
-
Introduction :: Chile
-
Background:Prior to the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, the Inca ruled northern Chile for nearly a century while an indigenous people, the Mapuche, inhabited central and southern Chile. Although Chile declared its independence in 1810, it did not achieve decisive victory over the Spanish until 1818. In the War of the Pacific (1879-83), Chile defeated Peru and Bolivia to win its present northern regions. In the 1880s, the Chilean central government gained control over the central and southern regions inhabited by the Mapuche. After a series of elected governments, the three-year-old Marxist government of Salvador ALLENDE was overthrown in 1973 by a military coup led by General Augusto PINOCHET, who ruled until a democratically-elected president was inaugurated in 1990. Economic reforms, maintained consistently since the 1980s, contributed to steady growth, reduced poverty rates by over half, and helped secure the country's commitment to democratic and representative government. Chile has increasingly assumed regional and international leadership roles befitting its status as a stable, democratic nation.
-
Geography :: Chile
-
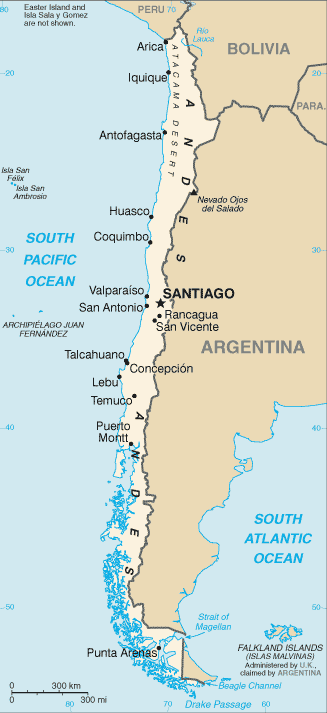
Location:Southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and PeruGeographic coordinates:30 00 S, 71 00 WMap references:South AmericaArea:total: 756,102 sq kmland: 743,812 sq kmwater: 12,290 sq km
note: includes Easter Island (Isla de Pascua) and Isla Sala y Gomez
country comparison to the world: 39Area - comparative:slightly smaller than twice the size of MontanaArea comparison map: The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Chile Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Chile Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly smaller than twice the size of Montana
Land boundaries:total: 7,801 kmborder countries (3): Argentina 6691 km, Bolivia 942 km, Peru 168 kmCoastline:6,435 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200/350 nmClimate:temperate; desert in north; Mediterranean in central region; cool and damp in southTerrain:low coastal mountains, fertile central valley, rugged Andes in eastElevation:mean elevation: 1,871 mlowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 mhighest point: Nevado Ojos del Salado 6,880 mNatural resources:copper, timber, iron ore, nitrates, precious metals, molybdenum, hydropowerLand use:agricultural land: 21.1% (2011 est.)arable land: 1.7% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.6% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 18.8% (2011 est.)forest: 21.9% (2011 est.)other: 57% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:11,100 sq km (2012)Population distribution:90% of the population is located in the middle third of the country around the capital of Santiago; the far north (anchored by the Atacama Desert) and the extreme south are relatively underpopulatedNatural hazards:severe earthquakes; active volcanism; tsunamis
volcanism: significant volcanic activity due to more than three-dozen active volcanoes along the Andes Mountains; Lascar (5,592 m), which last erupted in 2007, is the most active volcano in the northern Chilean Andes; Llaima (3,125 m) in central Chile, which last erupted in 2009, is another of the country's most active; Chaiten's 2008 eruption forced major evacuations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Cerro Hudson, Calbuco, Copahue, Guallatiri, Llullaillaco, Nevados de Chillan, Puyehue, San Pedro, and Villarrica; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Environment - current issues:air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage; noise pollution; improper garbage disposal; soil degradation; widespread deforestation and mining threaten the environment; wildlife conservationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:note 1: the longest north-south trending country in the world, extending across 39 degrees of latitude; strategic location relative to sea lanes between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage)
note 2: Chile is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
note 3: the Atacama Desert - the driest desert in the world - spreads across the northern part of the country; Ojos del Salado (6,893 m) in the Atacama Desert is the highest active volcano in the world, Chile's tallest mountain, and the second highest in the Western Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere - its small crater lake (at 6,390 m) is the world's highest lake
-
People and Society :: Chile
-
Population:17,925,262 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Nationality:noun: Chilean(s)adjective: ChileanEthnic groups:white and non-indigenous 88.9%, Mapuche 9.1%, Aymara 0.7%, other indigenous groups 1% (includes Rapa Nui, Likan Antai, Quechua, Colla, Diaguita, Kawesqar, Yagan or Yamana), unspecified 0.3% (2012 est.)Languages:Spanish 99.5% (official), English 10.2%, indigenous 1% (includes Mapudungun, Aymara, Quechua, Rapa Nui), other 2.3%, unspecified 0.2% (2012 est.)
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Religions:Roman Catholic 66.7%, Evangelical or Protestant 16.4%, Jehovah's Witness 1%, other 3.4%, none 11.5%, unspecified 1.1% (2012 est.)Demographic profile:Chile is in the advanced stages of demographic transition and is becoming an aging society - with fertility below replacement level, low mortality rates, and life expectancy on par with developed countries. Nevertheless, with its dependency ratio nearing its low point, Chile could benefit from its favorable age structure. It will need to keep its large working-age population productively employed, while preparing to provide for the needs of its growing proportion of elderly people, especially as women - the traditional caregivers - increasingly enter the workforce. Over the last two decades, Chile has made great strides in reducing its poverty rate, which is now lower than most Latin American countries. However, its severe income inequality ranks as the worst among members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Unequal access to quality education perpetuates this uneven income distribution.
Chile has historically been a country of emigration but has slowly become more attractive to immigrants since transitioning to democracy in 1990 and improving its economic stability (other regional destinations have concurrently experienced deteriorating economic and political conditions). Most of Chile's small but growing foreign-born population consists of transplants from other Latin American countries, especially Peru.
Age structure:0-14 years: 19.98% (male 1,827,657 /female 1,754,253)15-24 years: 14.63% (male 1,337,663 /female 1,285,514)25-54 years: 42.94% (male 3,851,775 /female 3,845,195)55-64 years: 11.32% (male 957,872 /female 1,070,975)65 years and over: 11.13% (male 836,489 /female 1,157,869) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Chile Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Chile Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Chile. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Chile. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 45.5 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 30.3 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 15.2 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 6.6 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 34.8 years (2018 est.)male: 33.6 yearsfemale: 36 yearscountry comparison to the world: 85Population growth rate:0.75% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 135Birth rate:13.4 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Death rate:6.3 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 150Net migration rate:0.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Population distribution:90% of the population is located in the middle third of the country around the capital of Santiago; the far north (anchored by the Atacama Desert) and the extreme south are relatively underpopulatedUrbanization:urban population: 87.6% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 0.87% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:6.724 million SANTIAGO (capital), 975,000 Valparaiso, 869,000 Concepcion (2019)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.89 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Maternal mortality rate:13 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Infant mortality rate:total: 6.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 6.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 6 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 163Life expectancy at birth:total population: 79.1 years (2018 est.)male: 76 yearsfemale: 82.2 yearscountry comparison to the world: 51Total fertility rate:1.79 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 148Contraceptive prevalence rate:76.3% (2015/16)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 99.7% of populationrural: 93.3% of populationtotal: 99% of populationunimproved: urban: 0.3% of populationrural: 6.7% of populationtotal: 1% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:8.5% (2016)Physicians density:1.08 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:2.2 beds/1,000 population (2013)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 100% of population (2015 est.)rural: 90.9% of population (2015 est.)total: 99.1% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 0% of population (2015 est.)rural: 9.1% of population (2015 est.)total: 0.9% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.5% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 69HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:71,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 53HIV/AIDS - deaths:<1000 (2018)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:28% (2016)country comparison to the world: 32Children under the age of 5 years underweight:0.5% (2014)country comparison to the world: 125Education expenditures:5.4% of GDP (2017)country comparison to the world: 41Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 96.9%male: 97%female: 96.7% (2015)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 16 yearsmale: 16 yearsfemale: 17 years (2016)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 18.1%male: 16.7%female: 20.2% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 76 -
Government :: Chile
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Chileconventional short form: Chilelocal long form: Republica de Chilelocal short form: Chileetymology: derivation of the name is unclear, but it may come from the Mapuche word "chilli" meaning "limit of the earth" or from the Quechua "chiri" meaning "cold"Government type:presidential republicCapital:name: Santiago; note - Valparaiso is the seat of the national legislaturegeographic coordinates: 33 27 S, 70 40 Wtime difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in August; ends second Sunday in May; note - Punta Arenas observes DST throughout the year
etymology: Santiago is named after the biblical figure Saint James (ca. A.D. 3-44), patron saint of Spain, but especially revered in Galicia; "Santiago" derives from the local Galician evolution of the Vulgar Latin "Sanctu Iacobu"; Valparaiso derives from the Spanish "Valle Paraiso" meaning "Paradise Valley"
note: Chile has three time zones: the continental portion at UTC-3; the southern Magallanes region, which does not use daylight savings time and remains at UTC-3 for the summer months; and Easter Island at UTC-5Administrative divisions:16 regions (regiones, singular - region); Aysen, Antofagasta, Araucania, Arica y Parinacota, Atacama, Biobio, Coquimbo, Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins, Los Lagos, Los Rios, Magallanes y de la Antartica Chilena (Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica), Maule, Nuble, Region Metropolitana (Santiago), Tarapaca, Valparaisonote: the US does not recognize any claims to Antarctica
Independence:18 September 1810 (from Spain)National holiday:Independence Day, 18 September (1810)Constitution:history: many previous; latest adopted 11 September 1980, effective 11 March 1981; note - in March 2018, days before her term ended, President BACHELET sent a proposal for a new constitution to the National Congress, but it has not been pursued by her successoramendments: proposed by members of either house of the National Congress or by the president of the republic; passage requires at least three-fifths majority vote of the membership in both houses and approval by the president; passage of amendments to constitutional articles, such as the republican form of government, basic rights and freedoms, the Constitutional Tribunal, electoral justice, the Council of National Security, or the constitutional amendment process, requires at least two-third majority vote by both houses of Congress and approval by the president; the president can opt to hold a referendum when Congress and the president disagree on an amendment; amended many times, last in 2018 (2019)Legal system:civil law system influenced by several West European civil legal systems; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional TribunalInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: yescitizenship by descent only: yesdual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Sebastian PINERA Echenique (since 11 March 2018); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Sebastian PINERA Echenique (since 11 March 2018)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a single 4-year term; election last held on 19 November 2017 with a runoff held 17 December 2017 (next to be held in November 2021)election results: Sebastian PINERA Echenique elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Sebastian PINERA Echenique (independent) 36.6%; Alejandro GUILLIER (independent) 22.7%; Beatriz SANCHEZ (independent) 20.3%; Jose Antonio KAST (independent) 7.9%; Carolina GOIC (PDC) 5.9%; Marco ENRIQUEZ-OMINAMI (PRO) 5.7%; other 0.9%; percent of vote in second round - Sebastian PINERA Echenique 54.6%, Alejandro GUILLIER 45.4%Legislative branch:description: bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of:
Senate or Senado (43 seats following the 2017 election; to increase to 50 in 2021); members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by open party-list proportional representation vote to serve 8-year terms with one-half of the membership renewed every 4 years)
Chamber of Deputies or Camara de Diputados (155 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by oen party-list proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)elections:
Senate - last held on 19 November 2017 (next to be held in 2021)
Chamber of Deputies - last held on 19 November 2017 (next to be held in 2021)election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - New Majority Coalition (formerly known as Concertacion) 19 (PDC 6, PS 6, PPD 6, MAS 1), Let's Go Chile Coalition (formerly known as the Coalition for Change and the Alianza coalition) 15 (RN 6, UDI 8, Amplitude Party 1), independent 4; composition - men 33, women 10, percent of women 23.3%
Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - New Majority 68 (PDC 21, PS 16, PPD 14, PC 6, PRSD 6, Citizen Left 1, independent 4), Coalition for Change 47 (UDI 29, RN 14, independent 3, EP 1), Liberal Party 1, independent 4; composition -men 120, women 35, percent of women 22.6%; note - total National Congress percent of women 22.7%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (consists of a court president and 20 members or ministros); Constitutional Court (consists of 10 members); Elections Qualifying Court (consists of 5 members)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and judges (ministers) appointed by the president of the republic and ratified by the Senate from lists of candidates provided by the court itself; judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 70; Constitutional Court members appointed - 3 by the Supreme Court, 3 by the president of the republic, 2 by the Chamber of Deputies, and 2 by the Senate; members serve 9-year terms with partial membership replacement every 3 years (the court reviews constitutionality of legislation); Elections Qualifying Court members appointed by lottery - 1 by the former president or vice president of the Senate and 1 by the former president or vice president of the Chamber of Deputies, 2 by the Supreme Court, and 1 by the Appellate Court of Valparaiso; members appointed for 4-year termssubordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; oral criminal tribunals; military tribunals; local police courts; specialized tribunals and courts in matters such as family, labor, customs, taxes, and electoral affairsPolitical parties and leaders:Amplitude (Amplitud) [Lily PEREZ]
Broad Front Coalition (Frente Amplio) or FA (includes RD, PL, PH, PEV, Igualdad, and Poder) [Beatriz SANCHEZ]
Broad Social Movement of Leftist Citizens (includes former MAS and Izquierda Ciudadana) [Fernando ZAMORANO]
Christian Democratic Party or PDC [Fuad CHAHIN]
Citizen Power (Poder) [Karina OLIVA]
Communist Party of Chile or PC [Guillermo TEILLIER del Valle]
Democratic Revolution or RD [Rodrigo ECHECOPAR]
Equality Party (Igualdad) [Guillermo GONZALEZ]
Green Ecological Party or PEV [Felix GONZALEZ]
Humanist Party or PH [Octavio GONZALEZ]
Independent Democratic Union or UDI [Jacqueline VAN RYSSELBERGHE Herrera])
Independent Regionalist Democratic Party or PRI [Hugo ORTIZ de Filippi]
Let’s Go Chile Coalition (Chile Vamos) [Sebastian PINERA] (includes EVOPOLI, PRI, RN, UDI)
Liberal Party (Partido Liberal de Chile) or PL [Luis Felipe RAMOS]
National Renewal or RN [Mario DESBORDES]
New Majority Coalition (Nueva Mayoria) [Michelle BACHELET] (includes PDC, PC, PPD, PRSD, PS); note - dissolved in March 2018
Party for Democracy or PPD [Heraldo MUNOZ]
Political Evolution or EVOPOLI [Hernan LARRAIN MATTE]
Progressive Party or PRO [Camilo LAGOS]
Radical Social Democratic Party or PRSD [Carlos MALDONADO Curti],
Socialist Party or PS [Alvaro ELIZALDE Soto] (formerly known as Concertacion)International organization participation:APEC, BIS, CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, G-15, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS, OECD (enhanced engagement), OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance, PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMOGIP, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Oscar Alfonso Sebastian SILVA Navarro (since 17 September 2018)chancery: 1732 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 785-1746FAX: [1] (202) 887-5579consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San FranciscoDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Baxter HUNT (since January 2019)telephone: [56] (2) 2330-3000embassy: Avenida Andres Bello 2800, Las Condes, Santiagomailing address: APO AA 34033FAX: [56] (2) 2330-3710, 2330-3160Flag description:two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red; a blue square the same height as the white band at the hoist-side end of the white band; the square bears a white five-pointed star in the center representing a guide to progress and honor; blue symbolizes the sky, white is for the snow-covered Andes, and red represents the blood spilled to achieve independencenote: design influenced by the US flag
National symbol(s):huemul (mountain deer), Andean condor; national colors: red, white, blueNational anthem:name: "Himno Nacional de Chile" (National Anthem of Chile)lyrics/music: Eusebio LILLO Robles and Bernardo DE VERA y Pintado/Ramon CARNICER y Battlenote: music adopted 1828, original lyrics adopted 1818, adapted lyrics adopted 1847; under Augusto PINOCHET's military rule, a verse glorifying the army was added; however, as a protest, some citizens refused to sing this verse; it was removed when democracy was restored in 1990
-
Economy :: Chile
-
Economy - overview:
Chile has a market-oriented economy characterized by a high level of foreign trade and a reputation for strong financial institutions and sound policy that have given it the strongest sovereign bond rating in South America. Exports of goods and services account for approximately one-third of GDP, with commodities making up some 60% of total exports. Copper is Chile’s top export and provides 20% of government revenue.
From 2003 through 2013, real growth averaged almost 5% per year, despite a slight contraction in 2009 that resulted from the global financial crisis. Growth slowed to an estimated 1.4% in 2017. A continued drop in copper prices prompted Chile to experience its third consecutive year of slow growth.
Chile deepened its longstanding commitment to trade liberalization with the signing of a free trade agreement with the US, effective 1 January 2004. Chile has 26 trade agreements covering 60 countries including agreements with the EU, Mercosur, China, India, South Korea, and Mexico. In May 2010, Chile signed the OECD Convention, becoming the first South American country to join the OECD. In October 2015, Chile signed the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade agreement, which was finalized as the Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and signed at a ceremony in Chile in March 2018.
The Chilean Government has generally followed a countercyclical fiscal policy, under which it accumulates surpluses in sovereign wealth funds during periods of high copper prices and economic growth, and generally allows deficit spending only during periods of low copper prices and growth. As of 31 October 2016, those sovereign wealth funds - kept mostly outside the country and separate from Central Bank reserves - amounted to more than $23.5 billion. Chile used these funds to finance fiscal stimulus packages during the 2009 economic downturn.
In 2014, then-President Michelle BACHELET introduced tax reforms aimed at delivering her campaign promise to fight inequality and to provide access to education and health care. The reforms are expected to generate additional tax revenues equal to 3% of Chile’s GDP, mostly by increasing corporate tax rates to OECD averages.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$452.1 billion (2017 est.)$445.5 billion (2016 est.)$439.9 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 44GDP (official exchange rate):$277 billion (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.5% (2017 est.)1.3% (2016 est.)2.3% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 170GDP - per capita (PPP):$24,600 (2017 est.)$24,500 (2016 est.)$24,400 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 82Gross national saving:20.5% of GDP (2017 est.)20.9% of GDP (2016 est.)21.4% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 94GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 62.3% (2017 est.)government consumption: 14% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 21.5% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0.5% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 28.7% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -27% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 4.2% (2017 est.)industry: 32.8% (2017 est.)services: 63% (2017 est.)Agriculture - products:grapes, apples, pears, onions, wheat, corn, oats, peaches, garlic, asparagus, beans; beef, poultry, wool; fish; timberIndustries:copper, lithium, other minerals, foodstuffs, fish processing, iron and steel, wood and wood products, transport equipment, cement, textilesIndustrial production growth rate:-0.4% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 170Labor force:8.881 million (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9.2%industry: 23.7%services: 67.1% (2013)Unemployment rate:6.7% (2017 est.)6.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Population below poverty line:14.4% (2013)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.7%highest 10%: 41.5% (2013 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:50.5 (2013)57.1 (2000)country comparison to the world: 15Budget:revenues: 57.75 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 65.38 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:20.8% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-2.8% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 124Public debt:23.6% of GDP (2017 est.)21% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 182Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.2% (2017 est.)3.8% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Central bank discount rate:3.35% (31 December 2015)3% (31 December 2014)country comparison to the world: 104Commercial bank prime lending rate:4.6% (31 December 2017 est.)5.59% (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Stock of narrow money:$52.54 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$44.01 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Stock of broad money:$52.54 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$44.01 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Stock of domestic credit:$244.3 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$211.6 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Market value of publicly traded shares:$190.4 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$233.2 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$265.2 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Current account balance:-$4.102 billion (2017 est.)-$3.484 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Exports:$69.23 billion (2017 est.)$60.6 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Exports - partners:China 27.5%, US 14.5%, Japan 9.3%, South Korea 6.2%, Brazil 5% (2017)Exports - commodities:copper, fruit, fish products, paper and pulp, chemicals, wineImports:$61.31 billion (2017 est.)$55.29 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Imports - commodities:petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, electrical and telecommunications equipment, industrial machinery, vehicles, natural gasImports - partners:China 23.9%, US 18.1%, Brazil 8.6%, Argentina 4.5%, Germany 4% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$38.98 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$40.49 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 44Debt - external:$183.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$158.1 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$206.2 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$199.8 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$95.37 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$90.54 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Exchange rates:Chilean pesos (CLP) per US dollar -653.9 (2017 est.)676.94 (2016 est.)676.94 (2015 est.)658.93 (2014 est.)570.37 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Chile
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2016)Electricity - production:76.09 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Electricity - consumption:73.22 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 135Electricity - installed generating capacity:24.53 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Electricity - from fossil fuels:59% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:26% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Electricity - from other renewable sources:15% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Crude oil - production:3,000 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 106Crude oil - imports:169,600 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Crude oil - proved reserves:150 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Refined petroleum products - production:216,200 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Refined petroleum products - consumption:354,500 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Refined petroleum products - exports:7,359 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Refined petroleum products - imports:166,400 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Natural gas - production:1.218 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Natural gas - consumption:5.125 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Natural gas - exports:277.5 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Natural gas - imports:4.446 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Natural gas - proved reserves:97.97 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:88.23 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 47
-
Communications :: Chile
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 3,193,131subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 18 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 23,013,147subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 129 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Telephone system:general assessment: most advanced telecommunications infrastructure in South America; modern system based on extensive microwave radio relay facilities; although Chile has one of the highest mobile penetration rates in the region, the number of subscribers has fallen due to subscribers ending multiple SIM card use; this downward trend is expected to be halted as the availability of LTE networks and services broaden; in terms of available broadband speeds the country ranks second highest in South and Central America (2018)domestic: number of fixed-line connections have stagnated to 18 per 100 in recent years as mobile-cellular usage continues to increase, reaching 130 telephones per 100 persons; domestic satellite system with 3 earth stations (2018)international: country code - 56; landing points for the Pan-Am, Prat, SAm-1, American Movil-Telxius West Coast Cable, FOS Quellon-Chacabuco, Fibra Optical Austral, SAC and Curie submarine cables providing links to the US, Caribbean and to Central and South America; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)Broadcast media:national and local terrestrial TV channels, coupled with extensive cable TV networks; the state-owned Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) network is self-financed through commercial advertising revenues and is not under direct government control; large number of privately owned TV stations; about 250 radio stationsInternet country code:.clInternet users:total: 11,650,840percent of population: 66% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 46Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 3,058,979subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 40
-
Military and Security :: Chile
-
Military expenditures:1.89% of GDP (2018)1.94% of GDP (2017)1.87% of GDP (2016)1.91% of GDP (2015)1.96% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 56Military and security forces:Armed Forces of Chile (Fuerzas Armadas de Chile): Chilean Army, Chilean Navy (Armada de Chile, includes Naval Aviation, Marine Corps, and Maritime Territory and Merchant Marine Directorate (Directemar)), Chilean Air Force (Fuerza Aerea de Chile, FACh); Carabineros de Chile (National Police Force) (2019)note: Carabineros de Chile are responsible to both the Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of InteriorMilitary service age and obligation:18-45 years of age for voluntary male and female military service, although the right to compulsory recruitment of males 18-45 is retained; service obligation is 12 months for Army and 22 months for Navy and Air Force (2015)
-
Transportation :: Chile
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 9 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 173 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 15,006,762 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 1,392,236,000 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:CC (2016)Airports:481 (2013)country comparison to the world: 15Airports - with paved runways:total: 90 (2017)over 3,047 m: 5 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 7 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 23 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 31 (2017)under 914 m: 24 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 391 (2013)2,438 to 3,047 m: 5 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 11 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 56 (2013)under 914 m: 319 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:3160 km gas, 781 km liquid petroleum gas, 985 km oil, 722 km refined products (2013)Railways:total: 7,282 km (2014)narrow gauge: 3,853.5 km 1.000-m gauge (2014)broad gauge: 3,428 km 1.676-m gauge (1,691 km electrified) (2014)country comparison to the world: 30Roadways:total: 77,801 km (2016)country comparison to the world: 62Merchant marine:total: 222by type: bulk carrier 9, container ship 5, general cargo 58, oil tanker 15, other 135 (2018)country comparison to the world: 61Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Coronel, Huasco, Lirquen, Puerto Ventanas, San Antonio, San Vicente, Valparaisocontainer port(s) (TEUs): San Antonio (1,296,890), Valparaiso (1,073,734) (2017)LNG terminal(s) (import): Mejillones, Quintero
-
Transnational Issues :: Chile
-
Disputes - international:
Chile and Peru rebuff Bolivia's reactivated claim to restore the Atacama corridor, ceded to Chile in 1884, but Chile has offered instead unrestricted but not sovereign maritime access through Chile to Bolivian natural gas; Chile rejects Peru's unilateral legislation to change its latitudinal maritime boundary with Chile to an equidistance line with a southwestern axis favoring Peru; in October 2007, Peru took its maritime complaint with Chile to the ICJ; territorial claim in Antarctica (Chilean Antarctic Territory) partially overlaps Argentine and British claims; the joint boundary commission, established by Chile and Argentina in 2001, has yet to map and demarcate the delimited boundary in the inhospitable Andean Southern Ice Field (Campo de Hielo Sur)
Refugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 330,186 (Venezuela) (economic and political crisis; includes Venezuelans who have claimed asylum or have received alternative legal stay) (2019)Illicit drugs:transshipment country for cocaine destined for Europe and the region; some money laundering activity, especially through the Iquique Free Trade Zone; imported precursors passed on to Bolivia; domestic cocaine consumption is rising, making Chile a significant consumer of cocaine