Introduction :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. In 1910, Tokyo formally annexed the entire Peninsula. Korea regained its independence following Japan's surrender to the US in 1945. After World War II, a democratic-based government (Republic of Korea, ROK) was set up in the southern half of the Korean Peninsula while a communist-style government was installed in the north (Democratic People's Republic of Korea, DPRK). During the Korean War (1950-53), US troops and UN forces fought alongside ROK soldiers to defend South Korea from a DPRK invasion supported by China and the Soviet Union. A 1953 armistice split the Peninsula along a demilitarized zone at about the 38th parallel. PARK Chung-hee took over leadership of the country in a 1961 coup. During his regime, from 1961 to 1979, South Korea achieved rapid economic growth, with per capita income rising to roughly 17 times the level of North Korea. South Korea held its first free presidential election under a revised democratic constitution in 1987, with former ROK Army general ROH Tae-woo winning a close race. In 1993, KIM Young-sam (1993-98) became the first civilian president of South Korea's new democratic era. President KIM Dae-jung (1998-2003) won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2000 for his contributions to South Korean democracy and his "Sunshine" policy of engagement with North Korea. President PARK Geun-hye, daughter of former ROK President PARK Chung-hee, took office in February 2013 and is South Korea's first female leader. South Korea held a non-permanent seat (2013-14) on the UN Security Council and will host the 2018 Winter Olympic Games. Discord with North Korea has permeated inter-Korean relations for much of the past decade, highlighted by the North's attacks on a South Korean ship and island in 2010, multiple nuclear and missile tests, and the exchange of artillery fire across the DMZ.
Geography :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
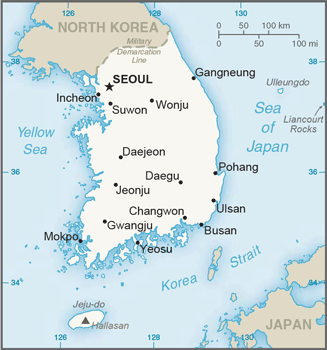
Eastern Asia, southern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Sea of Japan and the Yellow Sea
37 00 N, 127 30 E
Asia
total: 99,720 sq km
land: 96,920 sq km
water: 2,800 sq km
country comparison to the world: 109
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Indiana
Area comparison map:

East & Southeast Asia
::KOREA, SOUTH

Area Comparison
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Indiana
total: 237 km
border countries (1): North Korea 237 km
2,413 km
territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the Korea Strait
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: not specified
temperate, with rainfall heavier in summer than winter; cold winters
mostly hills and mountains; wide coastal plains in west and south
mean elevation: 282 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 m
highest point: Halla-san 1,950 m
coal, tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, lead, hydropower potential
agricultural land: 18.1%
arable land 15.3%; permanent crops 2.2%; permanent pasture 0.6%
forest: 63.9%
other: 18% (2011 est.)
7,780 sq km (2012)
occasional typhoons bring high winds and floods; low-level seismic activity common in southwest
volcanism: Halla (elev. 1,950 m) is considered historically active although it has not erupted in many centuries
air pollution in large cities; acid rain; water pollution from the discharge of sewage and industrial effluents; drift net fishing
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
strategic location on Korea Strait
People and Society :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
50,924,172 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
noun: Korean(s)
adjective: Korean
homogeneous
Korean, English (widely taught in junior high and high school)
Christian 31.6% (Protestant 24.0%, Catholic 7.6%), Buddhist 24.2%, other or unknown 0.9%, none 43.3% (2010 est.)
0-14 years: 13.45% (male 3,535,137/female 3,315,510)
15-24 years: 13.08% (male 3,515,779/female 3,146,084)
25-54 years: 45.93% (male 12,008,399/female 11,379,261)
55-64 years: 14.01% (male 3,521,569/female 3,611,481)
65 years and over: 13.53% (male 2,918,156/female 3,972,796) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

East & Southeast Asia
::KOREA, SOUTH

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 37.2%
youth dependency ratio: 19.2%
elderly dependency ratio: 18%
potential support ratio: 5.6% (2015 est.)
total: 41.2 years
male: 39.7 years
female: 42.8 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
0.53% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
8.4 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
5.8 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
2.6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
urban population: 82.5% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 0.66% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
SEOUL (capital) 9.774 million; Busan (Pusan) 3.216 million; Incheon (Inch'on) 2.685 million; Daegu (Taegu) 2.244 million; Daejon (Taejon) 1.564 million; Gwangju (Kwangju) 1.536 million (2015)
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.12 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
31 (2014 est.)
11 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
total: 3 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 3.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 215
total population: 82.4 years
male: 79.3 years
female: 85.8 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
1.25 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
80%
note: percent of women aged 15-44 (2009)
7.4% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 69
2.14 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
10.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)
improved:
urban: 99.7% of population
rural: 87.9% of population
total: 97.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.3% of population
rural: 12.1% of population
total: 2.2% of population (2012 est.)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
6.3% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 139
0.6% (2011)
country comparison to the world: 135
4.6% of GDP (2012)
country comparison to the world: 75
total: 17 years
male: 17 years
female: 16 years (2013)
total: 10%
male: 11.2%
female: 9.2% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
Government :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
conventional long form: Republic of Korea
conventional short form: South Korea
local long form: Taehan-min'guk
local short form: Han'guk
abbreviation: ROK
etymology: derived from the Chinese name for Goryeo, which was the Korean dynasty that united the peninsula in the 10th century A.D.; the South Korean name "Han'guk" means "land of the Han," where "han" refers to a "great [leader]" (similar to the title "khan")
presidential republic
name: Seoul; note - Sejong, located some 120 km (75 mi) south of Seoul, is being developed as a new capital
geographic coordinates: 37 33 N, 126 59 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
9 provinces (do, singular and plural), 6 metropolitan cities (gwangyeoksi, singular and plural), 1 special city (teugbyeolsi), and 1 special self-governing city (teukbyeoljachisi)
provinces: Chungbuk (North Chungcheong), Chungnam (South Chungcheong), Gangwon, Gyeongbuk (North Gyeongsang), Gyeonggi, Gyeongnam (South Gyeongsang), Jeju, Jeonbuk (North Jeolla), Jeonnam (South Jeolla)
metropolitan cities: Busan (Pusan), Daegu (Taegu), Daejeon (Taejon), Gwangju (Kwangju), Incheon (Inch'on), Ulsan
special city: Seoul
special self-governing city: Sejong
15 August 1945 (from Japan)
Liberation Day, 15 August (1945)
effective 17 July 1948; amended several times, last in 1987 (2016)
mixed legal system combining European civil law, Anglo-American law, and Chinese classical thought
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Korea
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
19 years of age; universal
chief of state: President PARK Geun-hye (since 25 February 2013)
head of government: Prime Minister HWANG Kyo-ahn (since 18 June 2015); Deputy Prime Ministers YOO Il-ho (since 13 January 2016), LEE Joon-sik (since 13 January 2016)
cabinet: State Council appointed by the president on the prime minister's recommendation
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a single 5-year term; election last held on 19 December 2012 (next to be held in December 2017); prime minister appointed by president, approved by National Assembly
election results: PARK Geun-Hye elected president; percent of vote - PARK Geun-Hye (NFP) 51.6%, MOON Jae-In (DUP) 48%, other 0.4%
description: unicameral National Assembly or Kuk Hoe (300 seats; 246 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 54 directly elected in a single national constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 13 April 2016 (next to be held in 2020)
election results: percent of vote by party - Saenuri 33.5%, PP 26.7%, MPK 25.5%, Justice Party 7.2%, other 7.1%; seats by party - MPK 123, Saenuri 122, PP 38, Justice Party 6, independent 11
note: seats by party as of October 2016 - Saenuri 129, MPK 122, PP 38, Justice Party 6, independent 5
highest court(s): Supreme Court of South Korea (consists of a chief justice and 13 justices); Constitutional Court (consists of a court head and 8 justices)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year non-renewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Branch Courts (organized under the District Courts); specialized courts for family and administrative issues
Justice Party [SIM Sang-jeong]
Minjoo Party of Korea or MPK [CHOO Mi-ae] (formerly New Politics Alliance for Democracy or NPAD) [KIM Jong-in] (NPAD was a merger of the Democratic Party or DP (formerly DUP) [KIM Han-gil] and the New Political Vision Party or NPVP [AHN Cheol-soo] in March 2014)
New Frontier Party (NFP) or Saenuri (formerly Grand National Party) [LEE Jung-hyun]
People's Party or PP [AHN Cheol-soo and CHUN Jung-bae]
Catholic Priests' Association for Justice
Christian Council of Korea
Citizen's Coalition for Economic Justice
Federation of Korean Industries
Federation of Korean Trade Unions
Korean Confederation of Trade Unions
Korean Veterans' Association
Lawyers for a Democratic Society
National Council of Churches in Korea
People's Solidarity for Participatory Democracy
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, Arctic Council (observer), ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CICA, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
chief of mission: Ambassador AHN Ho-young (since 7 June 2013)
chancery: 2450 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-5600
FAX: [1] (202) 797-0595
consulate(s) general: Agana (Guam), Anchorage (AK), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
chief of mission: Ambassador Mark William LIPPERT (since 21 November 2014)
embassy: 188 Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-710
mailing address: US Embassy Seoul, Unit
telephone: [82] (2) 397-4114
FAX: [82] (2) 725-0152
white with a red (top) and blue yin-yang symbol in the center; there is a different black trigram from the ancient I Ching (Book of Changes) in each corner of the white field; the South Korean national flag is called Taegukki; white is a traditional Korean color and represents peace and purity; the blue section represents the negative cosmic forces of the yin, while the red symbolizes the opposite positive forces of the yang; each trigram (kwae) denotes one of the four universal elements, which together express the principle of movement and harmony
taegeuk (yin yang symbol), Hibiscus syriacus (Rose of Sharon); national colors: red, white, blue, black
name: "Aegukga" (Patriotic Song)
lyrics/music: YUN Ch'i-Ho or AN Ch'ang-Ho/AHN Eaktay
note: adopted 1948, well-known by 1910; both North Korea's and South Korea's anthems share the same name and have a vaguely similar melody but have different lyrics
Economy :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
South Korea over the past four decades has demonstrated incredible economic growth and global integration to become a high-tech industrialized economy. In the 1960s, GDP per capita was comparable with levels in the poorer countries of Africa and Asia. In 2004, South Korea joined the trillion-dollar club of world economies.
A system of close government and business ties, including directed credit and import restrictions, initially made this success possible. The government promoted the import of raw materials and technology at the expense of consumer goods and encouraged savings and investment over consumption.
The Asian financial crisis of 1997-98 exposed longstanding weaknesses in South Korea's development model, including high debt/equity ratios and massive short-term foreign borrowing. GDP plunged by 7% in 1998, and then recovered by 9% in 1999-2000. South Korea adopted numerous economic reforms following the crisis, including greater openness to foreign investment and imports. Growth moderated to about 4% annually between 2003 and 2007.
South Korea's export focused economy was hit hard by the 2008 global economic downturn, but quickly rebounded in subsequent years, reaching over 6% growth in 2010. The US-Korea Free Trade Agreement was ratified by both governments in 2011 and went into effect in March 2012. Between 2012 and 2015, the economy experienced slow growth – 2%-3% per year - due to sluggish domestic consumption and investment. The administration in 2015 faced the challenge of balancing heavy reliance on exports with developing domestic-oriented sectors, such as services.
The South Korean economy's long-term challenges include a rapidly aging population, inflexible labor market, dominance of large conglomerates (chaebols), and the heavy reliance on exports, which comprise about half of GDP. In an effort to address the long term challenges and sustain economic growth, the current government has prioritized structural reforms, deregulation, promotion of entrepreneurship and creative industries, and the competitiveness of small- and medium-sized enterprises.
$1.849 trillion (2015 est.)
$1.802 trillion (2014 est.)
$1.744 trillion (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 14
$1.377 trillion (2015 est.)
2.6% (2015 est.)
3.3% (2014 est.)
2.9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$36,500 (2015 est.)
$35,700 (2014 est.)
$34,700 (2013 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 49
36.2% of GDP (2015 est.)
35.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
35.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
household consumption: 49.5%
government consumption: 15.2%
investment in fixed capital: 29.1%
investment in inventories: -0.7%
exports of goods and services: 45.9%
imports of goods and services: -38.9% (2015 est.)
agriculture: 2.3%
industry: 38%
services: 59.7% (2015 est.)
rice, root crops, barley, vegetables, fruit; cattle, pigs, chickens, milk, eggs; fish
electronics, telecommunications, automobile production, chemicals, shipbuilding, steel
1.7% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
26.91 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
agriculture: 5.7%
industry: 24.2%
services: 70.2% (2015 est.)
3.6% (2015 est.)
3.5% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
14.6% (2013 est.)
lowest 10%: 6.8%
highest 10%: 37.8% (Q4 2014)
30.2 (2014 est.)
35.8 (2000)
country comparison to the world: 121
revenues: $299.9 billion
expenditures: $300.1 billion (2015 est.)
21.8% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
0% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
44.8% of GDP (2015 est.)
43.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
calendar year
0.7% (2015 est.)
1.3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
1.5% (31 December 2015)
2% (31 December 2014)
country comparison to the world: 120
3.53% (31 December 2015 est.)
4.26% (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
$604.2 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$532.9 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$1.973 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.754 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$2.427 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)
$2.406 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
$1.263 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)
$1.269 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.193 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
$105.9 billion (2015 est.)
$84.37 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$548.8 billion (2015 est.)
$613 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
semiconductors, petrochemicals, automobile/auto parts, ships, wireless communication equipment, flat display displays, steel, electronics, plastics, computers
China 26%, US 13.3%, Hong Kong 5.8%, Vietnam 5.3%, Japan 4.9% (2015)
$428.5 billion (2015 est.)
$524.1 billion (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
crude oil/petroleum products, semiconductors, natural gas, coal, steel, computers, wireless communication equipment, automobiles, fine chemical, textiles
China 20.7%, Japan 10.5%, US 10.1%, Germany 4.8%, Saudi Arabia 4.5% (2015)
$367.9 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$363.6 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$381.8 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$407 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$174.6 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$179.2 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$286.9 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$259.3 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
South Korean won (KRW) per US dollar -
1,130.95 (2015 est.)
1,052.84 (2014 est.)
1,052.96 (2013 est.)
1,126.47 (2012 est.)
1,108.29 (2011 est.)
Energy :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)
513 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
495 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
0 kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
0 kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
100 million kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
69.6% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
26.8% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
1.7% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
1.9% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
6,510 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
2.815 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
0 bbl
country comparison to the world: 153
3.01 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
2.407 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
1.3 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
865,600 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
322 million cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
47.4 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
49.08 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
7.079 billion cu m (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 90
651 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
Communications :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
total subscriptions: 28,882,783
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 59 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
total: 58.935 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 120 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
general assessment: excellent domestic and international services featuring rapid incorporation of new technologies
domestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular services widely available with the latter subscribership up to about 120 per 100 persons; rapid assimilation of a full range of telecommunications technologies leading to a boom in e-commerce
international: country code - 82; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 66 (2015)
multiple national TV networks with 2 of the 3 largest networks publicly operated; the largest privately owned network, Seoul Broadcasting Service (SBS), has ties with other commercial TV networks; cable and satellite TV subscription services available; publicly operated radio broadcast networks and many privately owned radio broadcasting networks, each with multiple affiliates, and independent local stations (2010)
.kr
total: 44.153 million
percent of population: 89.9% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
Transportation :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
number of registered air carriers: 12
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 348
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 65,482,307
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 11.297 billion mt-km (2015)
HL (2016)
111 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 53
total: 71
over 3,047 m: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m: 19
1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
914 to 1,523 m: 13
under 914 m: 23 (2013)
total: 40
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 38 (2013)
466 (2013)
gas 2,216 km; oil 16 km; refined products 889 km (2013)
total: 3,460 km
standard gauge: 3,460 km 1.435-m gauge (1,422 km electrified) (2014)
country comparison to the world: 52
total: 104,983 km
paved: 83,199 km (includes 3,779 km of expressways)
unpaved: 21,784 km (2009)
country comparison to the world: 44
1,600 km (most navigable only by small craft) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 50
total: 786
by type: bulk carrier 191, cargo 235, carrier 8, chemical tanker 130, container 72, liquefied gas 44, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 15, petroleum tanker 55, refrigerated cargo 15, roll on/roll off 10, vehicle carrier 6
foreign-owned: 31 (China 6, France 2, Japan 14, Taiwan 1, US 8)
registered in other countries: 457 (Bahamas 1, Cambodia 10, Ghana 1, Honduras 6, Hong Kong 3, Indonesia 2, Kiribati 1, Liberia 2, Malta 2, Marshall Islands 41, North Korea 1, Panama 373, Philippines 1, Russia 1, Singapore 3, Tuvalu 1, unknown 8) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 14
major seaport(s): Busan, Incheon, Gunsan, Kwangyang, Mokpo, Pohang, Ulsan, Yeosu
container port(s) (TEUs): Busan (16,163,842), Kwangyang (2,061,958), Incheon (1,924,644)
LNG terminal(s) (import): Incheon, Kwangyang, Pyeongtaek, Samcheok, Tongyeong, Yeosu
Military and Security :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
Republic of Korea Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2011)
20-30 years of age for compulsory military service, with middle school education required; minimum conscript service obligation - 21 months (Army, Marines), 23 months (Navy), 24 months (Air Force); 18-26 years of age for voluntary military service; women, in service since 1950, admitted to 7 service branches, including infantry, but excluded from artillery, armor, anti-air, and chaplaincy corps; HIV-positive individuals are exempt from military service (2012)
2.8% of GDP (2012)
2.77% of GDP (2011)
2.8% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 25
Transnational Issues :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
Military Demarcation Line within the 4-km-wide Demilitarized Zone has separated North from South Korea since 1953; periodic incidents with North Korea in the Yellow Sea over the Northern Limit Line, which South Korea claims as a maritime boundary; South Korea and Japan claim Liancourt Rocks (Tok-do/Take-shima), occupied by South Korea since 1954
stateless persons: 197 (2015)