Introduction :: SRI LANKA
-
The first Sinhalese arrived in Sri Lanka late in the 6th century B.C., probably from northern India. Buddhism was introduced circa 250 B.C., and a great civilization developed at the cities of Anuradhapura (kingdom from circa 200 B.C. to circa A.D. 1000) and Polonnaruwa (from about 1070 to 1200). In the 14th century, a south Indian dynasty established a Tamil kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. The Portuguese controlled the coastal areas of the island in the 16th century and the Dutch in the 17th century. The island was ceded to the British in 1796, became a crown colony in 1802, and was formally united under British rule by 1815. As Ceylon, it became independent in 1948; its name was changed to Sri Lanka in 1972. Tensions between the Sinhalese majority and Tamil separatists erupted into war in 1983. After two decades of fighting, the government and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) formalized a cease-fire in February 2002 with Norway brokering peace negotiations. Violence between the LTTE and government forces intensified in 2006, but the government regained control of the Eastern Province in 2007 and by May 2009, the remnants of the LTTE had been defeated. Since the end of the conflict, the government has enacted an ambitious program of economic development projects, many of which are financed by loans from the Government of China. In addition to efforts at reconstructing its economy, the government has resettled more than 95% of those civilians displaced during the final phase of the conflict and released the vast majority of former LTTE combatants captured by Government Security Forces. At the same time, there has been little progress on more contentious and politically difficult issues such as reaching a political settlement with Tamil elected representatives and holding accountable those alleged to have been involved in human rights violations and other abuses during the conflict.
Geography :: SRI LANKA
-
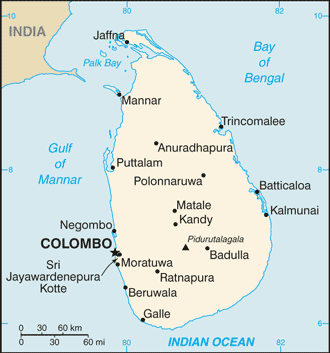
Southern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of India
7 00 N, 81 00 E
Asia
total: 65,610 sq km
land: 64,630 sq km
water: 980 sq km
country comparison to the world: 122
slightly larger than West Virginia
Area comparison map:

South Asia
::SRI LANKA

Area Comparison
slightly larger than West Virginia
0 km
1,340 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
tropical monsoon; northeast monsoon (December to March); southwest monsoon (June to October)
mostly low, flat to rolling plain; mountains in south-central interior
mean elevation: 228 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: Pidurutalagala 2,524 m
limestone, graphite, mineral sands, gems, phosphates, clay, hydropower, arable land
agricultural land: 43.5%
arable land 20.7%; permanent crops 15.8%; permanent pasture 7%
forest: 29.4%
other: 27.1% (2011 est.)
5,700 sq km (2012)
occasional cyclones and tornadoes
deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in Colombo
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanes
People and Society :: SRI LANKA
-
22.235 million (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
noun: Sri Lankan(s)
adjective: Sri Lankan
Sinhalese 74.9%, Sri Lankan Tamil 11.2%, Sri Lankan Moors 9.2%, Indian Tamil 4.2%, other 0.5% (2012 est.)
Sinhala (official and national language) 74%, Tamil (official and national language) 18%, other 8%
note: English, spoken competently by about 10% of the population, is commonly used in government and is referred to as the link language in the constitution
Buddhist (official) 70.2%, Hindu 12.6%, Muslim 9.7%, Roman Catholic 6.1%, other Christian 1.3%, other 0.05% (2012 est.)
0-14 years: 24.35% (male 2,760,821/female 2,652,747)
15-24 years: 14.7% (male 1,660,402/female 1,608,022)
25-54 years: 41.71% (male 4,544,253/female 4,729,544)
55-64 years: 9.89% (male 1,018,357/female 1,181,060)
65 years and over: 9.35% (male 882,740/female 1,197,054) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

South Asia
::SRI LANKA

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 51.2%
youth dependency ratio: 37.2%
elderly dependency ratio: 14.1%
potential support ratio: 7.1% (2015 est.)
total: 32.5 years
male: 31.2 years
female: 33.7 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
0.8% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
15.5 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
6.2 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
-1.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
urban population: 18.4% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 0.72% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital) 128,000 (2014); COLOMBO (capital) 707,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.86 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
25.4
note: median age at first birth among women 30-34 (2006/07 est.)
30 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
total: 8.6 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 9.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
total population: 76.8 years
male: 73.3 years
female: 80.4 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
2.09 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
68.4% (2006/07)
3.5% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 177
0.68 physicians/1,000 population (2010)
3.6 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 98.5% of population
rural: 95% of population
total: 95.6% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1.5% of population
rural: 5% of population
total: 4.4% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 88.1% of population
rural: 96.7% of population
total: 95.1% of population
unimproved:
urban: 11.9% of population
rural: 3.3% of population
total: 4.9% of population (2015 est.)
0.03% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
4,200 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
100 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A
vectorborne disease: dengue fever
water contact disease: leptospirosis
animal contact disease: rabies (2016)
6.8% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 155
26.3% (2012)
country comparison to the world: 23
1.6% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 168
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 92.6%
male: 93.6%
female: 91.7% (2015 est.)
total: 14 years
male: 14 years
female: 14 years (2013)
total: 20.1%
male: 15%
female: 27.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
Government :: SRI LANKA
-
conventional long form: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
conventional short form: Sri Lanka
local long form: Shri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Janarajaya/Ilankai Jananayaka Choshalichak Kutiyarachu
local short form: Shri Lanka/Ilankai
former: Serendib, Ceylon
note: the name means "resplendent island" in Sanskrit
presidential republic
name: Colombo; note - Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte is the legislative capital
geographic coordinates: 6 55 N, 79 50 E
time difference: UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
9 provinces; Central, Eastern, North Central, Northern, North Western, Sabaragamuwa, Southern, Uva, Western
4 February 1948 (from the UK)
Independence Day, 4 February (1948)
several previous; latest adopted 16 August 1978, certified 31 August 1978; amended many times, last in 2015 (2016)
mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and Jaffna Tamil customary law
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Sri Lanka
dual citizenship recognized: no, except in cases where the government rules it is to the benefit of Sri Lanka
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Maithripala SIRISENA (since 9 January 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government; Ranil WICKREMESINGHE (since 9 January 2015) holds the title of prime minister
head of government: President Maithripala SIRISENA (since 9 January 2015)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president in consultation with the prime minister
elections/appointments: president directly elected by preferential majority popular vote for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 8 January 2015 (next to be held by January 2021); note - the January 2015 election was held nearly 2 years ahead of schedule
election results: Maithripala SIRISENA elected president; percent of vote - Maithripala SIRISENA (Sri Lanka Freedom Party) 51.3%, Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA (Sri Lanka Freedom Party) 47.6%, other 1.1%
description: unicameral Parliament (225 seats; 196 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote using a preferential method in which voters select 3 candidates in order of preference; remaining 29 seats allocated to other political parties and groups in proportion to share of national vote; members serve 6-year terms)
elections: last held on 17 August 2015 following President SIRISENA's dissolution of Parliament in late June in an effort to consolidate power and pass reforms (next to be held in 2021)
election results: percent of vote by alliance/party - EYJP 45.7%, UPFA 42.4%, JVP 4.9%, TNA 4.6%, SLMC 0.4%, EPDP 0.3% other 1.7%; seats by alliance/party EYJP 106, UPFA 95, TNA 16, JVP 6, SLMC 1, EPDP 1
highest court(s): Supreme Court of the Republic (consists of the chief justice and 10 justices); note - the court has exclusive jurisdiction to review legislation
judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the president; other justices appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice; all justices hold office until age 65
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; High Courts; Magistrate's Courts; municipal and primary courts
Eelam People's Democratic Party or EPDP [Douglas DEVANANDA]
Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna or JVP [Anura Kumara DISSANAYAKE]
Jathika Hela Urumaya or JHU [Patali Champika RANAWAKA]
Sri Lanka Freedom Party or SLFP [Maithripala SIRISENA]
Sri Lanka Muslim Congress or SLMC [Rauff HAKEEM]
Tamil National Alliance or TNA [R. SAMPANTHAN]
United National Front for Good Governance or EYJP (coalition includes UNP)
United National Party or UNP [Ranil WICKREMESINGHE]
United People's Freedom Alliance or UPFA (coalition includes SLFP)
Buddhist clergy
Sinhalese Buddhist lay groups
other: labor unions; hard-line nationalist Sinhalese groups such as the National Movement Against Terrorism
ABEDA, ADB, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CICA (observer), CP, FAO, G-11, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Prasad KARIYAWASAM (since 14 July 2014)
chancery: 2148 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 483-4025 through 4028
FAX: [1] (202) 232-7181
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York
chief of mission: Ambassador Atul KESHAP (since 21 August 2015); note - also accredited to Maldives
embassy: 210 Galle Road, Colombo 3
mailing address: P. O. Box 106, Colombo
telephone: [94] (11) 249-8500
FAX: [94] (11) 243-7345
yellow with two panels; the smaller hoist-side panel has two equal vertical bands of green (hoist side) and orange; the other larger panel depicts a yellow lion holding a sword on a maroon rectangular field that also displays a yellow bo leaf in each corner; the yellow field appears as a border around the entire flag and extends between the two panels; the lion represents Sinhalese ethnicity, the strength of the nation, and bravery; the sword demonstrates the sovereignty of the nation; the four bo leaves - symbolizing Buddhism and its influence on the country - stand for the four virtues of kindness, friendliness, happiness, and equanimity; orange signifies Sri Lankan Tamils, green Sri Lankan Moors, and maroon the Sinhalese majority; yellow denotes other ethnic groups; also referred to as the Lion Flag
lion, water lily; national colors: maroon, yellow
name: "Sri Lanka Matha" (Mother Sri Lanka)
lyrics/music: Ananda SAMARKONE
note: adopted 1951
Economy :: SRI LANKA
-
Sri Lanka continues to experience strong economic growth following the end of the government's 26-year conflict with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. The government has been pursuing large-scale reconstruction and development projects in its efforts to spur growth in war-torn and disadvantaged areas, develop small and medium enterprises, and increase agricultural productivity.
The government's high debt payments and bloated civil service have contributed to historically high budget deficits and low tax revenues remain a concern. Government debt of about 72% of GDP remains among the highest in emerging markets.
The new government in 2015 drastically increased wages for public sector employees, which boosted demand for consumer goods but hurt the overall balance of payments and reduced foreign exchange reserves.
$223 billion (2015 est.)
$212 billion (2014 est.)
$203 billion (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 63
$82.1 billion (2015 est.)
5.2% (2015 est.)
4.5% (2014 est.)
3.4% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$10,600 (2015 est.)
$10,100 (2014 est.)
$9,700 (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 135
27.6% of GDP (2015 est.)
29.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
29.8% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
household consumption: 68.6%
government consumption: 8.8%
investment in fixed capital: 26.2%
investment in inventories: 3.9%
exports of goods and services: 20.5%
imports of goods and services: -28% (2015 est.)
agriculture: 8.7%
industry: 30.7%
services: 60.6% (2015 est.)
rice, sugarcane, grains, pulses, oilseed, spices, vegetables, fruit, tea, rubber, coconuts; milk, eggs, hides, beef; fish
processing of rubber, tea, coconuts, tobacco and other agricultural commodities; telecommunications, insurance, banking; tourism, shipping; clothing, textiles; cement, petroleum refining, information technology services, construction
3% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
8.928 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
agriculture: 28.4%
industry: 25.7%
services: 45.9% (30 Jun 2015)
4.7% (2015 est.)
4.3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
8.9% (2010 est.)
lowest 10%: 1.6%
highest 10%: 39.5% (2009)
49 (2010)
46 (1995)
country comparison to the world: 22
revenues: $10.75 billion
expenditures: $16.95 billion (2015 est.)
13.1% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
-7.5% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
76% of GDP (2015 est.)
70.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
note: covers central government debt, and excludes debt instruments directly owned by government entities other than the treasury (e.g. commercial bank borrowings of a government corporation); the data includes treasury debt held by foreign entities as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement; sub-national entities are usually not permitted to sell debt instruments
country comparison to the world: 34
calendar year
0.9% (2015 est.)
3.3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
6% (31 December 2015)
6.5% (31 December 2013)
country comparison to the world: 68
6.96% (31 December 2015 est.)
7.84% (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
$4.963 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$4.671 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$26.79 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$25.95 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
$39.22 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$33.79 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
$18.48 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$17.05 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$19.44 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
-$1.681 billion (2015 est.)
-$2.018 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
$10.5 billion (2015 est.)
$11.13 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
textiles and apparel, tea and spices; rubber manufactures; precious stones; coconut products, fish
US 26%, UK 9%, India 7.2%, Germany 4.3% (2015)
$18.93 billion (2015 est.)
$19.42 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
petroleum, textiles, machinery and transportation equipment, building materials, mineral products, foodstuffs
India 24.6%, China 20.6%, UAE 7.2%, Singapore 5.9%, Japan 5.7% (2015)
$7.303 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$8.209 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$45.47 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$43.61 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$NA
$NA
Sri Lankan rupees (LKR) per US dollar -
135.86 (2015 est.)
130.57 (2014 est.)
130.57 (2013 est.)
127.6 (2012 est.)
110.57 (2011 est.)
Energy :: SRI LANKA
-
population without electricity: 1,334,100
electrification - total population: 94%
electrification - urban areas: 99%
electrification - rural areas: 93% (2013)
12 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
11 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
3.4 million kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
51.1% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
47% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
1.9% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
34,860 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
0 bbl (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 116
32,780 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
98,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
2,682 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
56,570 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
0 cu m (1 January 2014 es)
country comparison to the world: 123
16 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
Communications :: SRI LANKA
-
total subscriptions: 2,601,196
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 12 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
total: 24.385 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 111 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
general assessment: telephone services have improved significantly and are available in most parts of the country
domestic: national trunk network consists mostly of digital microwave radio relay; fiber-optic links now in use in Colombo area and fixed wireless local loops have been installed; competition is strong in mobile cellular systems and mobile cellular subscribership is increasing
international: country code - 94; the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cables provide connectivity to Asia, Australia, Middle East, Europe, US; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2015)
government operates 8 TV channels and a radio network; multi-channel satellite and cable TV subscription services available; 35 private TV stations and about 50 radio stations (2012)
.lk
total: 6.614 million
percent of population: 30% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
Transportation :: SRI LANKA
-
number of registered air carriers: 3
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 25
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 4,911,730
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 381,381,300 mt-km (2015)
4R (2016)
19 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 137
total: 15
over 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 6
914 to 1,523 m: 7 (2013)
total: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 3 (2013)
1 (2013)
total: 1,447 km
broad gauge: 1,447 km 1.676-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 79
total: 114,093 km
paved: 16,977 km
unpaved: 97,116 km (2010)
country comparison to the world: 41
160 km (primarily on rivers in southwest) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 100
total: 21
by type: bulk carrier 4, cargo 13, chemical tanker 1, container 1, petroleum tanker 2
foreign-owned: 8 (Germany 8) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 94
major seaport(s): Colombo
container port(s) (TEUs): Colombo (3,651,963)
Military and Security :: SRI LANKA
-
Sri Lanka Army, Sri Lanka Navy, Sri Lanka Air Force, Sri Lanka Coast Guard (2015)
18-22 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; 5-year service obligation (Air Force) (2012)
2.43% of GDP (2012)
2.89% of GDP (2011)
2.43% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 29
Transnational Issues :: SRI LANKA
-
none
IDPs: 44,934 (civil war; more than half displaced prior to 2008; many of the more than 480,000 IDPs registered as returnees have not reached durable solutions) (2015)
current situation: Sri Lanka is primarily a source and, to a lesser extent, a destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; some Sri Lankan adults and children who migrate willingly to the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Afghanistan to work in the construction, garment, and domestic service sectors are subsequently subjected to forced labor or debt bondage (incurred through high recruitment fees or money advances); some Sri Lankan women are forced into prostitution in Jordan, Maldives, Malaysia, Singapore, and other countries; within Sri Lanka, women and children are subjected to sex trafficking, and children are also forced to beg and work in the agriculture, fireworks, and fish-drying industries; a small number of women from Asia, Central Asia, Europe, and the Middle East have been forced into prostitution in Sri Lanka in recent years
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Sri Lanka does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; in 2014, Sri Lanka was granted a waiver from an otherwise required downgrade to Tier 3 because its government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; law enforcement continues to demonstrate a lack of understanding of trafficking crimes and inadequate investigations, relying on trafficking cases to be prosecuted under the procurement statute rather than the trafficking statute, which carries more stringent penalties; authorities convicted only one offender under the procurement statue, a decrease from 2013; the government approved guidelines for the identification of victims and their referral to protective services but failed to ensure that victims were not jailed and charged for crimes committed as a direct result of being trafficked; no government employees were investigated or prosecuted, despite allegations of complicity (2015)