
Europe ::
Jan Mayen
-
Introduction :: Jan Mayen
-
Background:This desolate, arctic, mountainous island was named after a Dutch whaling captain who indisputably discovered it in 1614 (earlier claims are inconclusive). Visited only occasionally by seal hunters and trappers over the following centuries, the island came under Norwegian sovereignty in 1929. The long dormant Beerenberg volcano, the northernmost active volcano on earth, resumed activity in 1970 and the most recent eruption occurred in 1985.
-
Geography :: Jan Mayen
-
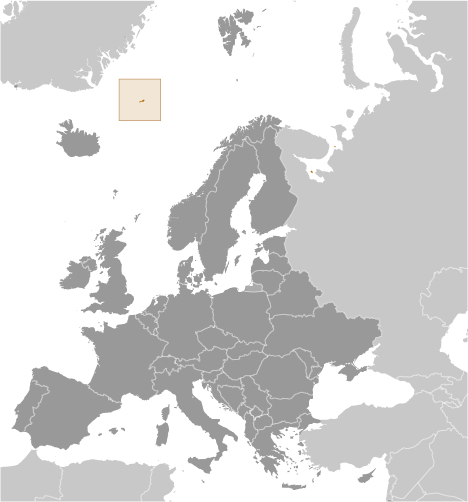
Location:Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the Norwegian Sea, northeast of IcelandGeographic coordinates:71 00 N, 8 00 WMap references:Arctic RegionArea:total: 377 sq kmland: 377 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 206Area - comparative:slightly more than twice the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:124.1 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitationClimate:arctic maritime with frequent storms and persistent fogTerrain:volcanic island, partly covered by glaciersElevation:lowest point: Norwegian Sea 0 mhighest point: Haakon VII Toppen on Beerenberg 2,277note: Beerenberg volcano has numerous peaks; the highest point on the volcano rim is named Haakon VII Toppen, after Norway's first king following the reestablishment of Norwegian independence in 1905Natural resources:noneLand use:agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:0 sq km (2012)Natural hazards:
dominated by the volcano Beerenberg
volcanism: Beerenberg (2,227 m) is Norway's only active volcano; volcanic activity resumed in 1970; the most recent eruption occurred in 1985
Environment - current issues:pollutants transported from southerly latitudes by winds, ocean currents, and rivers accumulate in the food chains of native animals; climate changeGeography - note:barren volcanic spoon-shaped island with some moss and grass flora; island consists of two parts: a larger northeast Nord-Jan (the spoon "bowl") and the smaller Sor-Jan (the "handle"), linked by a 2.5 km-wide isthmus (the "stem") with two large lakes, Sorlaguna (South Lagoon) and Nordlaguna (North Lagoon) -
People and Society :: Jan Mayen
-
Population:no indigenous inhabitants
note: military personnel operate the the weather and coastal services radio station
-
Government :: Jan Mayen
-
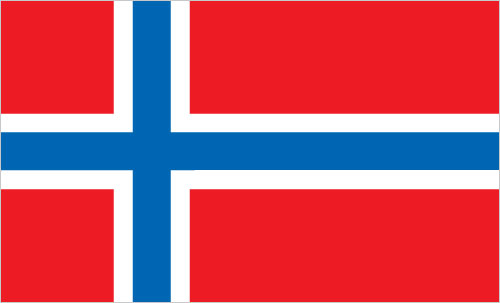
Country name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Jan Mayenetymology: named after Dutch Captain Jan Jacobszoon MAY, one of the first explorers to reach the island in 1614Dependency status:territory of Norway; since August 1994, administered from Oslo through the county governor (fylkesmann) of Nordland; however, authority has been delegated to a station commander of the Norwegian Defense Communication Service; in 2010, Norway designated the majority of Jan Mayen as a nature reserveLegal system:the laws of Norway apply where applicableFlag description:the flag of Norway is used
-
Economy :: Jan Mayen
-
Economy - overview:Jan Mayen is a volcanic island with no exploitable natural resources, although surrounding waters contain substantial fish stocks and potential untapped petroleum resources. Economic activity is limited to providing services for employees of Norway's radio and meteorological stations on the island.
-
Communications :: Jan Mayen
-
Broadcast media:a coastal radio station has been remotely operated since 1994
-
Military and Security :: Jan Mayen
-
Military - note:defense is the responsibility of Norway
-
Transportation :: Jan Mayen
-
Airports:1 (2013)country comparison to the world: 225Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)Roadways:Ports and terminals:none; offshore anchorage only
-
Transnational Issues :: Jan Mayen
-
Disputes - international:
none