Central America and Caribbean :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
Introduction :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
First colonized by the Spanish, the islands came under British control in the early 19th century. The islands' sugar industry was hurt by the emancipation of the slaves in 1834. Manpower was replaced with the importation of contract laborers from India between 1845 and 1917, which boosted sugar production as well as the cocoa industry. The discovery of oil on Trinidad in 1910 added another important export. Independence was attained in 1962. The country is one of the most prosperous in the Caribbean thanks largely to petroleum and natural gas production and processing. Tourism, mostly in Tobago, is targeted for expansion and is growing. The government is coping with a rise in violent crime.
Geography :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
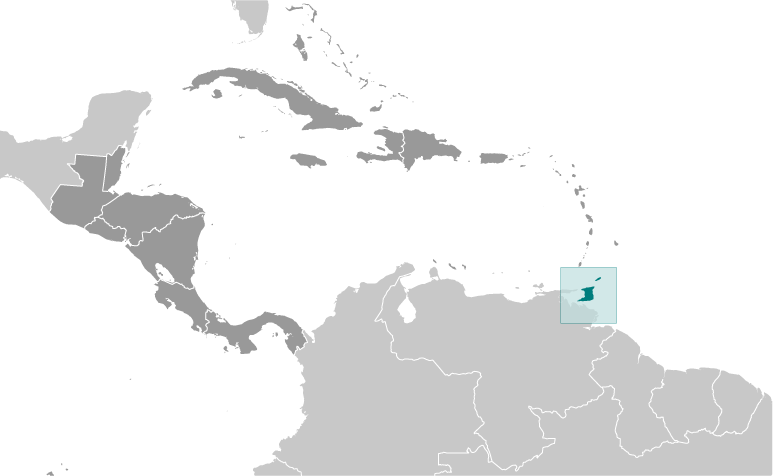
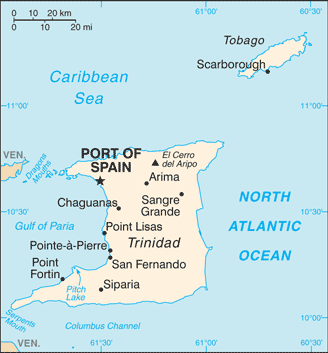
Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela11 00 N, 61 00 WCentral America and the Caribbeantotal: 5,128 sq kmland: 5,128 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 174slightly smaller than Delaware0 km362 kmmeasured from claimed archipelagic baselinesterritorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the outer edge of the continental margintropical; rainy season (June to December)mostly plains with some hills and low mountainsmean elevation: 83 melevation extremes: lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 mhighest point: El Cerro del Aripo 940 mpetroleum, natural gas, asphaltagricultural land: 10.6%arable land 4.9%; permanent crops 4.3%; permanent pasture 1.4%forest: 44%other: 45.4% (2011 est.)70 sq km (2012)population on Trinidad concentrated in the western half of the island; on Tobago in the southern halfoutside usual path of hurricanes and other tropical stormswater pollution from agricultural chemicals, industrial wastes, and raw sewage; oil pollution of beaches; deforestation; soil erosionparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsPitch Lake, on Trinidad's southwestern coast, is the world's largest natural reservoir of asphalt
People and Society :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
1,220,479 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160noun: Trinidadian(s), Tobagonian(s)adjective: Trinidadian, TobagonianEast Indian 35.4%, African 34.2%, mixed - other 15.3%, mixed African/East Indian 7.7%, other 1.3%, unspecified 6.2% (2011 est.)English (official), Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), French, Spanish, ChineseProtestant 32.1% (Pentecostal/Evangelical/Full Gospel 12%, Baptist 6.9%, Anglican 5.7%, Seventh-Day Adventist 4.1%, Presbyterian/Congretational 2.5%, other Protestant 0.9%), Roman Catholic 21.6%, Hindu 18.2%, Muslim 5%, Jehovah's Witness 1.5%, other 8.4%, none 2.2%, unspecified 11.1% (2011 est.)0-14 years: 19.34% (male 120,214/female 115,821)15-24 years: 12.24% (male 77,738/female 71,629)25-54 years: 46.1% (male 292,819/female 269,855)55-64 years: 12.09% (male 73,457/female 74,062)65 years and over: 10.23% (male 54,334/female 70,550) (2016 est.)total dependency ratio: 43.2%youth dependency ratio: 29.8%elderly dependency ratio: 13.5%potential support ratio: 7.4% (2015 est.)total: 35.5 yearsmale: 35 yearsfemale: 36 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 75-0.17% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 21213.1 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1528.7 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 74-6.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 200population on Trinidad is concentrated in the western half of the island, on Tobago in the southern halfurban population: 8.4% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: -1.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)PORT-OF-SPAIN (capital) 34,000 (2014)at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.09 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.09 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2016 est.)63 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 112total: 23 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 24.4 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 21.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 72total population: 72.9 yearsmale: 69.9 yearsfemale: 75.9 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1381.71 children born/woman (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 17042.5% (2006)5.9% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1311.18 physicians/1,000 population (2007)2.7 beds/1,000 population (2012)improved:urban: 95.1% of populationrural: 95.1% of populationtotal: 95.1% of populationunimproved:urban: 4.9% of populationrural: 4.9% of populationtotal: 4.9% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 91.5% of populationrural: 91.5% of populationtotal: 91.5% of populationunimproved:urban: 8.5% of populationrural: 8.5% of populationtotal: 8.5% of population (2015 est.)1.22% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 3010,800 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 90200 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 74note: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus (2016)32.3% (2014)country comparison to the world: 31definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99%male: 99.2%female: 98.7% (2015 est.)total number: 1,201percentage: 1% (2006 est.)total: 9.2%male: 7.7%female: 11.4% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 98
Government :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
conventional long form: Republic of Trinidad and Tobagoconventional short form: Trinidad and Tobagoetymology: explorer Christopher COLUMBUS named the larger island "La Isla de la Trinidad" (The Island of the Trinity) on 31 July 1498 on his third voyage; the tobacco grown and smoked by the natives of the smaller island or its elongated cigar shape may account for the "tobago" name, which is spelled "tobaco" in Spanishparliamentary republicname: Port of Spaingeographic coordinates: 10 39 N, 61 31 Wtime difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)9 regions, 3 boroughs, 2 cities, 1 wardregions: Couva/Tabaquite/Talparo, Diego Martin, Mayaro/Rio Claro, Penal/Debe, Princes Town, Sangre Grande, San Juan/Laventille, Siparia, Tunapuna/Piarcoborough: Arima, Chaguanas, Point Fortincities: Port of Spain, San Fernandoward: Tobago31 August 1962 (from the UK)Independence Day, 31 August (1962)previous 1962; latest 1976; amended many times, last in 2007 (2016)English common law; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Courthas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: yescitizenship by descent: yesdual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 8 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Anthony CARMONA (since 18 March 2013)head of government: Prime Minister Keith ROWLEY (since 9 September 2015)cabinet: Cabinet appointed from among members of Parliamentelections/appointments: president indirectly elected by an electoral college of selected Senate and House of Representatives members for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 15 February 2013 (next to be held by February 2018); the president usually appoints the leader of the majority party in the House of Representatives as prime ministerelection results: Anthony CARMONA (independent) elected president; electoral college vote - 100%description: bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (31 seats; 16 members appointed by the ruling party, 9 by the president, and 6 by the opposition party; members serve 5-year terms;) and the House of Representatives (41 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)note: Tobago has a unicameral House of Assembly (16 seats; 12 assemblymen directly elected by simple majority vote and 4 appointed councillors - 3 on the advice of the chief secretary and 1 on the advice of the minority leader; members serve 4-year terms)elections: House of Representatives - last held on 7 September 2015 (next to be held in 2020)election results: House of Representatives - percent of vote - NA; seats by party - PNM 23, UNC 18highest resident court(s): Supreme Court of the Judicature (consists of a chief justice for both the Court of Appeal with 12 judges and the High Court with 24 judges); note - Trinidad and Tobago can file appeals beyond its Supreme Court to the Caribbean Court of Justice, with final appeal to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president after consultation with the prime minister and the parliamentary leader of the opposition; other judges appointed by the Judicial Legal Services Commission, headed by the chief justice and 5 members with judicial experience; all judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement normally at age 65subordinate courts: Courts of Summary Criminal Jurisdiction; Petty Civil Courts; Family CourtCongress of the People or COP [Prakash RAMADHAR]Democratic Action Congress or DAC [Hochoy CHARLES] (only active in Tobago)Democratic National Alliance or DNA [Charles CARSON] (coalition of NAR, DDPT, MND)Movement for National Development or MND [Garvin NICHOLAS]National Alliance for Reconstruction or NAR [Lennox SANKERSINGH]People's National Movement or PNM [Keith ROWLEY]Tobago Organization of the People or TOP [Ashworth JACK]United National Congress or UNC [Kamla PERSAD-BISSESSAR]Jamaat-al Muslimeen [Yasin ABU BAKR]ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club (associate), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador Anthony Wayne Jerome PHILLIPS SPENCER (since 27 June 2016)chancery: 1708 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 467-6490FAX: [1] (202) 785-3130consulate(s) general: Miami, New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador John L. ESTRADA (since 19 April 2016)embassy: 15 Queen's Park West, Port of Spainmailing address: P. O. Box 752, Port of Spaintelephone: [1] (868) 622-6371 through 6376FAX: [1] (868) 822-5905red with a white-edged black diagonal band from the upper hoist side to the lower fly side; the colors represent the elements of earth, water, and fire; black stands for the wealth of the land and the dedication of the people; white symbolizes the sea surrounding the islands, the purity of the country's aspirations, and equality; red symbolizes the warmth and energy of the sun, the vitality of the land, and the courage and friendliness of its peoplescarlet ibis (bird of Trinidad), cocrico (bird of Tobago), Chaconia flower; national colors: red, white, blackname: "Forged From the Love of Liberty"lyrics/music: Patrick Stanislaus CASTAGNEnote: adopted 1962; song originally created to serve as an anthem for the West Indies Federation; adopted by Trinidad and Tobago following the Federation's dissolution in 1962
Economy :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
Trinidad and Tobago attracts considerable foreign direct investment from international businesses, particularly in energy, and has one of the highest per capita incomes in Latin America. Economic growth between 2000 and 2007 averaged slightly over 8% per year, significantly above the regional average of about 3.7% for that same period; however, GDP has slowed down since then, contracting during 2009-2012, making small gains in 2013 and contracting again in 2014-2015.Energy production and downstream industrial use dominate the economy. Trinidad and Tobago produces about nine times more natural gas than crude oil on an energy equivalent basis with gas contributing about two-thirds of energy sector government revenue. Oil and gas account for about 40% of GDP and 80% of exports but less than 5% of employment. In 2013, Trinidad and Tobago was the world’s sixth-largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) exporter and is home to one of the largest natural gas liquefaction facilities in the Western Hemisphere. The United States is the country’s largest trading partner, accounting for 33% of its total imports and taking 44% of its exports.Trinidad and Tobago is buffered by considerable foreign reserves and a sovereign wealth fund that equals about one-and-a-half times the national budget, but the country is in a recession and the government faces the dual challenge of gas shortages and a low price environment. A projected 70% decrease in energy revenue to the government in 2016 will likely force cuts to the government budget, which has increased by 35% over the past six years.Economic diversification is a longstanding government talking point, and Trinidad and Tobago has much potential due to its stable, democratic government and its educated, English speaking workforce. Although Trinidad and Tobago enjoys cheap electricity from natural gas, the renewable energy sector has recently garnered increased interest. The country is also a regional financial center with a well-regulated and stable financial system. Other sectors the Government of Trinidad and Tobago has targeted for increased investment and projected growth include tourism, agriculture, information and communications technology, and shipping. Unfortunately, a host of other factors, including low labor productivity, inefficient government bureaucracy, and corruption, have hampered economic development.$45.19 billion (2015 est.)$45.1 billion (2014 est.)$45.56 billion (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 111$25.43 billion (2015 est.)0.2% (2015 est.)-1% (2014 est.)2.3% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 207$30,900 (2015 est.)$31,500 (2014 est.)$31,400 (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 588% of GDP (2015 est.)18.1% of GDP (2014 est.)20.7% of GDP (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 159household consumption: 60.2%government consumption: 13%investment in fixed capital: 13.8%investment in inventories: 0%exports of goods and services: 44.4%imports of goods and services: -31.5% (2014 est.)agriculture: 0.5%industry: 37.7%services: 61.4% (2015 est.)cocoa, dasheen, pumpkin, cassava, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplant, hot pepper, pommecythere, coconut water, poultrypetroleum and petroleum products, liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, urea, steel products, beverages, food processing, cement, cotton textiles-5% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 188649,100 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 155agriculture: 3.6%manufacturing, mining, and quarrying: 11.2%construction and utilities: 85.2%services: 62.9% (2014 est.)3.2% (2015 est.)3.3% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 2417% (2007 est.)lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%revenues: $8.731 billionexpenditures: $9.758 billion (2014 est.)34.3% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 64-4% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 14367.4% of GDP (2015 est.)57.6% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 471 October - 30 September4.7% (2015 est.)5.7% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1706.75% (04 March 2016 est.)6.75% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 508% (31 December 2015 est.)7.9% (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 106$7.422 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$6.907 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 89$13.51 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$11.94 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 97$7.432 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$6.93 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 111$177.4 million (31 December 2015 est.)$171.6 million (31 December 2014)$170 million (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 117-$166 million (2015 est.)$1.822 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 134$11.81 billion (2014 est.)$12.77 billion (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 81petroleum and petroleum products, liquefied natural gas, methanol, ammonia, urea, steel products, beverages, cereal and cereal products, cocoa, fish, preserved fruits, , cosmetics, household cleaners, plastic packagingUS 26.3%, Argentina 12%, Brazil 6.6%, Chile 5.3%, Dominican Republic 5.2%, Barbados 5% (2015)$8.386 billion (2014 est.)$8.871 billion (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 104mineral fuels, lubricants, machinery, transportation equipment, manufactured goods, food, chemicals, live animalsUS 35.6%, China 6.8%, Gabon 6.6% (2015)$13.59 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$12.33 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 70$2.115 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$2.072 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 149$382.9 million (31 December 2014 est.)$311.7 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 115$1.266 billion (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Trinidad and Tobago dollars (TTD) per US dollar -6.57 (2016 est.)6.4 (2015 est.)6.4041 (2014 est.)6.4041 (2013 est.)6.39 (2012 est.)
Energy :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
population without electricity: 12,452electrification - total population: 99.8%electrification - urban areas: 100%electrification - rural areas: 99% (2012)9.3 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1009.1 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 960 kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2010 kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2062.353 million kW (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 105100% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 390% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1860% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2050% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 11578,630 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 4830,800 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 5178,340 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 54700 million bbl (1 January 2015 es)country comparison to the world: 44139,200 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 7156,000 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 106113,800 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4431,630 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 14041.59 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 2024.67 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 3717.41 billion cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 140 cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 138325.7 billion cu m (1 January 2014 es)country comparison to the world: 3748 million Mt (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 58
Communications :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
total subscriptions: 270,872subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 22 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 116total: 2.123 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 174 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 152general assessment: excellent international service; good local servicedomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity over 190 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 1-868; submarine cable systems provide connectivity to US and parts of the Caribbean and South America; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean); tropospheric scatter to Barbados and Guyana (2015)16 TV networks (11 commercial, 5 non-commercial), 2 of which are state-owned that broadcast on multiple stations; 9 TV subscription service providers (cable and satellite); 19 radio networks, 1 state-owned, broadcast over about 35 stations (2016).tttotal: 846,000percent of population: 69.2% (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 126
Transportation :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
number of registered air carriers: 1inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 17annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 2,617,842annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 43,198,176 mt-km (2015)9Y (2016)4 (2013)country comparison to the world: 187total: 2over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)total: 2914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 1 (2013)condensate 257 km; condensate/gas 11 km; gas 1,567 km; oil 587 km (2013)total: 9,592 kmpaved: 5,524 kmunpaved: 4,068 km (2015)country comparison to the world: 140total: 4by type: passenger 1, passenger/cargo 2, petroleum tanker 1registered in other countries: 2 (unknown 2) (2010)country comparison to the world: 131major seaport(s): Point Fortin, Point Lisas, Port of Spain, Scarboroughoil terminals: Galeota Point terminalLNG terminal(s) (export): Port Fortin
Military and Security :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
Trinidad and Tobago Defense Force (TTDF): Trinidad and Tobago Army, Coast Guard, Air Guard, Defense Force Reserves (2010)18-25 years of age for voluntary military service (16 years of age with parental consent); no conscription; Trinidad and Tobago citizenship and completion of secondary school required (2012)
Transnational Issues :: TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
-
Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago abide by the April 2006 Permanent Court of Arbitration decision delimiting a maritime boundary and limiting catches of flying fish in Trinidad and Tobago's EEZ; in 2005, Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago agreed to compulsory international arbitration under UN Convention on the Law of the Sea challenging whether the northern limit of Trinidad and Tobago's and Venezuela's maritime boundary extends into Barbadian waters; Guyana has expressed its intention to include itself in the arbitration, as the Trinidad and Tobago-Venezuela maritime boundary may also extend into its waterscurrent situation: Trinidad and Tobago is a destination, transit, and possible source country for adults and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; women and girls from Venezuela, the Dominican Republic, Guyana, and Colombia have been subjected to sex trafficking in Trinidad and Tobago’s brothels and clubs; some economic migrants from the Caribbean region and Asia are vulnerable to forced labor in domestic service and the retail sector; the steady flow of vessels transiting Trinidad and Tobago’s territorial waters may also increase opportunities for forced labor for fishing; international crime organizations are increasingly involved in trafficking, and boys are coerced to sell drugs and guns; corruption among police and immigration officials impedes anti-trafficking effortstier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Trinidad and Tobago does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; anti-trafficking law enforcement efforts decreased from the initiation of 12 prosecutions in 2013 to 1 in 2014; the government has yet to convict anyone under its 2011 anti-trafficking law, and all prosecutions from previous years remain pending; the government sustained efforts to identify victims and to refer them for care at NGO facilities, which it provided with funding; the government failed to draft a national action plan as mandated under the 2011 anti-trafficking law and did not launch a sufficiently robust awareness campaign to educate the public and officials (2015)transshipment point for South American drugs destined for the US and Europe; producer of cannabis