Europe :: MACEDONIA
Introduction :: MACEDONIA
-
Macedonia gained its independence peacefully from Yugoslavia in 1991. Greek objection to Macedonia’s name, insisting it implies territorial pretensions to the northern Greek province of the same name, and democratic backsliding have stalled the country’s movement toward Euro-Atlantic integration. Immediately after Macedonia declared independence, Greece sought to block Macedonian efforts to gain UN membership if the name “Macedonia” was used. Macedonia was eventually admitted to the UN in 1993 as “The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia,” and at the same time it agreed to UN-sponsored negotiations on the name dispute. In 1995, Greece lifted a 20-month trade embargo and the two countries agreed to normalize relations, but the issue of the name remained unresolved and negotiations for a solution are ongoing. Since 2004, the US and over 130 other nations have recognized Macedonia by its constitutional name, Republic of Macedonia. Ethnic Albanian grievances over perceived political and economic inequities escalated into an insurgency in 2001 that eventually led to the internationally brokered Ohrid Framework Agreement (OFA), which ended the fighting and established guidelines for constitutional amendments and the creation of new laws that enhanced the rights of minorities. Relations between Macedonians and ethnic Albanians remain fragile, however.Macedonia has been engulfed in a political crisis that began after the 2014 legislative and presidential election, and which escalated in 2015 when opposition party began releasing wiretap content that it alleged showed widespread government corruption. Although Macedonia became an EU candidate in 2005, the country still faces challenges, including overcoming the political crisis, fully implementing OFA, resolving the outstanding name dispute with Greece, improving relations with Bulgaria, halting democratic backsliding, and stimulating economic growth and development. At the 2008 NATO Summit in Bucharest, Romania, the Allies agreed that Macedonia would be invited to join the Alliance as soon as a mutually acceptable resolution to the name dispute was reached with Greece.
Geography :: MACEDONIA
-
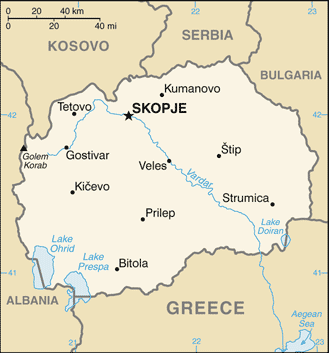
Southeastern Europe, north of Greece41 50 N, 22 00 EEuropetotal: 25,713 sq kmland: 25,433 sq kmwater: 280 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 150slightly larger than Vermonttotal: 838 kmborder countries (5): Albania 181 km, Bulgaria 162 km, Greece 234 km, Kosovo 160 km, Serbia 101 km0 km (landlocked)none (landlocked)warm, dry summers and autumns; relatively cold winters with heavy snowfallmountainous with deep basins and valleys; three large lakes, each divided by a frontier line; country bisected by the Vardar Rivermean elevation: 741 melevation extremes: lowest point: Vardar River 50 mhighest point: Golem Korab (Maja e Korabit) 2,764 mlow-grade iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, chromite, manganese, nickel, tungsten, gold, silver, asbestos, gypsum, timber, arable landagricultural land: 44.3%arable land 16.4%; permanent crops 1.4%; permanent pasture 26.5%forest: 39.8%other: 15.9% (2011 est.)1,280 sq km (2012)a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populationshigh seismic risksair pollution from metallurgical plantsparty to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementslandlocked; major transportation corridor from Western and Central Europe to Aegean Sea and Southern Europe to Western Europe
People and Society :: MACEDONIA
-
2,100,025 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 146noun: Macedonian(s)adjective: MacedonianMacedonian 64.2%, Albanian 25.2%, Turkish 3.9%, Roma (Gypsy) 2.7%, Serb 1.8%, other 2.2% (2002 est.)Macedonian (official) 66.5%, Albanian (official) 25.1%, Turkish 3.5%, Roma 1.9%, Serbian 1.2%, other 1.8% (2002 est.)Macedonian Orthodox 64.8%, Muslim 33.3%, other Christian 0.4%, other and unspecified 1.5% (2002 est.)0-14 years: 17.27% (male 187,752/female 174,935)15-24 years: 13.69% (male 148,340/female 139,195)25-54 years: 43.65% (male 465,622/female 451,028)55-64 years: 12.3% (male 126,548/female 131,749)65 years and over: 13.09% (male 117,787/female 157,069) (2016 est.)total dependency ratio: 41.4%youth dependency ratio: 24%elderly dependency ratio: 17.4%potential support ratio: 5.7% (2015 est.)total: 37.5 yearsmale: 36.4 yearsfemale: 38.6 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 650.18% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 18811.5 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1709.1 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 66-0.5 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 129a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populationsurban population: 57.1% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: 0.11% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)SKOPJE (capital) 503,000 (2015)at birth: 1.08 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.03 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2016 est.)26.6 (2013 est.)8 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 153total: 7.5 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 7.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 7.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 158total population: 76.2 yearsmale: 73.6 yearsfemale: 79 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 891.6 children born/woman (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 18140.2% (2011)6.5% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 792.62 physicians/1,000 population (2009)4.5 beds/1,000 population (2011)improved:urban: 99.8% of populationrural: 98.9% of populationtotal: 99.4% of populationunimproved:urban: 0.2% of populationrural: 1.1% of populationtotal: 0.6% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 97.2% of populationrural: 82.6% of populationtotal: 90.9% of populationunimproved:urban: 2.8% of populationrural: 17.4% of populationtotal: 9.1% of population (2015 est.)0.01% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 131200 (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 126fewer than 100 (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 10620.8% (2014)country comparison to the world: 921.3% (2011)country comparison to the world: 128definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 97.8%male: 98.8%female: 96.8% (2015 est.)total: 13 yearsmale: 13 yearsfemale: 13 years (2012)total number: 16,782percentage: 6% (2005 est.)total: 53.1%male: 52%female: 55% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 4
Government :: MACEDONIA
-
conventional long form: Republic of Macedoniaconventional short form: Macedonialocal long form: Republika Makedonijalocal short form: Makedonijanote: the provisional designation used by the UN, EU, and NATO is the "former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM)former: People's Republic of Macedonia, Socialist Republic of Macedoniaetymology: the country name derives from the ancient kingdom of Macedon (7th to 2nd centuries B.C.)parliamentary republicname: Skopjegeographic coordinates: 42 00 N, 21 26 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October70 municipalities (opstini, singular - opstina) and 1 city* (grad); Aracinovo, Berovo, Bitola, Bogdanci, Bogovinje, Bosilovo, Brvenica, Caska, Centar Zupa, Cesinovo-Oblesevo, Cucer Sandevo, Debar, Debarca, Delcevo, Demir Hisar, Demir Kapija, Dojran, Dolneni, Gevgelija, Gostivar, Gradsko, Ilinden, Jegunovce, Karbinci, Kavadarci, Kicevo, Kocani, Konce, Kratovo, Kriva Palanka, Krivogastani, Krusevo, Kumanovo, Lipkovo, Lozovo, Makedonska Kamenica, Makedonski Brod, Mavrovo i Rostusa, Mogila, Negotino, Novaci, Novo Selo, Ohrid, Pehcevo, Petrovec, Plasnica, Prilep, Probistip, Radovis, Rankovce, Resen, Rosoman, Skopje*, Sopiste, Staro Nagoricane, Stip, Struga, Strumica, Studenicani, Sveti Nikole, Tearce, Tetovo, Valandovo, Vasilevo, Veles, Vevcani, Vinica, Vrapciste, Zelenikovo, Zelino, Zrnovci8 September 1991 (referendum by registered voters endorsed independence from Yugoslavia)Independence Day, 8 September (1991); also known as National Dayhistory: several previous; latest adopted 17 November 1991, effective 20 November 1991amendments: proposed by the president of the republic, by the government, by at least 30 members of the Assembly, or by petition of at least 150,000 citizens; draft amendments require approval by majority vote of Assembly members, followed by public debate; final passage requires two-thirds majority vote of Assembly members; amended several times, last in 2015 (2016)civil law system; judicial review of legislative actshas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Macedoniadual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 8 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Gjorge IVANOV (since 12 May 2009)head of government: Interim Prime Minister Emil DIMITRIEV (since 18 January 2016); Prime Minister Nikola GRUEVSKI (since 26 August 2006) resigned on 15 January 2016cabinet: Council of Ministers elected by the Assembly by simple majority vote; note - the 2014 cabinet formed by the government coalition parties VMRO-DPMNE, DUI, and several small parties; as a result of an agreement reached in July 2015 between the largest parties to resolve a 16-month opposition boycott of the Assembly, several minister and deputy minister positions were also given to the opposition SDSMelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 13 and 27 April 2014 (next to be held in 2019); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually elected prime minister by the Assemblyelection results: Gjorge IVANOV reelected president in second round; percent of vote - Gjorge IVANOV (independent) 55.3%, Stevo PENDAROVSKI (SDSM) 41.1%, other 3.6%description: unicameral Assembly or Sobranie (123 seats; 120 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote and 3 directly elected in diaspora constituencies worldwide by simple majority vote; members serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 11 December 2016 (next to be held in 2020)election results: percent of vote by party - VMRO-DPMNE 39.4%, SDSM coalition 37.9%, BDI 7.5%, Besa Movement 5.0%, Alliance for Albanians 3.1%, PDSh 2.7%, other 4.4%; seats by party - VMRO-DPMNE 51, SDSM coalition 49, BDI 10, Besa Movement 5, Alliance for Albanians 3, PDSh 2highest court(s): Supreme Court (consist of NA judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the Judicial Council, a 7-member body of legal professionals, and appointed by the Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the Assembly for nonrenewable, 9-year termssubordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Basic CourtsAlliance for AlbaniansBesa Movement [Bilal KASAMI]Citizens Option for Macedonia or GROM [Stevco JAKIMOVSKI]Democratic Party of Albanians or PDSh [Menduh THACI]Democratic Union for Integration or BDI [Ali AHMETI]Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization - Democratic Party for Macedonian National Unity or VMRO-DPMNE [Nikola GRUEVSKI]National Democratic Revival or RDK [Vesel MEMEDI]Social Democratic Union of Macedonia or SDSM [Zoran ZAEV]note: during the 2016 parliamentary elections VMRO-DPMNE and SDSM each led coalitionsFederation of Free Trade Unions [Mirjana ANDREVSKA]Federation of Trade Unions [Zivko MITREVSKI]Trade Union of Education, Science and Culture or SONK [Jakim NEDELKOV]Student PlenumEco Guerilla [Arianit XHAFERI]BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, EU (candidate country), FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, OAS (observer), OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador Vasko NAUMOVSKI (since 18 November 2014)chancery: 2129 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 667-0501FAX: [1] (202) 667-2131consulate(s) general: Chicago, Detroit, New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador Jess L. BAILY (since 12 February 2015)embassy: Str. Samolilova, Nr. 21, 1000 Skopjemailing address: American Embassy Skopje, US Department of State, 7120 Skopje Place, Washington, DC 20521-7120 (pouch)telephone: [389] (2) 310-2000FAX: [389] (2) 310-2499a yellow sun (the Sun of Liberty) with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field; the red and yellow colors have long been associated with Macedoniaeight-rayed sun; national colors: red, yellowname: "Denes nad Makedonija" (Today Over Macedonia)lyrics/music: Vlado MALESKI/Todor SKALOVSKInote: written in 1943 and adopted in 1991 , the song previously served as the anthem of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia while part of Yugoslavia
Economy :: MACEDONIA
-
Since its independence in 1991, Macedonia has made progress in liberalizing its economy and improving its business environment, but has lagged the Balkan region in attracting foreign investment. Corruption and weak rule of law remain significant problems. Some businesses complain of opaque regulations and unequal enforcement of the law.Macedonia’s economy is closely linked to Europe as a customer for exports and source of investment, and has suffered as a result of prolonged weakness in the euro zone. Unemployment has remained consistently high at about 30% since 2008, but may be overstated based on the existence of an extensive gray market, estimated to be between 20% and 45% of GDP, which is not captured by official statistics.Macedonia maintained macroeconomic stability through the global financial crisis by conducting prudent monetary policy, which keeps the domestic currency pegged against the euro, and by limiting fiscal deficits. The government has been loosening fiscal policy, however, and the budget deficit was 4.2% of GDP in both 2013 and 2014, gradually falling to 3.7% in 2015. By yearend 2015, public debt was 40.3%, which although low by regional comparison, is significant for a small economy.$29.04 billion (2015 est.)$28.01 billion (2014 est.)$27.05 billion (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollars; Macedonia has a large informal sector that may not be reflected in these datacountry comparison to the world: 132$9.922 billion (2015 est.)3.7% (2015 est.)3.5% (2014 est.)2.9% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 75$14,000 (2015 est.)$13,500 (2014 est.)$13,100 (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 11422.5% of GDP (2015 est.)21.2% of GDP (2014 est.)22.1% of GDP (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 30household consumption: 67.7%government consumption: 16.7%investment in fixed capital: 18.2%investment in inventories: 13.7%exports of goods and services: 48.5%imports of goods and services: -64.8% (2015 est.)agriculture: 11.2%industry: 26.1%services: 62.7% (2015 est.)grapes, tobacco, vegetables, fruits; milk, eggsfood processing, beverages, textiles, chemicals, iron, steel, cement, energy, pharmaceuticals, automotive parts7.8% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 20954,900 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 146agriculture: 18.3%industry: 29.1%services: 52.6% (2014 est.)26.1% (2015 est.)28% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 18230.4% (2011 est.)lowest 10%: 2.2%highest 10%: 34.5% (2009 est.)43.6 (2013)39.2 (2011)country comparison to the world: 48revenues: $2.903 billionexpenditures: $3.252 billion (2015 est.)29.3% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 87-3.5% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 13246.5% of GDP (2015 est.)46% of GDP (2014 est.)note: official data from Ministry of Finance; data cover central government debt; this data exclude debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; include treasury debt held by foreign entitites; exclude debt issued by sub-national entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; there are no debt instruments sold for social fundscountry comparison to the world: 91calendar year-0.2% (2015 est.)-0.1% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 413.25% (31 December 2014)3.25% (31 December 2013)note: series discontinued in January 2010; the discount rate has been replaced by a referent rate for calculating the penalty ratecountry comparison to the world: 1017.08% (31 December 2015 est.)7.46% (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 118$1.797 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$1.692 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 134$6.129 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$6.282 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 123$5.308 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$5.111 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 121$2.084 billion (31 December 2014)$2.302 billion (31 December 2013)$2.423 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 98-$141 million (2015 est.)-$91 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 72$3.372 billion (2015 est.)$3.682 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 122foodstuffs, beverages, tobacco; textiles, miscellaneous manufactures, iron, steel; automotive partsGermany 33.2%, Kosovo 11.5%, Bulgaria 5.1%, Greece 4.5% (2015)$5.393 billion (2015 est.)$6.15 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 121machinery and equipment, automobiles, chemicals, fuels, food productsGermany 15.9%, UK 13.6%, Greece 10.9%, Serbia 8.7%, Bulgaria 6.7%, Turkey 5.5%, Italy 4.7% (2015)$2.471 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$2.963 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$7.029 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$7.241 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 120$6.123 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$5.93 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 97$599.6 million (31 December 2015 est.)$600.3 million (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Macedonian denars (MKD) per US dollar -55.537 (2015 est.)46.437 (2014 est.)46.437 (31 December 2013 est.)47.89 (2012 est.)44.231 (2011 est.)
Energy :: MACEDONIA
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)4.569 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1206.96 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 105112.9 million kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 783.073 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 522.011 million kW (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 10864.5% of total installed capacity (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1210% of total installed capacity (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 14033% of total installed capacity (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 702.6% of total installed capacity (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 760 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1670 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 160146 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 810 bbl (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 1671,719 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 10620,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1412,616 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 10117,950 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1170 cu m (2014)country comparison to the world: 102134.7 million cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1070 cu m (2014)country comparison to the world: 145134.7 million cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 710 cu m (31 December 2014 )country comparison to the world: 1707.9 million Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 111
Communications :: MACEDONIA
-
total subscriptions: 372,557subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 18 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 105total: 2.223 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 106 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 147general assessment: competition from the mobile-cellular segment of the telecommunications market has led to a drop in fixed-line telephone subscriptionsdomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership about 120 per 100 personsinternational: country code - 389 (2015)public TV broadcaster operates 3 national channels and a satellite network; 5 privately owned TV channels broadcast nationally using terrestrial transmitters and about 15 broadcast on national level via satellite; roughly 75 local commercial TV stations; large number of cable operators offering domestic and international programming; public radio broadcaster operates over multiple stations; 3 privately owned radio stations broadcast nationally; about 70 local commercial radio stations (2012).mk1.475 million70.4% (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 121
Transportation :: MACEDONIA
-
Z3 (2016)10 (2013)country comparison to the world: 155total: 82,438 to 3,047 m: 2under 914 m: 6 (2013)total: 2914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 1 (2013)gas 268 km; oil 120 km (2013)total: 699 kmstandard gauge: 699 km 1.435-m gauge (223 km electrified) (2014)country comparison to the world: 101total: 14,182 km (includes 242 km of expressways)paved: 9,633 kmunpaved: 4,549 km (2014)country comparison to the world: 124
Military and Security :: MACEDONIA
-
Army of the Republic of Macedonia (ARM; includes General Staff and subordinate Joint Operational Command, Training and Doctrine Command, Special Operations Regiment) (2012)18 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription abolished in 2008 (2013)1.08% of GDP (2015)1.17% of GDP (2014)1.14% of GDP (2013)1.2% of GDP (2012)1.3% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 92
Transnational Issues :: MACEDONIA
-
Kosovo and Macedonia completed demarcation of their boundary in September 2008; Greece continues to reject the use of the name Macedonia or Republic of Macedoniastateless persons: 667 (2015)note: 478,004 refugee and migrant arrivals (2015 - November 2016 est.)major transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and hashish; minor transit point for South American cocaine destined for Europe; although not a financial center and most criminal activity is thought to be domestic, money laundering is a problem due to a mostly cash-based economy and weak enforcement