Africa :: ALGERIA
Introduction :: ALGERIA
-
After more than a century of rule by France, Algerians fought through much of the 1950s to achieve independence in 1962. Algeria's primary political party, the National Liberation Front (FLN), was established in 1954 as part of the struggle for independence and has since largely dominated politics. The Government of Algeria in 1988 instituted a multi-party system in response to public unrest, but the surprising first round success of the Islamic Salvation Front (FIS) in the December 1991 balloting led the Algerian army to intervene and postpone the second round of elections to prevent what the secular elite feared would be an extremist-led government from assuming power. The army began a crackdown on the FIS that spurred FIS supporters to begin attacking government targets. Fighting escalated into an insurgency, which saw intense violence from 1992-98, resulting in over 100,000 deaths - many attributed to indiscriminate massacres of villagers by extremists. The government gained the upper hand by the late-1990s, and FIS's armed wing, the Islamic Salvation Army, disbanded in January 2000.Abdelaziz BOUTEFLIKA, with the backing of the military, won the presidency in 1999 in an election widely viewed as fraudulent and won subsequent elections in 2004, 2009, and 2014. The government in 2011 introduced some political reforms in response to the Arab Spring, including lifting the 19-year-old state of emergency restrictions and increasing women's quotas for elected assemblies, while also increasing subsidies to the populace. Algeria’s reliance on hydrocarbon revenues to finance the government and large subsidies for the population is under stress because of declining oil prices.
Geography :: ALGERIA
-
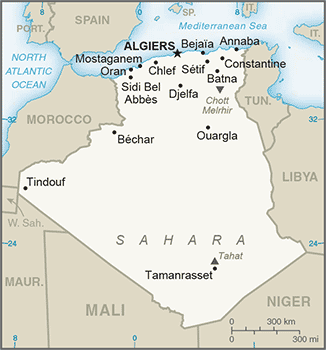
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Morocco and Tunisia28 00 N, 3 00 EAfricatotal: 2,381,741 sq kmland: 2,381,741 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 10slightly less than 3.5 times the size of Texastotal: 6,734 kmborder countries (7): Libya 989 km, Mali 1,359 km, Mauritania 460 km, Morocco 1,900 km, Niger 951 km, Tunisia 1,034 km, Western Sahara 41 km998 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmexclusive fishing zone: 32-52 nmarid to semiarid; mild, wet winters with hot, dry summers along coast; drier with cold winters and hot summers on high plateau; sirocco is a hot, dust/sand-laden wind especially common in summermostly high plateau and desert; some mountains; narrow, discontinuous coastal plainmean elevation: 800 melevation extremes: lowest point: Chott Melrhir -40 mhighest point: Tahat 3,003 mpetroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zincagricultural land: 17.3%arable land 3.1%; permanent crops 0.4%; permanent pasture 13.8%forest: 0.6%other: 82% (2011 est.)5,700 sq km (2012)the vast majority of the populace is found in the extreme northern part of the country along the Mediterranean Coastmountainous areas subject to severe earthquakes; mudslides and floods in rainy seasonsoil erosion from overgrazing and other poor farming practices; desertification; dumping of raw sewage, petroleum refining wastes, and other industrial effluents is leading to the pollution of rivers and coastal waters; Mediterranean Sea, in particular, becoming polluted from oil wastes, soil erosion, and fertilizer runoff; inadequate supplies of potable waterparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementslargest country in Africa
People and Society :: ALGERIA
-
40,263,711 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 34noun: Algerian(s)adjective: AlgerianArab-Berber 99%, European less than 1%note: although almost all Algerians are Berber in origin (not Arab), only a minority identify themselves as Berber, about 15% of the total population; these people live mostly in the mountainous region of Kabylie east of Algiers; the Berbers are also Muslim but identify with their Berber rather than Arab cultural heritage; Berbers have long agitated, sometimes violently, for autonomy; the government is unlikely to grant autonomy but has offered to begin sponsoring teaching Berber language in schoolsArabic (official), French (lingua franca), Berber or Tamazight (official); dialects include Kabyle Berber (Taqbaylit), Shawiya Berber (Tacawit), Mzab Berber, Tuareg Berber (Tamahaq)Muslim (official; predominantly Sunni) 99%, other (includes Christian and Jewish) <1% (2012 est.)For the first two-thirds of the 20th century, Algeria’s high fertility rate caused its population to grow rapidly. However, about a decade after independence from France in 1962 the total fertility rate fell dramatically from 7 children per woman in the 1970s to about 2.4 in 2000, slowing Algeria’s population growth rate by the late 1980s. The lower fertility rate was mainly the result of women’s rising age at first marriage (virtually all Algerian children being born in wedlock) and to a lesser extent the wider use of contraceptives. Later marriages and a preference for smaller families are attributed to increases in women’s education and participation in the labor market; higher unemployment; and a shortage of housing forcing multiple generations to live together. The average woman’s age at first marriage increased from about 19 in the mid-1950s to 24 in the mid-1970s to 30.5 in the late 1990s.Thousands of Algerian peasants – mainly Berber men from the Kabylia region – faced with land dispossession and economic hardship under French rule migrated temporarily to France to work in manufacturing and mining during the first half of the 20th century. This movement accelerated during World War I, when Algerians filled in for French factory workers or served as soldiers. In the years following independence, low-skilled Algerian workers and Algerians who had supported the French (harkis) emigrated en masse to France. Tighter French immigration rules and Algiers’ decision to cease managing labor migration to France in the 1970s limited legal emigration largely to family reunification.Not until Algeria’s civil war in the 1990s did the country again experience substantial outmigration. Many Algerians legally entered Tunisia without visas claiming to be tourists and then stayed as workers. Other Algerians headed to Europe seeking asylum, although France imposed restrictions. Sub-Saharan African migrants came to Algeria after its civil war to work in agriculture and mining. In the 2000s, a wave of educated Algerians went abroad seeking skilled jobs in a wider range of destinations, increasing their presence in North America and Spain. At the same time, legal foreign workers principally from China and Egypt came to work in Algeria’s construction and oil sectors. Illegal migrants from sub-Saharan Africa, particularly Malians, Nigeriens, and Gambians, continue to come to Algeria in search of work or to use it as a stepping stone to Libya and Europe.Since 1975, Algeria also has been the main recipient of Sahrawi refugees from the ongoing conflict in Western Sahara. An estimated 90,000 Sahrawis live in five refugee camps in southwestern Algeria near Tindouf.0-14 years: 29.06% (male 5,991,164/female 5,709,616)15-24 years: 15.95% (male 3,287,448/female 3,136,624)25-54 years: 42.88% (male 8,737,944/female 8,526,137)55-64 years: 6.61% (male 1,349,291/female 1,312,339)65 years and over: 5.5% (male 1,027,126/female 1,186,022) (2016 est.)total dependency ratio: 52.6%youth dependency ratio: 43.6%elderly dependency ratio: 9.1%potential support ratio: 11% (2015 est.)total: 27.8 yearsmale: 27.5 yearsfemale: 28.1 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1371.77% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 6423 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 684.3 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 205-0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 139the vast majority of the populace is found in the extreme northern part of the country along the Mediterranean Coasturban population: 70.7% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: 2.77% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)ALGIERS (capital) 2.594 million; Oran 858,000 (2015)at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2016 est.)140 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 75total: 20.3 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 21.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 18.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 83total population: 76.8 yearsmale: 75.5 yearsfemale: 78.2 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 812.74 children born/woman (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 6761.4% (2006)7.2% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1351.21 physicians/1,000 population (2007)improved:urban: 84.3% of populationrural: 81.8% of populationtotal: 83.6% of populationunimproved:urban: 15.7% of populationrural: 18.2% of populationtotal: 16.4% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 89.8% of populationrural: 82.2% of populationtotal: 87.6% of populationunimproved:urban: 10.2% of populationrural: 17.8% of populationtotal: 12.4% of population (2015 est.)0.04% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1258,800 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 92100 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 10123.6% (2014)country comparison to the world: 1163% (2013)country comparison to the world: 1024.3% of GDP (2008)country comparison to the world: 97definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 80.2%male: 87.2%female: 73.1% (2015 est.)total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 15 years (2011)total number: 304,358percentage: 5% (2006 est.)total: 25.3%male: 22.1%female: 41.4% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 47
Government :: ALGERIA
-
conventional long form: People's Democratic Republic of Algeriaconventional short form: Algerialocal long form: Al Jumhuriyah al Jaza'iriyah ad Dimuqratiyah ash Sha'biyahlocal short form: Al Jaza'iretymology: the country name derives from the capital city of Algierspresidential republicname: Algiersgeographic coordinates: 36 45 N, 3 03 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)48 provinces (wilayas, singular - wilaya); Adrar, Ain Defla, Ain Temouchent, Alger, Annaba, Batna, Bechar, Bejaia, Biskra, Blida, Bordj Bou Arreridj, Bouira, Boumerdes, Chlef, Constantine, Djelfa, El Bayadh, El Oued, El Tarf, Ghardaia, Guelma, Illizi, Jijel, Khenchela, Laghouat, Mascara, Medea, Mila, Mostaganem, M'Sila, Naama, Oran, Ouargla, Oum el Bouaghi, Relizane, Saida, Setif, Sidi Bel Abbes, Skikda, Souk Ahras, Tamanrasset, Tebessa, Tiaret, Tindouf, Tipaza, Tissemsilt, Tizi Ouzou, Tlemcen5 July 1962 (from France)Revolution Day, 1 November (1954)several previous; latest approved by referendum 23 February 1989; amended several times, last in 2016 (2016)mixed legal system of French civil law and Islamic law; judicial review of legislative acts in ad hoc Constitutional Council composed of various public officials including several Supreme Court justiceshas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtcitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: the mother must be a citizen of Algeriadual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 7 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Abdelaziz BOUTEFLIKA (since 28 April 1999)head of government: Prime Minister Abdelmalek SELLAL (since 28 April 2014)cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in two rounds if needed for a 5-year term (2-term limit reinstated by constitutional amendment in February 2016); election last held on 17 April 2014 (next to be held in April 2019); prime minister nominated by the president from the majority party in Parliamentelection results: Abdelaziz BOUTEFLIKA reelected president for a fourth term; percent of vote - Abdelaziz BOUTEFLIKA (FLN) 81.5%, Ali BENFLIS (FLN) 12.2%, Abdelaziz BELAID (Future Front) 3.4%, other 2.9%description: bicameral Parliament consists of the Council of the Nation (upper house with 144 seats; one-third of members appointed by the president, two-thirds indirectly elected by simple majority vote by an electoral college composed of local council members; members serve 6-year terms with one-half of the membership renewed every 3 years) and the National People's Assembly (lower house with 462 seats including 8 seats for Algerians living abroad); members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)elections: Council of the Nation - last held on 29 December 2012 (next to be held in December 2017); National People's Assembly - last held on 10 May 2012 (next to be held on 17 May 2017)election results: Council of the Nation - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; National People's Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - FLN 221, RND 70, AAV 47, FFS 21, PT 17, FNA 9, El Adala 7, MPA 6, PFJ 5, FC 4, PNSD 4, other 32, independent 19highest court(s): Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (consists of 150 judges organized into 4 divisions: civil and commercial; social security and labor; criminal; and administrative; Constitutional Council (consists of 9 members including the court president); note - Algeria's judicial system does not include sharia courtsjudge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the High Council of Magistracy, an administrative body presided over by the president of the republic, and includes the republic vice-president and several members; judges appointed for life; Constitutional Council members - 3 appointed by the president of the republic, 2 each by the 2 houses of Parliament, 1 by the Supreme Court, and 1 by the Council of State; Council president and members appointed for single 6-year terms with half the membership renewed every 3 yearssubordinate courts: appellate or wilaya courts; first instance or daira tribunalsAlgerian National Front or FNA [Moussa TOUATI]Algerian Popular Movement or MPA [Amara BENYOUNES]Algerian Rally or RA [Ali ZAGHDOUD]Algeria's Hope Rally or TAJ [Amar GHOUL]Dignity or El Karama [Mohamed BENHAMOU]Ennour El Djazairi Party (Algerian Radiance Party) or PED [Badreddine BELBAZ]Front for Change or FC [Abdelmadjid MENASRA]Front for Justice and Development or El Adala [Abdallah DJABALLAH]Future Front or El Mostakbel [Abdelaziz BELAID]Green Algeria Alliance or AAV (includes Islah, Ennahda Movement, and MSP)Islamic Renaissance Movement or Ennahda Movement [Fatah RABEI]Movement of Society for Peace or MSP [Abderrazak MOKRI]National Democratic Rally (Rassemblement National Democratique) or RND [Ahmed OUYAHIA]National Front for Social Justice or FNJS [Khaled BOUNEDJEMA]National Liberation Front or FLN [Amar SAIDANI]National Party for Solidarity and Development or PNSDNational Reform Movement or Islah [Djahid YOUNSI]National Republican AllianceNew Dawn Party or PFJNew Generation or Jil Jadid [Soufiane DJILALI]Oath of 1954 or Ahd 54 [Ali Fawzi REBAINE]Party of Justice and Liberty [Mohammed SAID]Rally for Culture and Democracy or RCD [Mohcine BELABBAS]Socialist Forces Front or FFS [Mustafa BOUCHACHI]Union of Democratic and Social Forces or UFDS [Noureddine BAHBOUH]Youth Party or PJ [Hamana BOUCHARMA]Workers Party or PT [Louisa HANOUNE]note: a law banning political parties based on religion was enacted in March 1997Algerian League for the Defense of Human Rights or LADDH [Noureddine BENISSAD]SOS Disparus [Nacera DUTOUR]Youth Action Rally or RAJABEDA, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, BIS, CAEU, CD, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAS, MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, OPEC, OSCE (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)chief of mission: Ambassador Madjid BOUGUERRA (since 23 February 2015)chancery: 2118 Kalorama Road NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 265-2800FAX: [1] (202) 986-5906consulate(s) general: New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador Joan A. POLASCHIK (since 22 September 2014)embassy: 05 Chemin Cheikh Bachir, El-Ibrahimi, El-Biar 16030 Algiersmailing address: B. P. 408, Alger-Gare, 16030 Algierstelephone: [213] (0) 770-08-2000FAX: [213] (0) 770-08-2064two equal vertical bands of green (hoist side) and white; a red, five-pointed star within a red crescent centered over the two-color boundary; the colors represent Islam (green), purity and peace (white), and liberty (red); the crescent and star are also Islamic symbols, but the crescent is more closed than those of other Muslim countries because Algerians believe the long crescent horns bring happinessstar and crescent, fennec fox; national colors: green, white, redname: "Kassaman" (We Pledge)lyrics/music: Mufdi ZAKARIAH/Mohamed FAWZInote: adopted 1962; ZAKARIAH wrote "Kassaman" as a poem while imprisoned in Algiers by French colonial forces
Economy :: ALGERIA
-
Algeria's economy remains dominated by the state, a legacy of the country's socialist postindependence development model. In recent years the Algerian Government has halted the privatization of state-owned industries and imposed restrictions on imports and foreign involvement in its economy.Hydrocarbons have long been the backbone of the economy, accounting for roughly 60% of budget revenues, 30% of GDP, and over 95% of export earnings. Algeria has the 10th-largest reserves of natural gas in the world and is the sixth-largest gas exporter. It ranks 16th in oil reserves. Hydrocarbon exports have enabled Algeria to maintain macroeconomic stability and amass large foreign currency reserves and a large budget stabilization fund available for tapping. In addition, Algeria's external debt is extremely low at about 2% of GDP. However, Algeria has struggled to develop non-hydrocarbon industries because of heavy regulation and an emphasis on state-driven growth.The government's efforts have done little to reduce high youth unemployment rates or to address housing shortages. A wave of economic protests in February and March 2011 prompted the Algerian Government to offer more than $23 billion in public grants and retroactive salary and benefit increases, moves which continue to weigh on public finances. Since late 2014, declining oil prices forced the government to spend down its reserves at a high rate in order to sustain social spending on salaries and subsidies, particularly since the government has been unable to boost exports of hydrocarbons or significantly grow its nonoil sector. In 2015, the Algerian Government imposed further restrictions on imports in an effort to reduce withdrawals from its foreign exchange reserves. The Government also increased the value-added tax on electricity and fuel, but said it would address subsidies at a later date.Long-term economic challenges include diversifying the economy away from its reliance on hydrocarbon exports, bolstering the private sector, attracting foreign investment, and providing adequate jobs for younger Algerians.$578.7 billion (2015 est.)$557.8 billion (2014 est.)$537.4 billion (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 34$172.3 billion (2015 est.)3.7% (2015 est.)3.8% (2014 est.)2.8% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 71$14,500 (2015 est.)$14,300 (2014 est.)$14,000 (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 11234.1% of GDP (2015 est.)41.1% of GDP (2014 est.)43.9% of GDP (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 16household consumption: 40.6%government consumption: 21.1%investment in fixed capital: 41.1%investment in inventories: 7.2%exports of goods and services: 26.9%imports of goods and services: -36.9% (2015 est.)agriculture: 13.1%industry: 39%services: 47.9% (2015 est.)wheat, barley, oats, grapes, olives, citrus, fruits; sheep, cattlepetroleum, natural gas, light industries, mining, electrical, petrochemical, food processing2.1% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 10111.93 million (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 47agriculture: 30.9%industry: 30.9%services: 58.4% (2011 est.)11.2% (2015 est.)10.6% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 12723% (2006 est.)lowest 10%: 2.8%highest 10%: 26.8% (1995)35.3 (1995)country comparison to the world: 92revenues: $49.36 billionexpenditures: $76.93 billion (2015 est.)28.6% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 89-16% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2149.9% of GDP (2015 est.)7.2% of GDP (2014 est.)note: data cover central government debt, as well as debt issued by subnational entities and intra-governmental debtcountry comparison to the world: 169calendar year4.8% (2015 est.)2.9% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1714% (31 December 2010)4% (31 December 2009)country comparison to the world: 988% (31 December 2015 est.)8% (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 107$86.43 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$109 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 38$164.5 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$152.8 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 47$61.78 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$35.28 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 61$NA-$27.04 billion (2015 est.)-$9.436 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 189$36 billion (2015 est.)$60 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 56petroleum, natural gas, and petroleum products 97% (2009 est.)Spain 18.8%, France 11.2%, US 8.8%, Italy 8.7%, UK 7.1%, Brazil 5.2%, Tunisia 4.9%, Germany 4.5% (2015)$50.7 billion (2015 est.)$59.67 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 51capital goods, foodstuffs, consumer goodsChina 15.6%, France 14.4%, Italy 9.4%, Spain 7.4%, Germany 5.6%, Russia 4.1% (2015)$144.9 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$179.9 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 16$5.143 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$5.453 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 128$25.89 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$26.48 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 71$1.95 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$1.847 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Algerian dinars (DZD) per US dollar -100.691 (2015 est.)80.579 (2014 est.)80.579 (2013 est.)77.54 (2012 est.)72.938 (2011 est.)
Energy :: ALGERIA
-
population without electricity: 400,000electrification - total population: 99%electrification - urban areas: 100%electrification - rural areas: 97% (2016)60 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 5149 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 54900 million kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 57700 million kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 6516 million kW (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 4798% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 550% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 381.8% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1390.2% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1111.37 million bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 181.146 million bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 152,920 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 7712 billion bbl (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 16505,900 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 34430,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 37435,400 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 17108,800 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 5583.29 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1137.5 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 2640.8 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 80 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1534.504 trillion cu m (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 10128 million Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 35
Communications :: ALGERIA
-
total subscriptions: 3,267,592subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 8 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 46total: 45.928 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 116 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 33general assessment: privatization of Algeria's telecommunications sector began in 2000; three mobile cellular licenses have been issued and, in 2005, a consortium led by Egypt's Orascom Telecom won a 15-year license to build and operate a fixed-line network in Algeria; the license will allow Orascom to develop high-speed data and other specialized services and contribute to meeting the large unfulfilled demand for basic residential telephony; Internet broadband services began in 2003domestic: a limited network of fixed lines with a teledensity of less than 10 telephones per 100 persons has been offset by the rapid increase in mobile-cellular subscribership; in 2015, mobile-cellular teledensity was roughly 116 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 213; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-4 fiber-optic submarine cable system that provides links to Europe, the Middle East, and Asia; microwave radio relay to Italy, France, Spain, Morocco, and Tunisia; coaxial cable to Morocco and Tunisia; participant in Medarabtel; satellite earth stations - 51 (Intelsat, Intersputnik, and Arabsat) (2015)state-run Radio-Television Algerienne operates the broadcast media and carries programming in Arabic, Berber dialects, and French; use of satellite dishes is widespread, providing easy access to European and Arab satellite stations; state-run radio operates several national networks and roughly 40 regional radio stations (2007).dztotal: 15.105 millionpercent of population: 38.2% (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 55
Transportation :: ALGERIA
-
number of registered air carriers: 4inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 74annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 5,910,835annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 24,723,377 mt-km (2015)7T (2016)157 (2016)country comparison to the world: 36total: 64over 3,047 m: 122,438 to 3,047 m: 291,524 to 2,437 m: 17914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m: 1 (2013)total: 932,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 18914 to 1,523 m: 39under 914 m: 34 (2013)3 (2013)condensate 2,600 km; gas 16,415 km; liquid petroleum gas 3,447 km; oil 7,036 km; refined products 144 km (2013)total: 3,973 kmstandard gauge: 2,888 km 1.432-m gauge (283 km electrified)narrow gauge: 1,085 km 1.055-m gauge (2014)country comparison to the world: 45total: 113,655 kmpaved: 87,605 km (includes 645 km of expressways)unpaved: 26,050 km (2010)country comparison to the world: 42total: 38by type: bulk carrier 6, cargo 8, chemical tanker 3, liquefied gas 11, passenger/cargo 3, petroleum tanker 4, roll on/roll off 3foreign-owned: 15 (UK, 15) (2010)country comparison to the world: 78major seaport(s): Algiers, Annaba, Arzew, Bejaia, Djendjene, Jijel, Mostaganem, Oran, SkikdaLNG terminal(s) (export): Arzew, Bethioua, Skikda
Military and Security :: ALGERIA
-
People's National Army (Armee Nationale Populaire, ANP), Land Forces (Forces Terrestres, FT), Navy of the Republic of Algeria (Marine de la Republique Algerienne, MRA), Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Jaza'eriya, QJJ), Territorial Air Defense Force (2009)17 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; 19-30 years of age for compulsory service; conscript service obligation is 18 months (6 months basic training, 12 months civil projects) (2012)4.48% of GDP (2012)4.36% of GDP (2011)4.48% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 8
Transnational Issues :: ALGERIA
-
Algeria and many other states reject Moroccan administration of Western Sahara; the Polisario Front, exiled in Algeria, represents the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic; Algeria's border with Morocco remains an irritant to bilateral relations, each nation accusing the other of harboring militants and arms smuggling; dormant disputes include Libyan claims of about 32,000 sq km still reflected on its maps of southeastern Algeria and the National Liberation Front's (FLN) assertions of a claim to Chirac Pastures in southeastern Moroccorefugees (country of origin): 90,000 (Western Saharan Sahrawi, mostly living in Algerian-sponsored camps in the southwestern Algerian town of Tindouf) (2015)IDPs: undetermined (civil war during 1990s) (2013)current situation: Algeria is a transit and, to a lesser extent, a destination and source country for women subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking and, to a lesser extent, men subjected to forced labor; criminal networks, sometimes extending to sub-Saharan Africa and to Europe, are involved in human smuggling and trafficking in Algeria; sub-Saharan adults enter Algeria voluntarily but illegally, often with the aid of smugglers, for onward travel to Europe, but some of the women are forced into prostitution, domestic service, and begging; some sub-Saharan men, mostly from Mali, are forced into domestic servitude; some Algerian women and children are also forced into prostitution domesticallytier rating: Tier 3 – Algeria does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so: some officials denied the existence of human trafficking, hindering law enforcement efforts; the government reported its first conviction under its anti-trafficking law; one potential trafficking case was investigated in 2014, but no suspected offenders were arrested; no progress was made in identifying victims among vulnerable groups or referring them to NGO-run protection service, which left trafficking victims subject to arrest and detention; no anti-trafficking public awareness or educational campaigns were conducted (2015)