Introduction :: CAMEROON
-
French Cameroon became independent in 1960 as the Republic of Cameroon. The following year the southern portion of neighboring British Cameroon voted to merge with the new country to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. In 1972, a new constitution replaced the federation with a unitary state, the United Republic of Cameroon. The country has generally enjoyed stability, which has enabled the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a petroleum industry. Despite slow movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Paul BIYA.
Geography :: CAMEROON
-
Central Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial Guinea and Nigeria
6 00 N, 12 00 E
Africa
total: 475,440 sq km
land: 472,710 sq km
water: 2,730 sq km
country comparison to the world: 54
slightly larger than California
total: 5,018 km
border countries (6): Central African Republic 901 km, Chad 1,116 km, Republic of the Congo 494 km, Equatorial Guinea 183 km, Gabon 349 km, Nigeria 1,975 km
402 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in north
diverse, with coastal plain in southwest, dissected plateau in center, mountains in west, plains in north
mean elevation: 667 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Fako 4,095 m (on Cameroon Mountain)
petroleum, bauxite, iron ore, timber, hydropower
agricultural land: 20.6%
arable land 13.1%; permanent crops 3.3%; permanent pasture 4.2%
forest: 41.7%
other: 37.7% (2011 est.)
290 sq km (2012)
volcanic activity with periodic releases of poisonous gases from Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun volcanoes
volcanism: Mt. Cameroon (elev. 4,095 m), which last erupted in 2000, is the most frequently active volcano in West Africa; lakes in Oku volcanic field have released fatal levels of gas on occasion, killing some 1,700 people in 1986
waterborne diseases are prevalent; deforestation; overgrazing; desertification; poaching; overfishing
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
sometimes referred to as the hinge of Africa; throughout the country there are areas of thermal springs and indications of current or prior volcanic activity; Mount Cameroon, the highest mountain in Sub-Saharan west Africa, is an active volcano
People and Society :: CAMEROON
-
24,360,803
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
noun: Cameroonian(s)
adjective: Cameroonian
Cameroon Highlanders 31%, Equatorial Bantu 19%, Kirdi 11%, Fulani 10%, Northwestern Bantu 8%, Eastern Nigritic 7%, other African 13%, non-African less than 1%
24 major African language groups, English (official), French (official)
Catholic 38.4%, Protestant 26.3%, other Christian 4.5%, Muslim 20.9%, animist 5.6%, other 1%, non-believer 3.2% (2005 est.)
Cameroon has a large youth population, with more than 60% of the populace under the age of 25. Fertility is falling but remains at a high level, especially among poor, rural, and uneducated women, in part because of inadequate access to contraception. Life expectancy remains low at about 55 years due to the prevalence of HIV and AIDs and an elevated maternal mortality rate, which has remained high since 1990. Cameroon, particularly the northern region, is vulnerable to food insecurity largely because of government mismanagement, corruption, high production costs, inadequate infrastructure, and natural disasters. Despite economic growth in some regions, poverty is on the rise, and is most prevalent in rural areas, which are especially affected by a shortage of jobs, declining incomes, poor school and health care infrastructure, and a lack of clean water and sanitation. Underinvestment in social safety nets and ineffective public financial management also contribute to Cameroon’s high rate of poverty.
International migration has been driven by unemployment (including fewer government jobs), poverty, the search for educational opportunities, and corruption. The US and Europe are preferred destinations, but, with tighter immigration restrictions in these countries, young Cameroonians are increasingly turning to neighboring states, such as Gabon and Nigeria, South Africa, other parts of Africa, and the Near and Far East. Cameroon’s limited resources make it dependent on UN support to host more than 300,000 refugees and asylum seekers. These refugees and asylum seekers are primarily from the Central African Republic and more recently Nigeria.
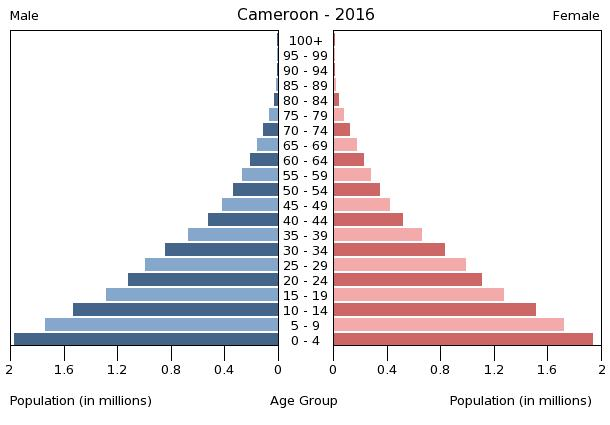
0-14 years: 42.6% (male 5,228,047/female 5,149,228)
15-24 years: 19.55% (male 2,393,598/female 2,368,557)
25-54 years: 30.71% (male 3,762,054/female 3,718,266)
55-64 years: 3.97% (male 471,306/female 495,462)
65 years and over: 3.18% (male 360,386/female 413,899) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

Africa
::CAMEROON

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 84.3%
youth dependency ratio: 78.4%
elderly dependency ratio: 5.9%
potential support ratio: 16.9% (2015 est.)
total: 18.5 years
male: 18.4 years
female: 18.6 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
2.58% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
35.8 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
9.8 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
-0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
urban population: 54.4% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 3.6% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
YAOUNDE (capital) 3.066 million; Douala 2.943 million (2015)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
19.7
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011 est.)
596 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
total: 52.2 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 55.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 48.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
total population: 58.5 years
male: 57.1 years
female: 59.9 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
4.7 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
23.4% (2011)
4.1% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 139
0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2010)
improved:
urban: 94.8% of population
rural: 52.7% of population
total: 75.6% of population
unimproved:
urban: 5.2% of population
rural: 47.3% of population
total: 24.4% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 61.8% of population
rural: 26.8% of population
total: 45.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 38.2% of population
rural: 73.2% of population
total: 54.2% of population (2015 est.)
4.46% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
619,200 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
33,100 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and yellow fever
water contact disease: schistosomiasis
respiratory disease: meningococcal meningitis
animal contact disease: rabies (2016)
9.6% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 130
14.8% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 47
3% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 133
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 75%
male: 81.2%
female: 68.9% (2015 est.)
total: 10 years
male: 11 years
female: 10 years (2011)
total number: 1,396,281
percentage: 31% (2006 est.)
total: 6.4%
male: 5.3%
female: 7.5% (2010 est.)
Government :: CAMEROON
-
conventional long form: Republic of Cameroon
conventional short form: Cameroon
local long form: Republique du Cameroun/Republic of Cameroon
local short form: Cameroun/Cameroon
former: French Cameroon, British Cameroon, Federal Republic of Cameroon, United Republic of Cameroon
etymology: in the 15th century, Portuguese explorers named the area near the mouth of the Wouri River the Rio dos Camaroes (River of Prawns) after the abundant shrimp in the water; over time the designation became Cameroon in English; this is the only instance where a country is named afer a crustacean
presidential republic
name: Yaounde
geographic coordinates: 3 52 N, 11 31 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
10 regions (regions, singular - region); Adamaoua, Centre, East (Est), Far North (Extreme-Nord), Littoral, North (Nord), North-West (Nord-Ouest), West (Ouest), South (Sud), South-West (Sud-Ouest)
1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship)
State Unification Day (National Day), 20 May (1972)
several previous; latest effective 18 January 1996; amended 2008 (2016)
mixed legal system of English common law, French civil law, and customary law
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; non-party state to the ICCt
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Cameroon
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
20 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Paul BIYA (since 6 November 1982)
head of government: Prime Minister Philemon YANG (since 30 June 2009)
cabinet: Cabinet proposed by the prime minister, appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 7-year term (no term limits); election last held on 9 October 2011 (next to be held in October 2018); prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Paul BIYA reelected president; percent of vote - Paul BIYA (CPDM) 78.0%, John FRU NDI (SDF) 10.7%, Garga Haman ADJI 3.2%, other 8.1%
description: bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (100 seats; 70 members indirectly elected by regional councils and 30 appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms) and the National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (180 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms); note - the 100-member Senate was formed at the time of the April 2013 election
elections: Senate last held on 14 April 2013 (next to be held in 2018); National Assembly last held on 30 September 2013 (next to be held in 2018)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CPDM 56, SDF 14; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CPDM 73.1%, SDF 17.6%, UNDP 6.1%, UDC 2.5%, other 0.7%; seats by party - CPDM 148, SDF 18, UNDP 5, UDC 4, UPC 3, other 2
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Cameroon (consists of 9 titular and 6 surrogate judges and organized into judicial, administrative, and audit chambers); Constitutional Council (consists of 11 members)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president with the advice of the Higher Judicial Council of Cameroon, a body chaired by the president and includes the minister of justice, selected magistrates, and representatives of the National Assembly; judge term NA; Constitutional Council members appointed by the president for single 9-year terms
subordinate courts: Parliamentary Court of Justice (jurisdiction limited to cases involving the president and prime minister); appellate and first instance courts; circuit and magistrate's courts
Cameroon People's Democratic Movement or CPDM [Paul BIYA]
Cameroon People's Party or CPP [Edith Kah WALLA]
Cameroon Renaissance Movement or MRC [Maurice KAMTO]
Cameroonian Democratic Union or UDC [Adamou Ndam NJOYA]
Movement for the Defense of the Republic or MDR [Dakole DAISSALA]
Movement for the Liberation and Development of Cameroon or MLDC [Marcel YONDO]
National Union for Democracy and Progress or UNDP [Maigari BELLO BOUBA]
Progressive Movement or MP [Jean-Jacques EKINDI]
Social Democratic Front or SDF [John FRU NDI]
Union of Peoples of Cameroon or UPC [Provisionary Management Bureau]
Network of Human Rights Defenders in Central Africa or REDHAC [Maximilliene Ngo MBE]
Tribunal 53 [Patrice NGANANG]
ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, C, CEMAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Essomba ETOUNDI (since 27 June 2016)
chancery: 2349 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008; current temporary address - 3400 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-8790
FAX: [1] (202) 387-3826
chief of mission: Ambassador Michael Stephen HOZA (since 19 September 2014)
embassy: Avenue Rosa Parks, Yaounde
mailing address: P.O. Box 817, Yaounde; pouch: American Embassy, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-2520
telephone: [237] 22220 1500; Consular: [237] 22220 1603
FAX: [237] 22220 1500 Ext. 4531; Consular FAX: [237] 22220 1752
branch office(s): Douala
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), red, and yellow, with a yellow five-pointed star centered in the red band; the vertical tricolor recalls the flag of France; red symbolizes unity, yellow the sun, happiness, and the savannahs in the north, and green hope and the forests in the south; the star is referred to as the "star of unity"
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
lion; national colors: green, red, yellow
name: "O Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancetres" (O Cameroon, Cradle of Our Forefathers)
lyrics/music: Rene Djam AFAME, Samuel Minkio BAMBA, Moise Nyatte NKO'O [French], Benard Nsokika FONLON [English]/Rene Djam AFAME
note: adopted 1957; Cameroon's anthem, also known as "Chant de Ralliement" (The Rallying Song), has been used unofficially since 1948 and officially adopted in 1957; the anthem has French and English versions whose lyrics differ
Economy :: CAMEROON
-
Modest oil resources and favorable agricultural conditions provide Cameroon with one of the best-endowed primary commodity economies in Sub-Saharan Africa. Oil remains Cameroon’s main export commodity, and despite falling global oil prices, still accounts for nearly 40% of export earnings. Cameroon’s economy suffers from factors that often impact underdeveloped countries, such as stagnant per capita income, a relatively inequitable distribution of income, a top-heavy civil service, endemic corruption, continuing inefficiencies of a large parastatal system in key sectors, and a generally unfavorable climate for business enterprise.
Since 1990, the government has embarked on various IMF and World Bank programs designed to spur business investment, increase efficiency in agriculture, improve trade, and recapitalize the nation's banks. The IMF continues to press for economic reforms, including increased budget transparency, privatization, and poverty reduction programs. The Government of Cameroon provides subsidies for electricity, food, and fuel that have strained the federal budget and diverted funds from education, healthcare, and infrastructure projects, especially in 2015, as low oil prices have led to lower revenues.
Cameroon devotes significant resources to several large infrastructure projects currently under construction, including a deep sea port in Kribi and the Lom Pangar Hydropower Project. Cameroon’s energy sector continues to diversify, recently opening a natural gas powered electricity generating plant. Cameroon continues to seek foreign investment to improve its inadequate infrastructure, create jobs, and improve its economic footprint, but its unfavorable business environment remains a significant deterrent to foreign investment.
$72.64 billion (2015 est.)
$68.61 billion (2014 est.)
$64.78 billion (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 97
$28.48 billion (2015 est.)
5.9% (2015 est.)
5.9% (2014 est.)
5.6% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$3,100 (2015 est.)
$3,000 (2014 est.)
$2,900 (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 189
22.2% of GDP (2015 est.)
20.8% of GDP (2014 est.)
19.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
household consumption: 77.6%
government consumption: 12.1%
investment in fixed capital: 21.9%
investment in inventories: 0.1%
exports of goods and services: 22%
imports of goods and services: -33.7% (2015 est.)
agriculture: 21.6%
industry: 30.6%
services: 47.7% (2015 est.)
coffee, cocoa, cotton, rubber, bananas, oilseed, grains, cassava (manioc, tapioca); livestock; timber
petroleum production and refining, aluminum production, food processing, light consumer goods, textiles, lumber, ship repair
7.2% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
9.379 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
agriculture: 70%
industry: 13%
services: 17% (2001 est.)
30% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
48% (2000 est.)
lowest 10%: 2.3%
highest 10%: 35.4% (2001)
44.6 (2001)
47.7 (1996)
country comparison to the world: 44
revenues: $4.788 billion
expenditures: $6.292 billion (2015 est.)
16.8% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
-5.3% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
28.6% of GDP (2015 est.)
22.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
1 July - 30 June
2.7% (2015 est.)
1.9% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
4.25% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 88
13% (31 December 2015 est.)
13% (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$3.691 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$3.877 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
$5.53 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$6.217 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
$4.448 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$4.769 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
$230 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
-$1.647 billion (2015 est.)
-$1.396 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
$5.756 billion (2015 est.)
$6.679 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
crude oil and petroleum products, lumber, cocoa beans, aluminum, coffee, cotton
China 16.7%, India 15.7%, Spain 6.2%, Belgium 6.1%, France 6.1%, Portugal 5.6%, Netherlands 5%, Italy 5% (2015)
$6.5 billion (2015 est.)
$6.915 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
machinery, electrical equipment, transport equipment, fuel, food
China 27.9%, Nigeria 13.9%, France 10.9%, Belgium 4.1% (2015)
$2.714 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$3.204 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
$6.3 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$5.289 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) per dollar -
591.45 (2015 est.)
494.42 (2014 est.)
494.42 (2013 est.)
510.53 (2012 est.)
471.87 (2011 est.)
Energy :: CAMEROON
-
population without electricity: 10,100,000
electrification - total population: 55%
electrification - urban areas: 88%
electrification - rural areas: 17% (2013)
6.8 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
6.1 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
1.1 million kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
28.5% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
71.5% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
95,960 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
50,830 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
37,600 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
200 million bbl (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 59
51,670 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
43,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
14,590 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
4,134 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
469 million cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
469 million cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
135.1 billion cu m (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 50
6.5 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
Communications :: CAMEROON
-
total subscriptions: 1,054,978
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
total: 16.807 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 71 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
general assessment: system includes cable, microwave radio relay, and tropospheric scatter; Camtel, the monopoly provider of fixed-line service, provides connections for only about 4 per 100 persons; equipment is old and outdated, and connections with many parts of the country are unreliable
domestic: mobile-cellular usage, in part a reflection of the poor condition and general inadequacy of the fixed-line network, has increased sharply, reaching a subscribership base of 70 per 100 persons
international: country code - 237; landing point for the SAT-3/WASC fiber-optic submarine cable that provides connectivity to Europe and Asia; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2015)
government maintains tight control over broadcast media; state-owned Cameroon Radio Television (CRTV), broadcasting on both a TV and radio network, was the only officially recognized and fully licensed broadcaster until August 2007, when the government finally issued licenses to 2 private TV broadcasters and 1 private radio broadcaster; about 70 privately owned, unlicensed radio stations operating but are subject to closure at any time; foreign news services required to partner with state-owned national station (2007)
.cm
total: 4.909 million
percent of population: 20.7% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
Transportation :: CAMEROON
-
number of registered air carriers: 1
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 3
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 267,208
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)
TJ (2016)
33 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 112
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)
total: 22
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 10
under 914 m: 8 (2013)
gas 53 km; liquid petroleum gas 5 km; oil 1,107 km; water 35 km (2013)
total: 987 km
narrow gauge: 987 km 1.000-m gauge
note: railway connections generally efficient but limited; rail lines connect major cities of Douala, Yaounde, Ngaoundere, and Garoua; passenger and freight service provided by CAMRAIL (2014)
country comparison to the world: 87
total: 51,350 km
paved: 4,108 km
unpaved: 47,242 km
note: there are 28,857 km of national roads (2011)
country comparison to the world: 76
(major rivers in the south, such as the Wouri and the Sanaga, are largely non-navigable; in the north, the Benue, which connects through Nigeria to the Niger River, is navigable in the rainy season only to the port of Garoua) (2010)
river port(s): Douala (Wouri); Garoua (Benoue)
oil terminal(s): Limboh Terminal
Military and Security :: CAMEROON
-
Cameroon Armed Forces (Forces Armees Camerounaises, FAC): Army (L'Armee de Terre), Navy (Marine Nationale Republique (MNR), includes naval infantry), Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Cameroun, AAC), Rapid Intervention Brigade, Fire Fighter Corps, Gendarmerie (2015)
18-23 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; no conscription; high school graduation required; service obligation 4 years; periodic government calls for volunteers (2012)
1.42% of GDP (2012)
1.37% of GDP (2011)
1.42% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 70
Transnational Issues :: CAMEROON
-
Joint Border Commission with Nigeria reviewed 2002 ICJ ruling on the entire boundary and bilaterally resolved differences, including June 2006 Greentree Agreement that immediately ceded sovereignty of the Bakassi Peninsula to Cameroon with a full phase-out of Nigerian control and patriation of residents in 2008; Cameroon and Nigeria agreed on maritime delimitation in March 2008; sovereignty dispute between Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon over an island at the mouth of the Ntem River; only Nigeria and Cameroon have heeded the Lake Chad Commission's admonition to ratify the delimitation treaty, which also includes the Chad-Niger and Niger-Nigeria boundaries
refugees (country of origin): 259,145 (Central African Republic); 86,212 (Nigeria) (2016)
IDPs: 198,889 (2016)