Silva NETO (since 18 November 2014)chancery: 2100-2108 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 785-1156FAX: [1] (202) 822-9049consulate(s) general: Houston, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Nina Maria FITE (since 14 February 2018)telephone: [244] 946440977embassy: number 32 Rua Houari Boumedienne (in the Miramar area of Luanda), Luanda, C.P. 6468, Angolamailing address: international mail: Caixa Postal 6468, Luanda; pouch: US Embassy Luanda, US Department of State, 2550 Luanda Place, Washington, DC 20521-2550FAX: [244] (222) 64-1000Flag description:two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and black with a centered yellow emblem consisting of a five-pointed star within half a cogwheel crossed by a machete (in the style of a hammer and sickle); red represents liberty and black the African continent; the symbols characterize workers and peasantsNational symbol(s):Palanca Negra Gigante (giant black sable antelope); national colors: red, black, yellowNational anthem:name: "Angola Avante" (Forward Angola)lyrics/music: Manuel Rui Alves MONTEIRO/Rui Alberto Vieira Dias MINGAOnote: adopted 1975
-
Economy :: Angola
-
Economy - overview:
Angola's economy is overwhelmingly driven by its oil sector. Oil production and its supporting activities contribute about 50% of GDP, more than 70% of government revenue, and more than 90% of the country's exports; Angola is an OPEC member and subject to its direction regarding oil production levels. Diamonds contribute an additional 5% to exports. Subsistence agriculture provides the main livelihood for most of the people, but half of the country's food is still imported.
Increased oil production supported growth averaging more than 17% per year from 2004 to 2008. A postwar reconstruction boom and resettlement of displaced persons led to high rates of growth in construction and agriculture as well. Some of the country's infrastructure is still damaged or undeveloped from the 27-year-long civil war (1975-2002). However, the government since 2005 has used billions of dollars in credit from China, Brazil, Portugal, Germany, Spain, and the EU to help rebuild Angola's public infrastructure. Land mines left from the war still mar the countryside, and as a result, the national military, international partners, and private Angolan firms all continue to remove them.
The global recession that started in 2008 stalled Angola’s economic growth and many construction projects stopped because Luanda accrued billions in arrears to foreign construction companies when government revenue fell. Lower prices for oil and diamonds also resulted in GDP falling 0.7% in 2016. Angola formally abandoned its currency peg in 2009 but reinstituted it in April 2016 and maintains an overvalued exchange rate. In late 2016, Angola lost the last of its correspondent relationships with foreign banks, further exacerbating hard currency problems. Since 2013 the central bank has consistently spent down reserves to defend the kwanza, gradually allowing a 40% depreciation since late 2014. Consumer inflation declined from 325% in 2000 to less than 9% in 2014, before rising again to above 30% from 2015-2017.
Continued low oil prices, the depreciation of the kwanza, and slower than expected growth in non-oil GDP have reduced growth prospects, although several major international oil companies remain in Angola. Corruption, especially in the extractive sectors, is a major long-term challenge that poses an additional threat to the economy.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$193.6 billion (2017 est.)$198.6 billion (2016 est.)$203.9 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 65GDP (official exchange rate):$126.5 billion (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:-2.5% (2017 est.)-2.6% (2016 est.)0.9% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 209GDP - per capita (PPP):$6,800 (2017 est.)$7,200 (2016 est.)$7,600 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 160Gross national saving:28.6% of GDP (2017 est.)24.5% of GDP (2016 est.)28.5% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 37GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 80.6% (2017 est.)government consumption: 15.6% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 10.3% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: -1.2% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 25.4% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -30.7% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 10.2% (2011 est.)industry: 61.4% (2011 est.)services: 28.4% (2011 est.)Agriculture - products:bananas, sugarcane, coffee, sisal, corn, cotton, cassava (manioc, tapioca), tobacco, vegetables, plantains; livestock; forest products; fishIndustries:petroleum; diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, feldspar, bauxite, uranium, and gold; cement; basic metal products; fish processing; food processing, brewing, tobacco products, sugar; textiles; ship repairIndustrial production growth rate:2.5% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Labor force:12.51 million (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 46Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 85%industry: 15% (2015 est.)industry and services: 15% (2003 est.)Unemployment rate:6.6% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Population below poverty line:36.6% (2008 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 0.6%highest 10%: 44.7% (2000)Distribution of family income - Gini index:42.7 (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Budget:revenues: 37.02 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 45.44 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:29.3% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6.7% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 189Public debt:65% of GDP (2017 est.)75.3% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):29.8% (2017 est.)30.7% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 222Central bank discount rate:9% (31 December 2014)25% (31 December 2010)country comparison to the world: 30Commercial bank prime lending rate:15.82% (31 December 2017 est.)15.78% (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Stock of narrow money:$32.39 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$23.17 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Stock of broad money:$32.39 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$23.17 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Stock of domestic credit:$16.02 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$14.25 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Current account balance:-$1.254 billion (2017 est.)-$4.834 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 150Exports:$33.07 billion (2017 est.)$31.03 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Exports - partners:China 61.2%, India 13%, US 4.2% (2017)Exports - commodities:crude oil, diamonds, refined petroleum products, coffee, sisal, fish and fish products, timber, cottonImports:$19.5 billion (2017 est.)$13.04 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 78Imports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment, vehicles and spare parts; medicines, food, textiles, military goodsImports - partners:Portugal 17.8%, China 13.5%, US 7.4%, South Africa 6.2%, Brazil 6.1%, UK 4% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$17.29 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$23.74 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Debt - external:$42.08 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$27.14 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$11.21 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$9.16 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$28 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$23.02 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Exchange rates:kwanza (AOA) per US dollar -172.6 (2017 est.)163.656 (2016 est.)163.656 (2015 est.)120.061 (2014 est.)98.303 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Angola
-
Electricity access:population without electricity: 15 million (2013)electrification - total population: 40.5% (2016)electrification - urban areas: 70.7% (2016)electrification - rural areas: 16% (2016)Electricity - production:10.2 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Electricity - consumption:9.036 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 101Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 98Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.613 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Electricity - from fossil fuels:34% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:64% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 23Electricity - from other renewable sources:2% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 132Crude oil - production:1.593 million bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Crude oil - exports:1.782 million bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Crude oil - proved reserves:9.523 billion bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Refined petroleum products - production:53,480 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 80Refined petroleum products - consumption:130,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Refined petroleum products - exports:30,340 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Refined petroleum products - imports:111,600 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Natural gas - production:3.115 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 55Natural gas - consumption:821.2 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Natural gas - exports:3.993 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Natural gas - proved reserves:308.1 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:20.95 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 85
-
Communications :: Angola
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 161,070subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 13,323,952subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Telephone system:general assessment: in the process of a restructure plan and opening up the telecom sector to new competitors, while still retaining a 45% govt portion of the share; slow progress in LTE network development, with only about 10% of the country covered by network infrastructure at the end of 2017 (2018)domestic: only about one fixed-line per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity about 45 telephones per 100 persons (2018)international: country code - 244; landing points for the SAT-3/WASC, WACS, ACE and SACS fiber-optic submarine cable that provides connectivity to other countries in west Africa, Brazil, Europe and Asia; satellite earth stations - 29 (2019)Broadcast media:state controls all broadcast media with nationwide reach; state-owned Televisao Popular de Angola (TPA) provides terrestrial TV service on 2 channels; a third TPA channel is available via cable and satellite; TV subscription services are available; state-owned Radio Nacional de Angola (RNA) broadcasts on 5 stations; about a half-dozen private radio stations broadcast locallyInternet country code:.aoInternet users:total: 2,622,403percent of population: 13% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 96,919subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 120
-
Military and Security :: Angola
-
Military expenditures:1.78% of GDP (2018)2.42% of GDP (2017)2.95% of GDP (2016)3.52% of GDP (2015)5.4% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 64Military and security forces:Angolan Armed Forces (Forcas Armadas Angolanas, FAA): Army, Navy (Marinha de Guerra Angola, MGA), Angolan National Air Force (Forca Aerea Nacional Angolana, FANA; under operational control of the Army) (2012)Military service age and obligation:20-45 years of age for compulsory male and 18-45 years for voluntary male military service (registration at age 18 is mandatory); 20-45 years of age for voluntary female service; 2-year conscript service obligation; Angolan citizenship required; the Navy (MGA) is entirely staffed with volunteers (2013)
-
Transportation :: Angola
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 10 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 55 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,244,491 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 46.043 million mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:D2 (2016)Airports:176 (2013)country comparison to the world: 32Airports - with paved runways:total: 31 (2017)over 3,047 m: 7 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 8 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 12 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 4 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 145 (2013)over 3,047 m: 2 (2013)2,438 to 3,047 m: 3 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 31 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 66 (2013)under 914 m: 43 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:352 km gas, 85 km liquid petroleum gas, 1065 km oil, 5 km oil/gas/water (2013)Railways:total: 2,852 km (2014)narrow gauge: 2,729 km 1.067-m gauge (2014)123 km 0.600-m gaugecountry comparison to the world: 63Roadways:total: 26,000 km (2018)paved: 13,600 km (2018)unpaved: 12,400 km (2018)country comparison to the world: 101Waterways:1,300 km (2011)country comparison to the world: 53Merchant marine:total: 55by type: general cargo 14, oil tanker 8, other 33 (2018)country comparison to the world: 110Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Cabinda, Lobito, Luanda, NamibeLNG terminal(s) (export): Angola Soyo
-
Transnational Issues :: Angola
-
Disputes - international:
Democratic Republic of Congo accuses Angola of shifting monuments
Refugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 6,448 (Cote d'Ivoire), 5,709 (Mauritania) (2017); 22,463 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (refugees and asylum seekers) (2019)Illicit drugs:used as a transshipment point for cocaine destined for Western Europe and other African states, particularly South Africa