South America :: SURINAME
Introduction :: SURINAME
-
First explored by the Spaniards in the 16th century and then settled by the English in the mid-17th century, Suriname became a Dutch colony in 1667. With the abolition of African slavery in 1863, workers were brought in from India and Java. The Netherlands granted the colony independence in 1975. Five years later the civilian government was replaced by a military regime that soon declared a socialist republic. It continued to exert control through a succession of nominally civilian administrations until 1987, when international pressure finally forced a democratic election. In 1990, the military overthrew the civilian leadership, but a democratically elected government - a four-party coalition - returned to power in 1991. The coalition expanded to eight parties in 2005 and ruled until August 2010, when voters returned former military leader Desire BOUTERSE and his opposition coalition to power. President BOUTERSE was reelected unopposed in 2015.
Geography :: SURINAME
-
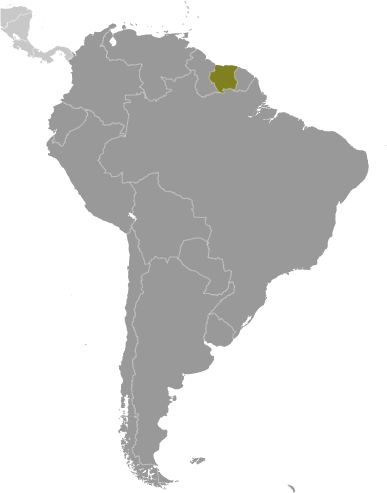
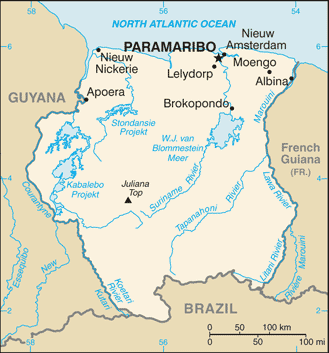
Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana4 00 N, 56 00 WSouth Americatotal: 163,820 sq kmland: 156,000 sq kmwater: 7,820 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 92slightly larger than Georgiatotal: 1,907 kmborder countries (3): Brazil 515 km, French Guiana 556 km, Guyana 836 km386 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmtropical; moderated by trade windsmostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swampsmean elevation: 246 melevation extremes: lowest point: unnamed location in the coastal plain -2 mhighest point: Juliana Top 1,230 mtimber, hydropower, fish, kaolin, shrimp, bauxite, gold, and small amounts of nickel, copper, platinum, iron oreagricultural land: 0.5%arable land 0.4%; permanent crops 0%; permanent pasture 0.1%forest: 94.6%other: 4.9% (2011 est.)570 sq km (2012)population concentrated along the nothern coastal strip; the remainder of the country is sparsely populatedNAdeforestation as timber is cut for export; pollution of inland waterways by small-scale mining activitiesparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementssmallest independent country on South American continent; mostly tropical rain forest; great diversity of flora and fauna that, for the most part, is increasingly threatened by new development; relatively small population, mostly along the coast
People and Society :: SURINAME
-
585,824 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 172noun: Surinamer(s)adjective: SurinameseHindustani (also known locally as "East Indians"; their ancestors emigrated from northern India in the latter part of the 19th century) 37%, Creole (mixed white and black) 31%, Javanese 15%, "Maroons" (their African ancestors were brought to the country in the 17th and 18th centuries as slaves and escaped to the interior) 10%, Amerindian 2%, Chinese 2%, white 1%, other 2%Dutch (official), English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes called Taki-Taki, is native language of Creoles and much of the younger population and is lingua franca among others), Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), JavaneseHindu 27.4%, Protestant 25.2% (predominantly Moravian), Roman Catholic 22.8%, Muslim 19.6%, indigenous beliefs 5%Suriname is a pluralistic society consisting primarily of Creoles (persons of mixed African and European heritage), the descendants of escaped African slaves known as Maroons, and the descendants of Indian and Javanese contract workers. The country overall is in full, post-industrial demographic transition, with a low fertility rate, a moderate mortality rate, and a rising life expectancy. However, the Maroon population of the rural interior lags behind because of lower educational attainment and contraceptive use, higher malnutrition, and significantly less access to electricity, potable water, sanitation, infrastructure, and health care.Some 350,000 people of Surinamese descent live in the Netherlands, Suriname's former colonial ruler. In the 19th century, better-educated, largely Dutch-speaking Surinamese began emigrating to the Netherlands. World War II interrupted the outflow, but it resumed after the war when Dutch labor demands grew - emigrants included all segments of the Creole population. Suriname still is strongly influenced by the Netherlands because most Surinamese have relatives living there and it is the largest supplier of development aid. Other emigration destinations include French Guiana and the United States. Suriname's immigration rules are flexible, and the country is easy to enter illegally because rainforests obscure its borders. Since the mid-1980s, Brazilians have settled in Suriname's capital, Paramaribo, or eastern Suriname, where they mine gold. This immigration is likely to slowly re-orient Suriname toward its Latin American roots.0-14 years: 25.15% (male 75,088/female 72,261)15-24 years: 17.46% (male 52,129/female 50,141)25-54 years: 44.36% (male 132,334/female 127,562)55-64 years: 7.16% (male 20,564/female 21,394)65 years and over: 5.86% (male 14,848/female 19,503) (2016 est.)total dependency ratio: 50.8%youth dependency ratio: 40.4%elderly dependency ratio: 10.4%potential support ratio: 9.6% (2015 est.)total: 29.5 yearsmale: 29.1 yearsfemale: 29.9 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1201.05% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 11116 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1186.1 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1540.6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 67population concentrated along the nothern coastal strip; the remainder of the country is sparsely populatedurban population: 66% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: 0.78% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)PARAMARIBO (capital) 234,000 (2014)at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2016 est.)155 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 63total: 25.3 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 29.5 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 20.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 69total population: 72.2 yearsmale: 69.8 yearsfemale: 74.8 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1471.95 children born/woman (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 12647.6% (2010)5.7% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1153.1 beds/1,000 population (2010)improved:urban: 98.1% of populationrural: 88.4% of populationtotal: 94.8% of populationunimproved:urban: 1.9% of populationrural: 11.6% of populationtotal: 5.2% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 88.4% of populationrural: 61.4% of populationtotal: 79.2% of populationunimproved:urban: 11.6% of populationrural: 38.6% of populationtotal: 20.8% of population (2015 est.)1.08% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 473,800 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 110100 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 100degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne disease: dengue fever and malarianote: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus (2016)26.1% (2014)country comparison to the world: 605.8% (2010)country comparison to the world: 83NAdefinition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 95.6%male: 96.1%female: 95% (2015 est.)total number: 6,094percentage: 6% (2006 est.)total: 15.3%male: 11.6%female: 21.7% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 51
Government :: SURINAME
-
conventional long form: Republic of Surinameconventional short form: Surinamelocal long form: Republiek Surinamelocal short form: Surinameformer: Netherlands Guiana, Dutch Guianaetymology: name may derive from the indigenous "Surinen" people who inhabited the area at the time of European contactpresidential republicname: Paramaribogeographic coordinates: 5 50 N, 55 10 Wtime difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)10 districts (distrikten, singular - distrikt); Brokopondo, Commewijne, Coronie, Marowijne, Nickerie, Para, Paramaribo, Saramacca, Sipaliwini, Wanica25 November 1975 (from the Netherlands)Independence Day, 25 November (1975)previous 1975; latest ratified 30 September 1987, effective 30 October 1987; amended 1992 (2016)civil law system influenced by Dutch civil law; note - the Commissie Nieuw Surinaamse Burgerlijk Wetboek completed drafting a new civil code in February 2009accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Surinamedual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Desire Delano BOUTERSE (since 12 August 2010); Vice President Ashwin ADHIN (since 12 August 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Desire Delano BOUTERSE (since 12 August 2010); Vice President Ashwin ADHIN (since 12 August 2015)cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly; president and vice president serve a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 25 May 2015 (next to be held on 25 May 2020)election results: Desire Delano BOUTERSE reelected president; National Assembly vote - NAdescription: unicameral National Assembly or Nationale Assemblee (51 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)elections: last held on 25 May 2015 (next to be held in May 2020)election results: percent of vote by party - NDP 45.5%, V7 37.2%, A-Com 10.5%, DOE 4.3%, PALU .7%, other 1.7%; seats by party - NDP 26, V7 18, A-Com 5, DOE 1, PALU 1highest resident court(s): High Court of Justice of Suriname (consists of the court president, vice president, and 4 judges); note - appeals beyond the High Court are referred to the Caribbean Court of Justice, with final appeal to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)judge selection and term of office: court judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the High Court; judges appointed for lifesubordinate courts: cantonal courtsAlternative Combination or A-Com (a coalition that includes ABOP, KTPI, PDO)Brotherhood and Unity in Politics or BEP [Celsius WATERBERG]Democratic Alternative '91 or DA91 [Winston JESSURUN]General Liberation and Development Party or ABOP [Ronnie BRUNSWIJK}National Democratic Party or NDP [Desire Delano BOUTERSE]National Party of Suriname or NPS [Gregory RUSLAND]Party for Democracy and Development or PDO [Waldy NAIN]Party for Democracy and Development in Unity or DOE [Carl BREEVELD]Party for National Unity and Solidarity or KTPI [Willy SOEMITA]People's Alliance, Pertjaja Luhur or PL [Paul SOMOHARDJO]Progressive Worker and Farmer's Union or PALU [Jim HOK]Surinamese Labor Party or SPA [Guno CASTELEN]United Reform Party or VHP [Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI]Victory 7 or V7 (formerly the New Front for Democracy and Development or NF) (a coalition including NPS, VHP, DA91, PL, SPA) [Chandrikapresad SANTOKHI]Association of Indigenous Village Chiefs [Ricardo PANE]Association of Saramaccan Authorities or Maroon [Head Captain WASE]Women's Parliament Forum or PVF [Iris GILLIAD]ACP, AOSIS, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Sylvana Elvira SIMSON (since 1 September 2015)chancery: Suite 460, 4301 Connecticut Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 244-7488FAX: [1] (202) 244-5878consulate(s) general: Miamichief of mission: Ambassador Jay N. ANANIA (since 1 October 2012)embassy: Dr. Sophie Redmondstraat 129, Paramaribomailing address: US Department of State, PO Box 1821, Paramaribotelephone: [597] 472-900FAX: [597] 410-972five horizontal bands of green (top, double width), white, red (quadruple width), white, and green (double width); a large, yellow, five-pointed star is centered in the red band; red stands for progress and love; green symbolizes hope and fertility; white signifies peace, justice, and freedom; the star represents the unity of all ethnic groups; from its yellow light the nation draws strength to bear sacrifices patiently while working toward a golden futureroyal palm, faya lobi (flower); national colors: green, white, red, yellowname: "God zij met ons Suriname!" (God Be With Our Suriname)lyrics/music: Cornelis Atses HOEKSTRA and Henry DE ZIEL/Johannes Corstianus DE PUYnote: adopted 1959; originally adapted from a Sunday school song written in 1893 and contains lyrics in both Dutch and Sranang Tongo
Economy :: SURINAME
-
The economy is dominated by the mining industry, with exports of oil, gold, and alumina accounting for about 85% of exports and 27% of government revenues, making the economy highly vulnerable to mineral price volatility.Economic growth has declined annually from just under 5% in 2012 to 1.5% in 2015. In January 2011, the government devalued the currency by 20% and raised taxes to reduce the budget deficit. As a result of these measures, inflation receded to less than 4% in 2015.Suriname's economic prospects for the medium term will depend on continued commitment to responsible monetary and fiscal policies and to the introduction of structural reforms to liberalize markets and promote competition. The government's reliance on revenue from extractive industries will temper Suriname's economic outlook, especially if gold prices continue their downward trend.$9.09 billion (2015 est.)$9.077 billion (2014 est.)$8.913 billion (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 160$5.192 billion (2015 est.)0.1% (2015 est.)1.8% (2014 est.)2.8% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 200$16,300 (2015 est.)$16,200 (2014 est.)$16,200 (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 10024.2% of GDP (2015 est.)24.5% of GDP (2014 est.)25.7% of GDP (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1household consumption: 75.8%government consumption: 11.5%investment in fixed capital: 12%investment in inventories: 26.5%exports of goods and services: 25.6%imports of goods and services: -24.9% (2015 est.)agriculture: 6.4%industry: 49.9%services: 43.7% (2015 est.)rice, bananas, palm kernels, coconuts, plantains, peanuts; beef, chickens; shrimp; forest productsbauxite and gold mining, alumina production; oil, lumbering, food processing, fishing2% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 109165,600 (2007 est.)country comparison to the world: 176agriculture: 11.2%industry: 19.5%services: 69.3% (2010)8.9% (2014 est.)8.5% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 10170% (2002 est.)lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%revenues: $878 millionexpenditures: $1.259 billion (2015 est.)16.9% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 180-7.3% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 194calendar year3% (2015 est.)3.4% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 19410% (2013)9% (2012)country comparison to the world: 2312.62% (31 December 2015 est.)12.28% (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 62$1.231 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$1.409 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 142$3.461 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$2.885 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 143$2.224 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$2.029 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 138$NA-$808 million (2015 est.)-$415 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 116$1.666 billion (2015 est.)$2.149 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 140alumina, gold, crude oil, lumber, shrimp and fish, rice, bananasSwitzerland 21.8%, UAE 14.5%, India 13.9%, Belgium 9.7%, US 8.9%, France 8.1%, Canada 6.6% (2015)$1.973 billion (2015 est.)$1.966 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 163capital equipment, petroleum, foodstuffs, cotton, consumer goodsUS 26.8%, Netherlands 14.3%, China 12.2%, Trinidad and Tobago 7.4%, Japan 4.8% (2015)$330.2 million (31 December 2015 est.)$625.2 million (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 155$1.15 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$1.088 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 161Surinamese dollars (SRD) per US dollar -3.4167 (2015 est.)3.3 (2014 est.)3.3 (2013 est.)3.3 (2012 est.)3.2683 (2011 est.)
Energy :: SURINAME
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)2.1 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1441.9 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1460 kWh (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1800 kWh (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 185400,000 kW (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 14554.1% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1440% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 15845.9% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 530% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21017,000 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 770 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1720 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 11188.97 million bbl (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 7319,120 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 9817,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 13712,980 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 8910,260 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1370 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1140 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1820 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1580 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1140 cu m (1 January 2011 es)country comparison to the world: 1812.4 million Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 148
Communications :: SURINAME
-
total subscriptions: 85,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 15 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 147total: 991,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 171 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 159general assessment: international facilities are gooddomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity 185 telephones per 100 persons; microwave radio relay networkinternational: country code - 597; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2015)2 state-owned TV stations; 1 state-owned radio station; multiple private radio and TV stations (2007).srtotal: 248,000percent of population: 42.8% (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 154
Transportation :: SURINAME
-
number of registered air carriers: 2inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 5annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 259,682annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 29,324,319 mt-km (2015)PZ (2016)55 (2013)country comparison to the world: 85total: 6over 3,047 m: 1under 914 m: 5 (2013)total: 49914 to 1,523 m: 4under 914 m: 45 (2013)oil 50 km (2013)total: 4,304 kmpaved: 1,130 kmunpaved: 3,174 km (2003)country comparison to the world: 1551,200 km (most navigable by ships with drafts up to 7 m) (2011)country comparison to the world: 58major seaport(s): Paramaribo, Wageningen
Military and Security :: SURINAME
-
Suriname Armed Forces: Ground Forces, Naval Forces, Air Forces (2010)18 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; no conscription; personnel drawn almost exclusively from the Creole community (2012)
Transnational Issues :: SURINAME
-
area claimed by French Guiana between Riviere Litani and Riviere Marouini (both headwaters of the Lawa); Suriname claims a triangle of land between the New and Kutari/Koetari rivers in a historic dispute over the headwaters of the Courantyne; Guyana seeks UN Convention on the Law of the Sea arbitration to resolve the longstanding dispute with Suriname over the axis of the territorial sea boundary in potentially oil-rich waterscurrent situation: Suriname is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children subjected to sex trafficking and men, women, and children subjected to forced labor; women and girls from Suriname, Guyana, Brazil, and the Dominican Republic are subjected to sex trafficking in the country, sometimes in interior mining camps; migrant workers in agriculture and on fishing boats and children working in informal urban sectors and gold mines are vulnerable to forced labor; traffickers from Suriname exploit victims in the Netherlandstier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Suriname does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; in 2014, Suriname was granted a waiver from an otherwise required downgrade to Tier 3 because its government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; authorities increased the number of trafficking investigations, prosecutions, and convictions as compared to 2013, but resources were insufficient to conduct investigations in the country’s interior; more trafficking victims were identified in 2014 than in 2013, but protective services for adults and children were inadequate, with a proposed government shelter for women and child trafficking victims remaining unopened (2015)growing transshipment point for South American drugs destined for Europe via the Netherlands and Brazil; transshipment point for arms-for-drugs dealing